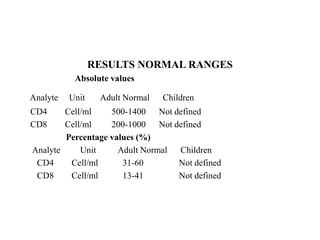
Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the proteins expressed by cells using flow cytometry. It is commonly used in research and clinical diagnostics. The document discusses immunophenotyping procedures including specimen collection and storage, reagents, staining patient samples, analyzing results, and reporting normal ranges and critical values. Challenges and improvements to the immunophenotyping section are also mentioned.