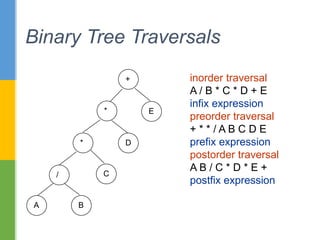
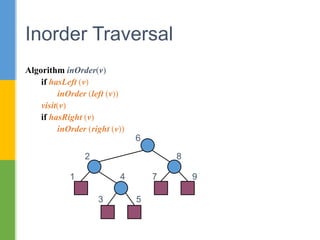
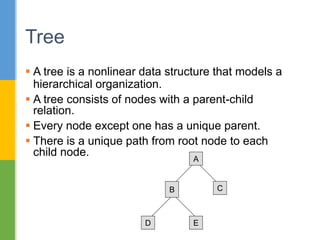
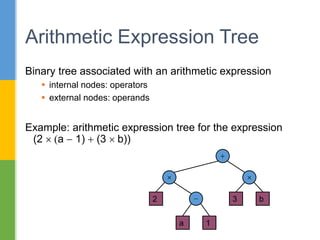
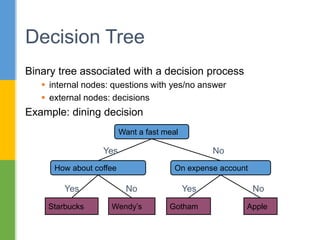
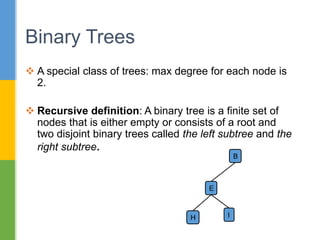
The document discusses trees as a nonlinear data structure with nodes connected in a parent-child relationship. It provides examples of different types of trees including binary trees, binary expression trees, and decision trees. Binary trees are defined recursively with each node having at most two children. The document also covers different methods of representing trees including sequentially and linked, as well as tree traversal algorithms including inorder, preorder and postorder traversal.


![Sequential Representation
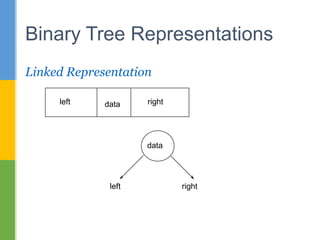
Binary Tree Representations
A
B
E
C
D
A
B
--
C
--
--
--
D
--
.
E
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
.
[16]
(1) waste space
(2) insertion/deletion
problem
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
A
B C
GE
I
D
H
F](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/implementationoftrees-140803000458-phpapp02/85/Implementation-of-trees-7-320.jpg)