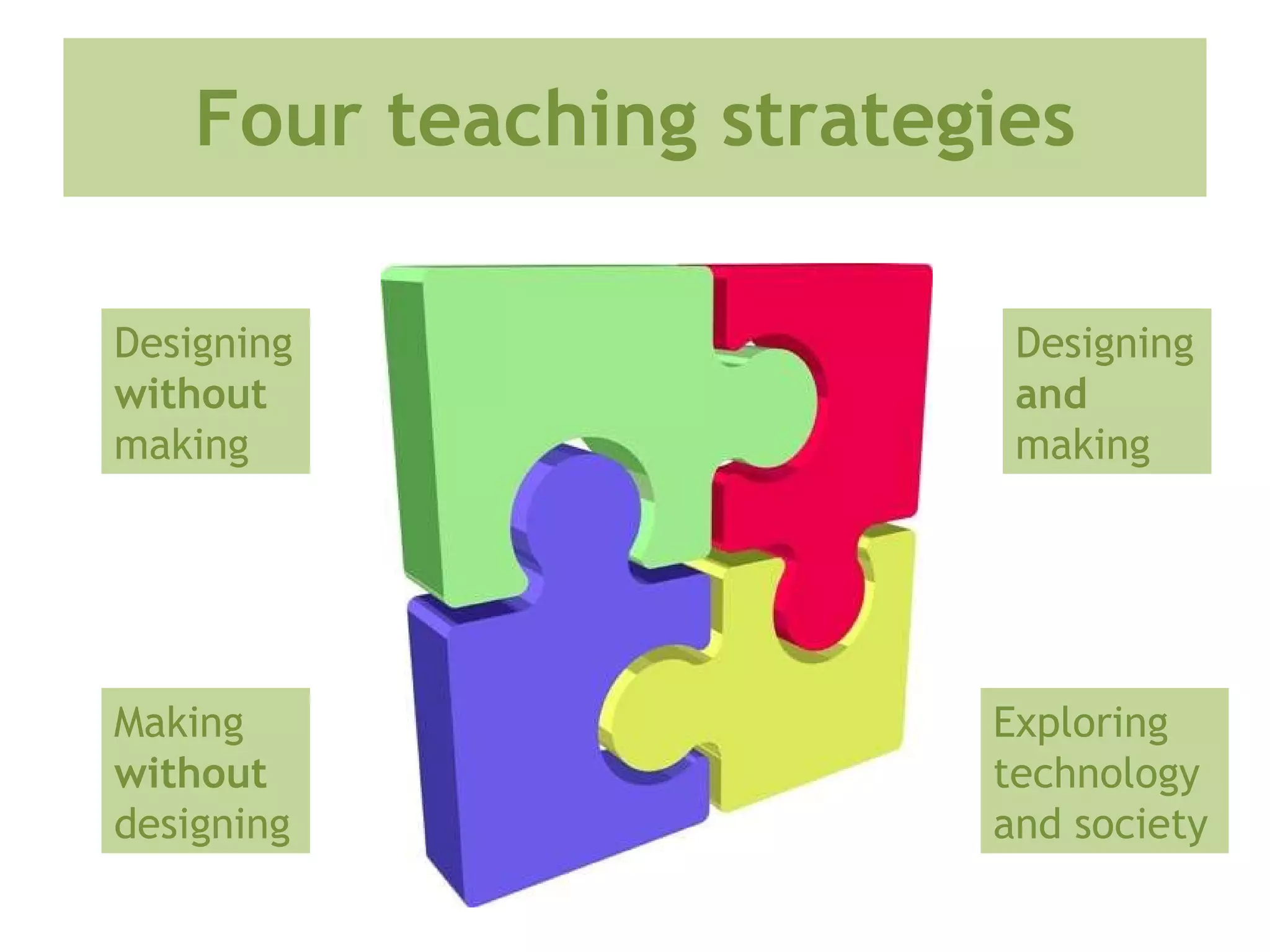
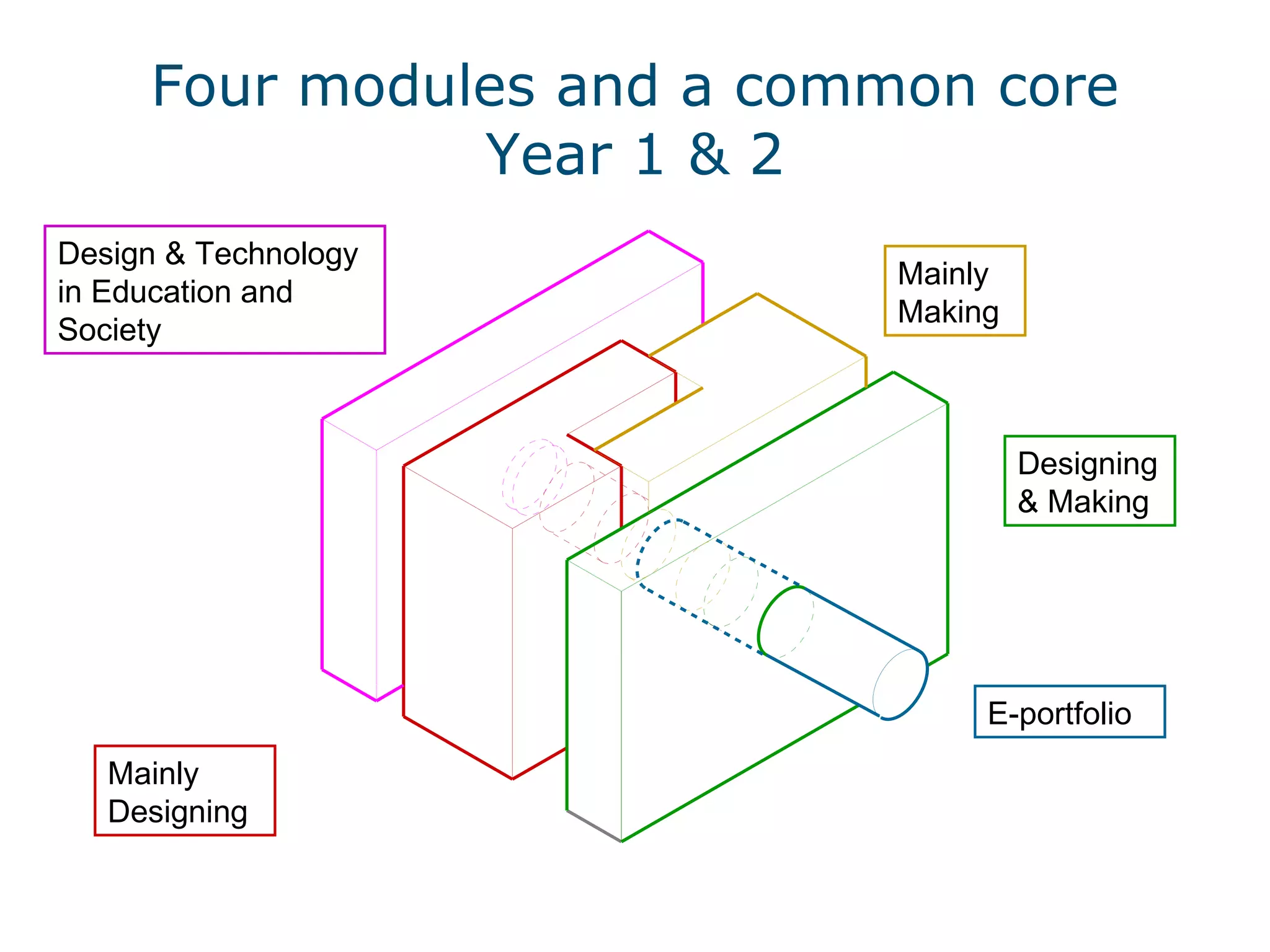
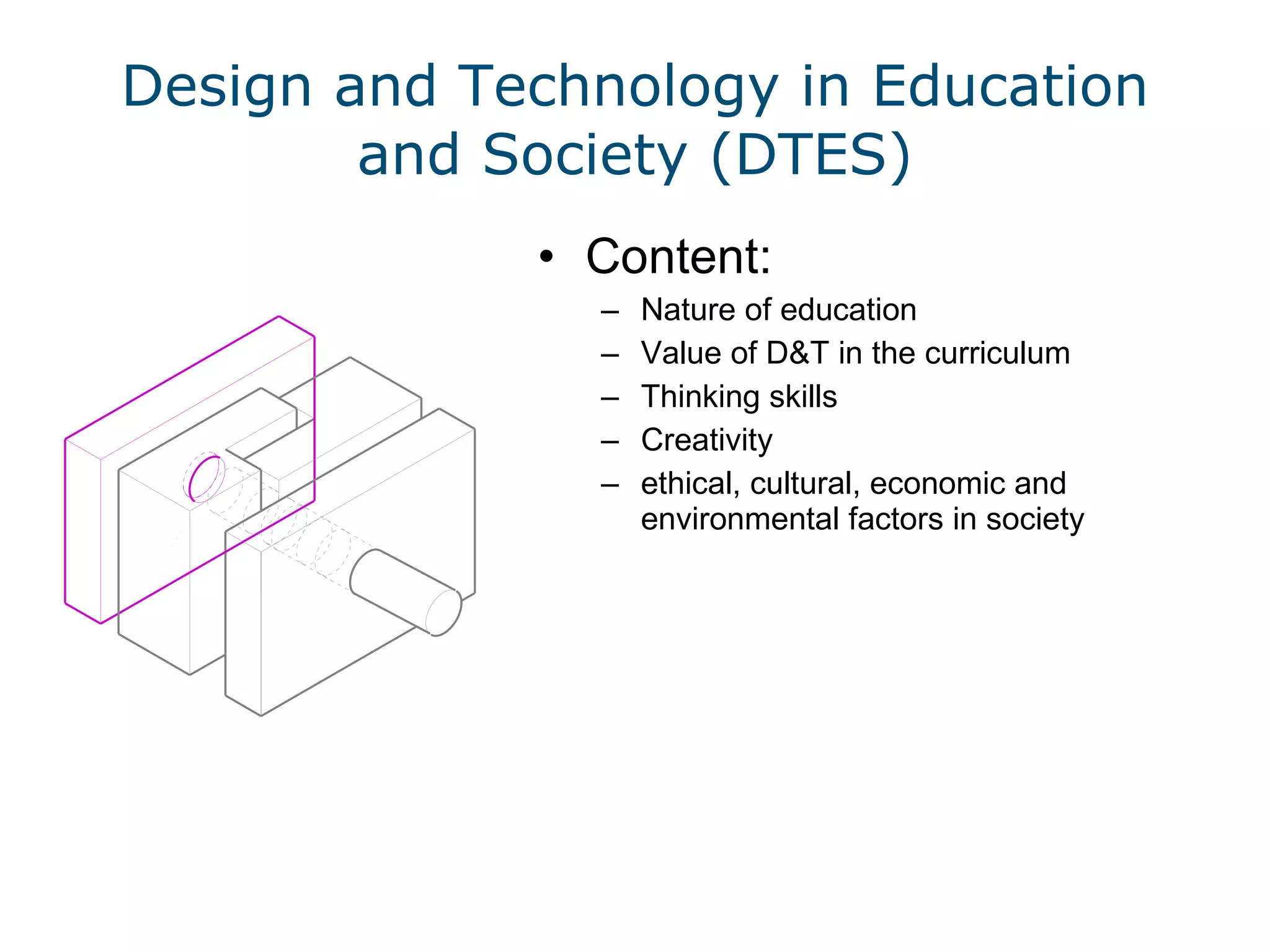
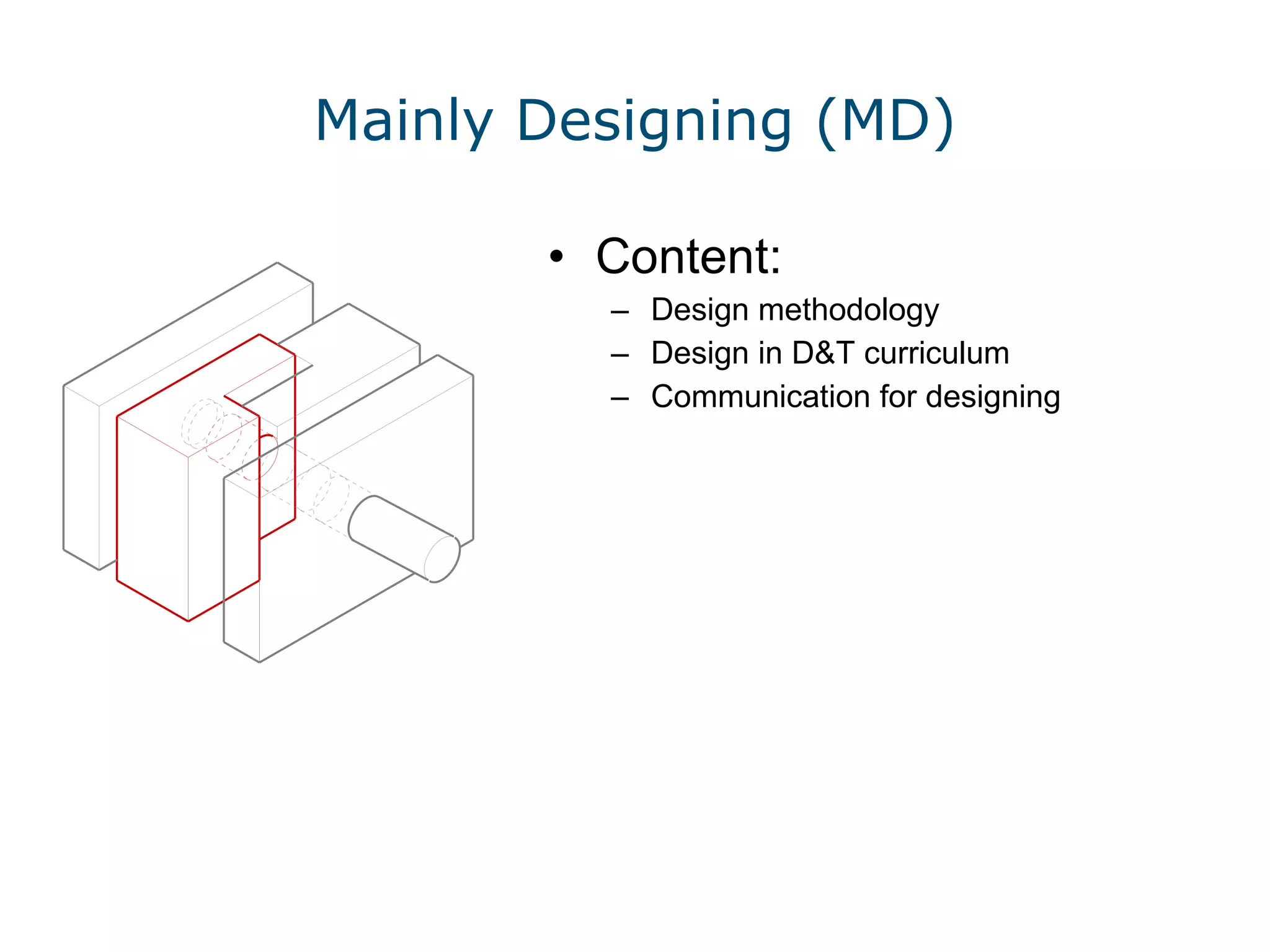
