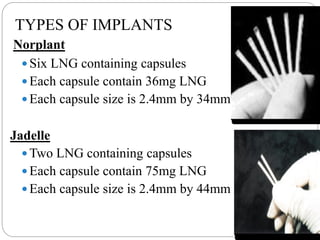
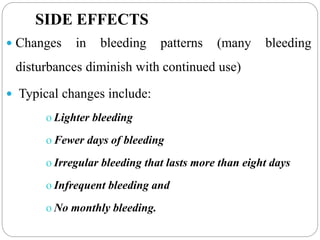
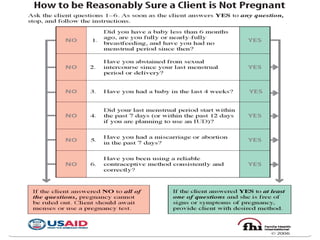
Implants are small, progesterone-only contraceptive rods placed under the skin by a trained provider that provide highly effective birth control for 3-5 years. They work by thickening cervical mucus and often preventing ovulation. Nearly all women can use implants, which have few limitations but do not protect against STIs. While irregular bleeding is common, implants are very effective, long-acting, reversible, and convenient to use once inserted. Proper client assessment and timing of insertion are important to ensure safe and effective use of this long-acting reversible contraceptive method.