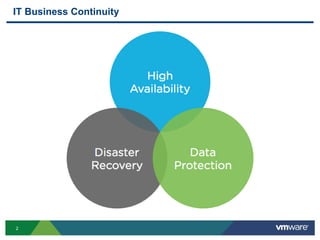
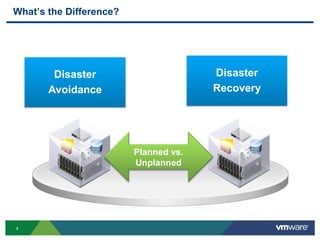
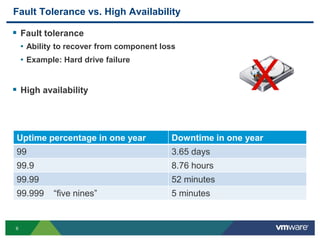
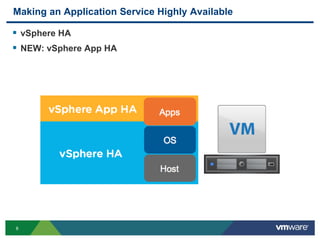
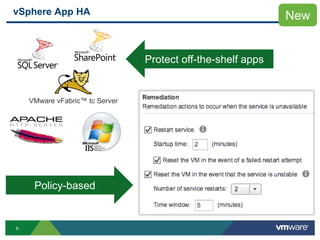
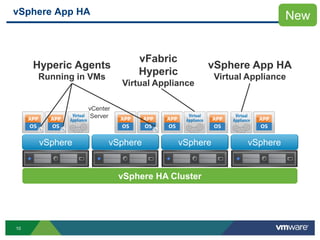
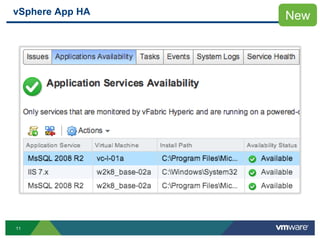
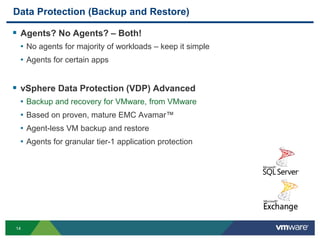
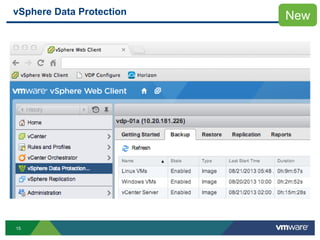
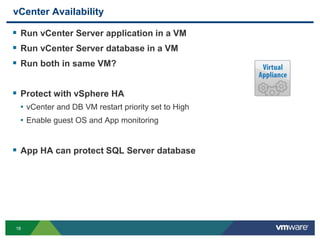
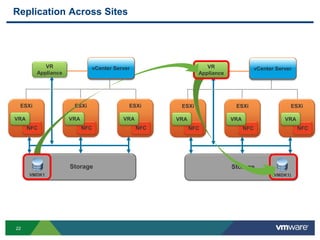
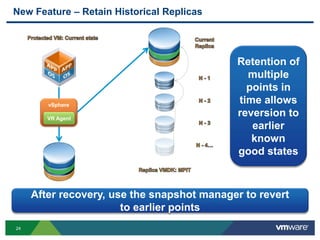
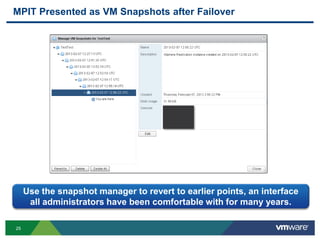
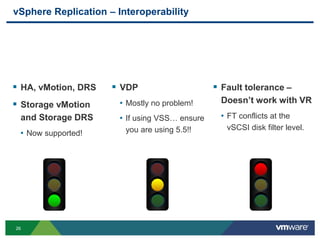
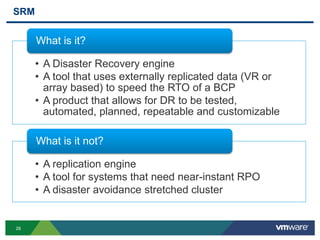
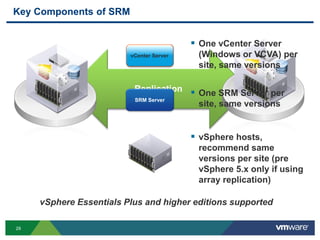
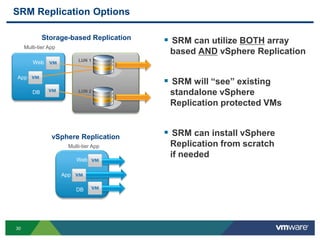
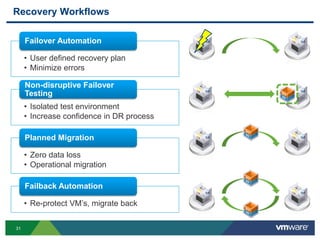
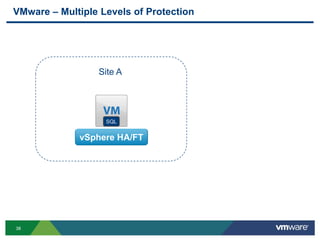
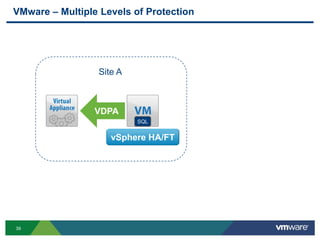
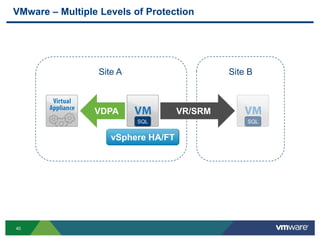
The document discusses the implementation of a holistic business continuity and disaster recovery (BC/DR) strategy using VMware technologies, highlighting differences between disaster recovery and business continuity. Key concepts such as recovery time objective (RTO), recovery point objective (RPO), and maximum tolerable downtime (MTD) are outlined, along with various VMware solutions for application availability, data protection, and site recovery manager (SRM). Best practices for optimizing VMware's capabilities for ensuring uptime, data recovery, and disaster preparedness are also shared.