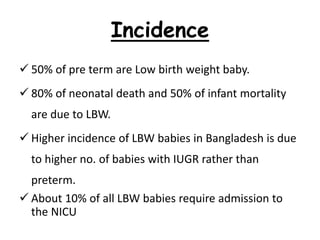
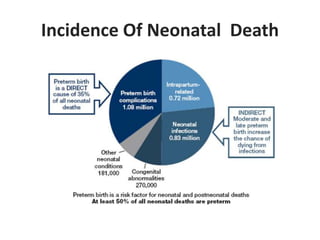
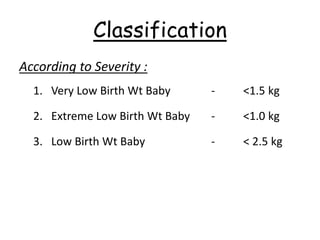
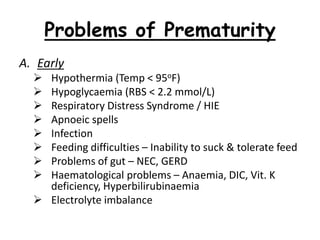
1) Low birth weight babies are those born weighing less than 2,500 grams. They are at higher risk of neonatal death and infant mortality.
2) Management of low birth weight babies depends on their weight - babies over 1.8kg can be managed at home, those 1.5-1.8kg require hospital care, and babies under 1.5kg need intensive care in the NICU.
3) Kangaroo mother care is a way to care for low birth weight babies that promotes warmth, breastfeeding, infection prevention, and bonding between mother and baby.