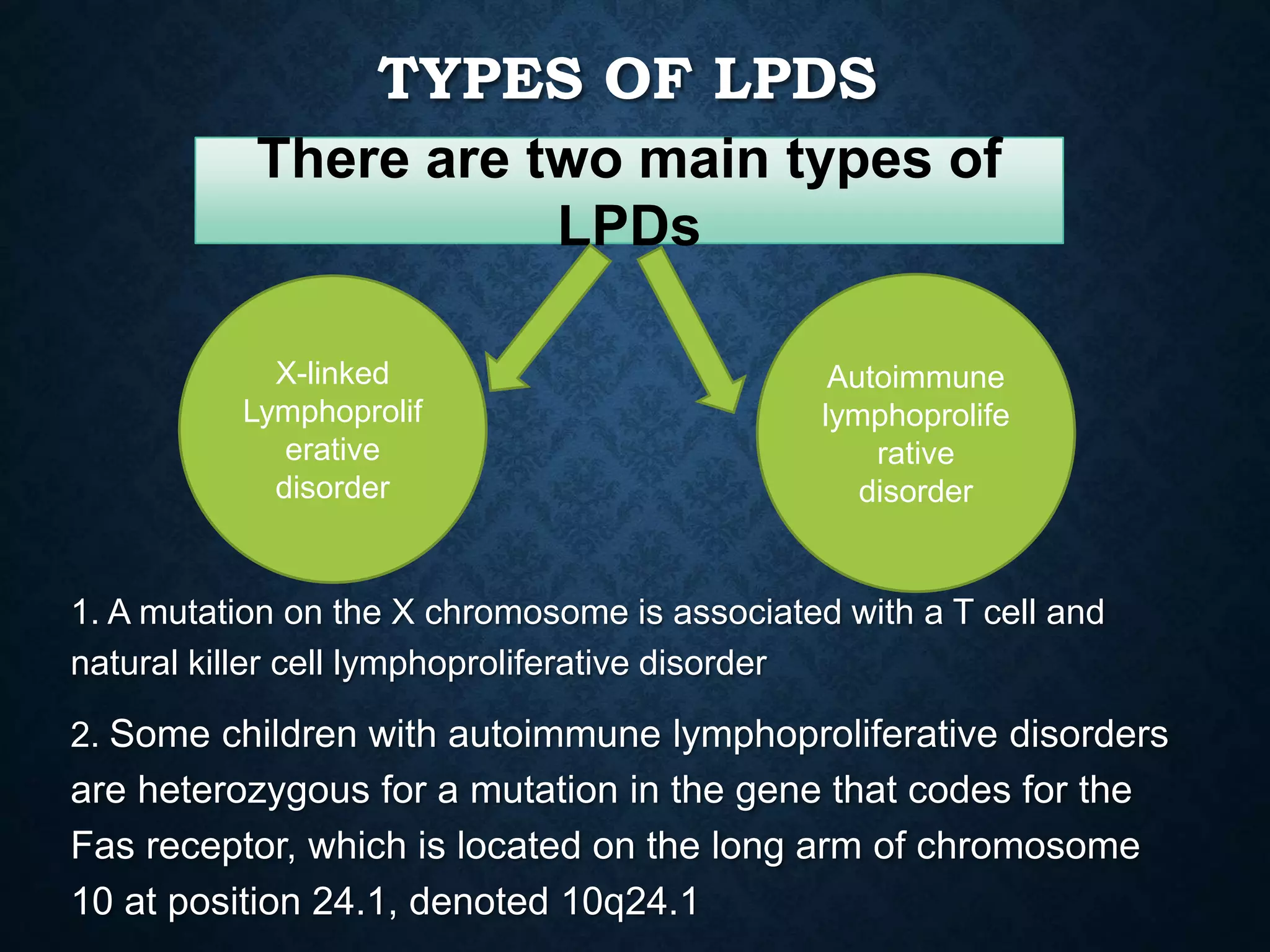
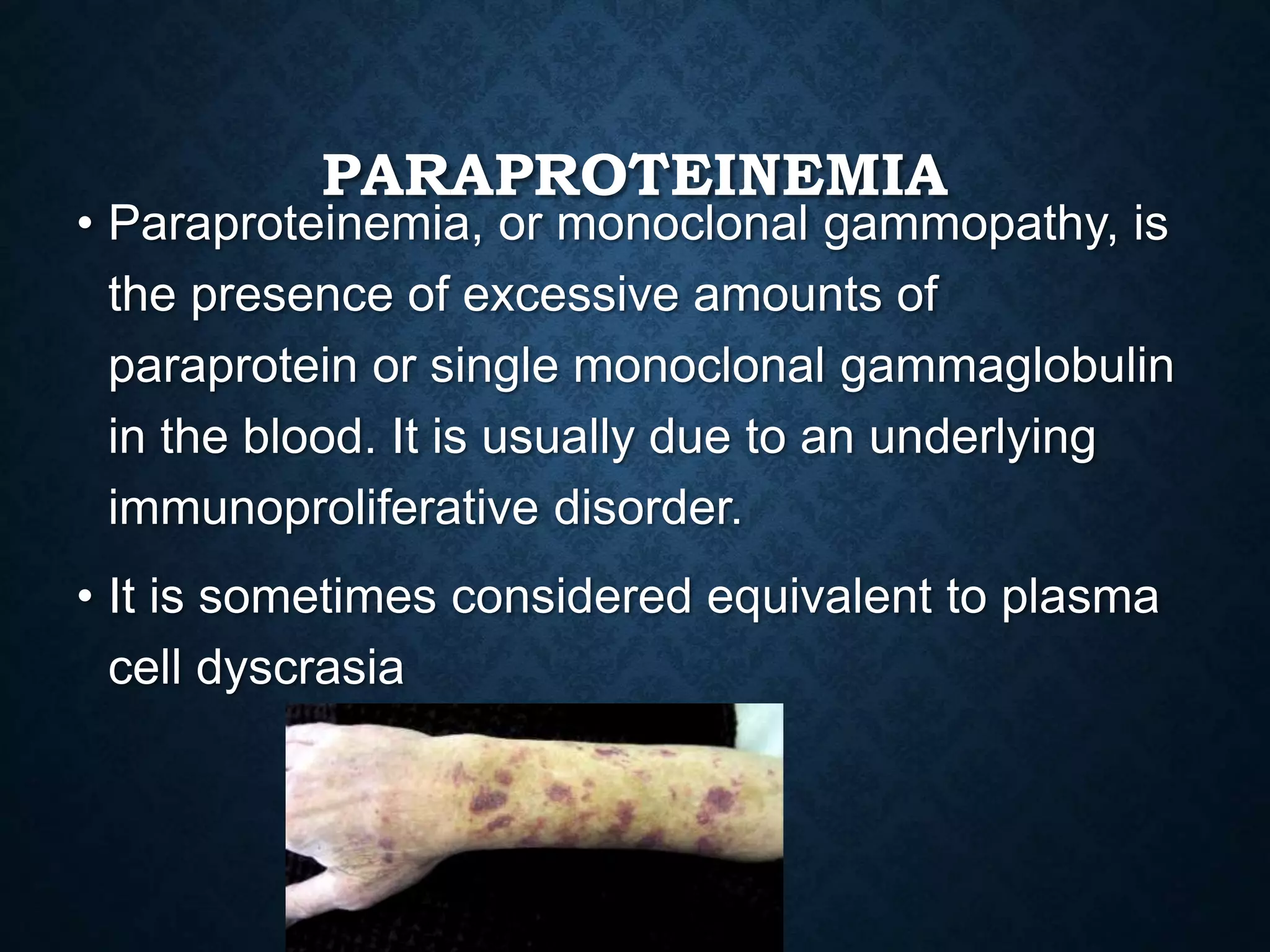
Immunoproliferative disorders are conditions characterized by the abnormal proliferation of immune cells. There are three main classes: lymphoproliferative disorders involving excessive lymphocytes, hypergammaglobulinemia with high gamma globulin levels, and paraproteinemia with monoclonal proteins. Common symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss and fatigue. Lymphoproliferative disorders occur in immunocompromised individuals and can be caused by genetic mutations or acquired/iatrogenic factors. Hypergammaglobulinemia and paraproteinemia involve excessive antibodies and can indicate underlying disorders. Diagnosis involves scans and blood tests, while treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation and surgery.