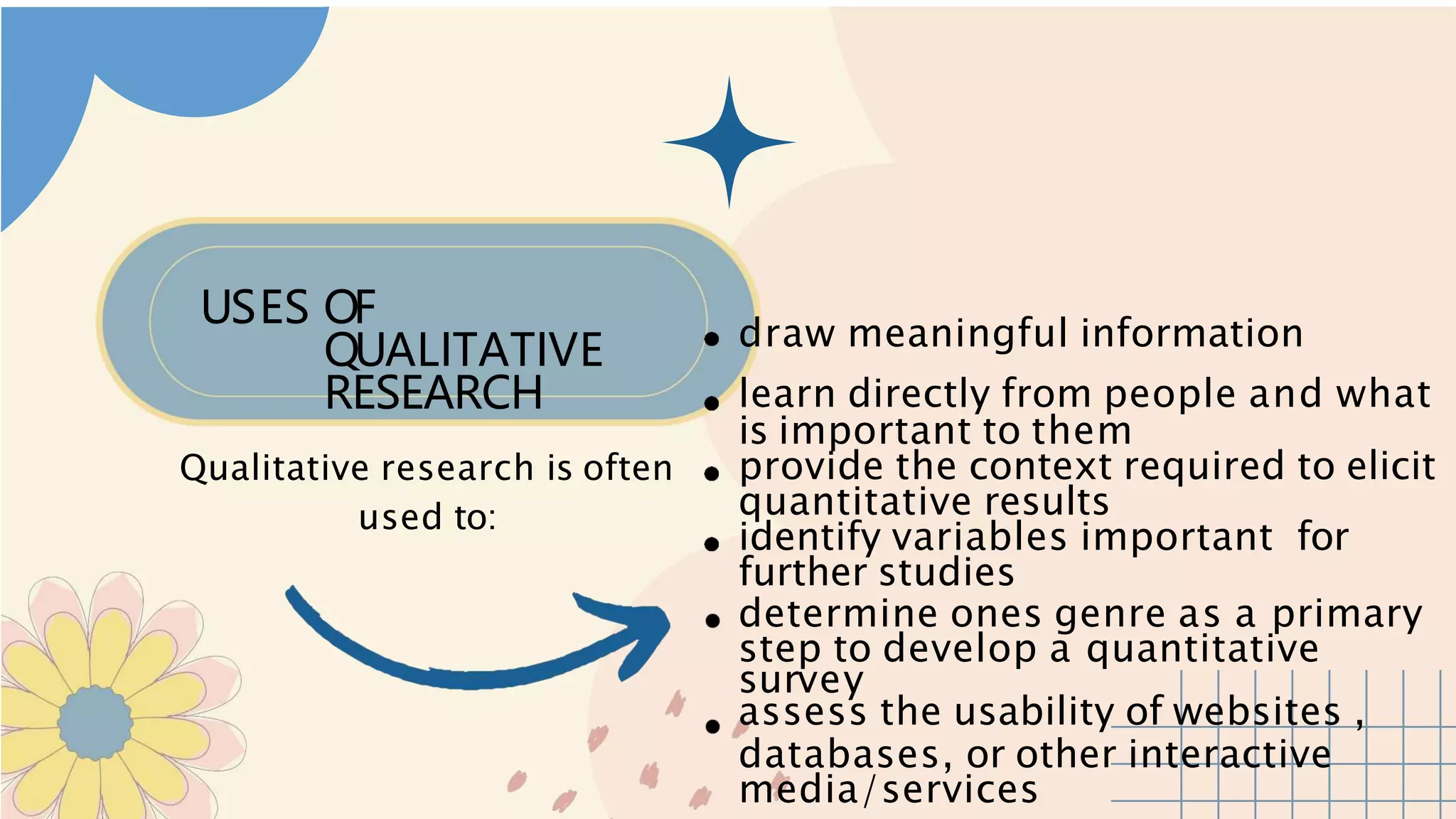
This document discusses qualitative research. It defines qualitative research as investigating relationships, activities, solutions or materials through their qualities rather than quantities. Some key characteristics are that the researcher is the main instrument, data is collected through words rather than numbers, and analysis is inductive. Qualitative research allows an in-depth understanding of complex phenomena and experiences. It is important across fields like social sciences, psychology, and healthcare as it provides context and explores individuals' perspectives.