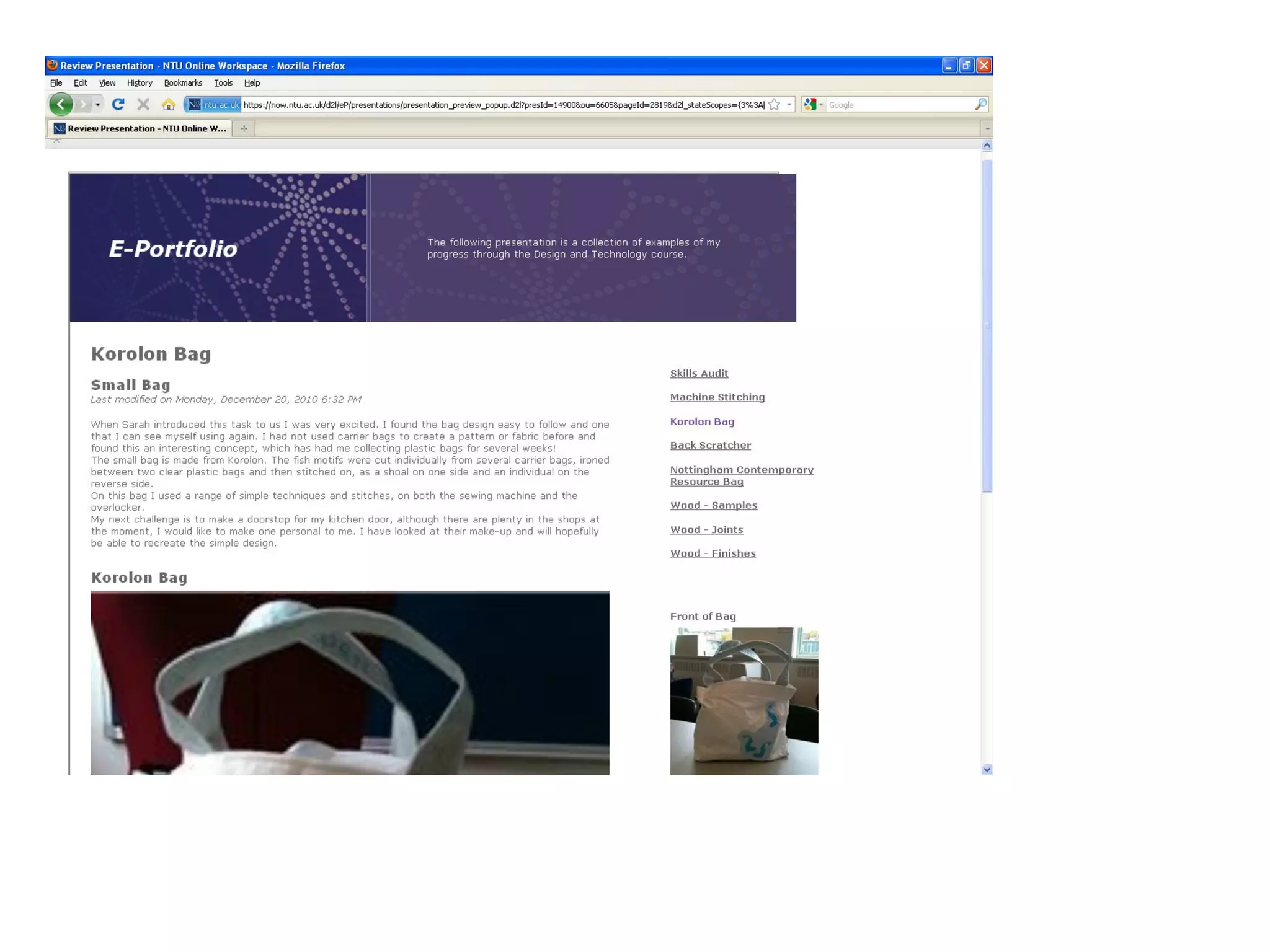
This document discusses the importance of design and technology (D&T) education and outlines the D&T teacher training program at Nottingham Trent University (NTU). It advocates for an integrated approach to designing and making. The program aims to equip trainee teachers with the skills and knowledge to teach all materials to key stage 3 and at least one specialism to key stage 5, while developing confidence in new technologies and innovative, creative teaching approaches. The program reflects the model of delivery and teaching believed to be effective for D&T in secondary education.