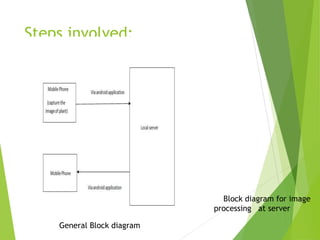
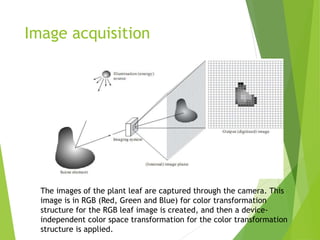
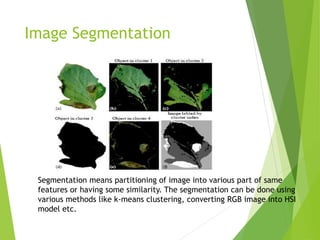
This document describes a proposed app for plant health monitoring using digital image processing. The app would allow farmers to capture images of plant leaves using a camera phone and send them to an image processing server. The server would preprocess the images to remove noise, segment the leaves from the background, extract features like color and texture, and classify the leaves as healthy or diseased using a support vector machine model. This would help farmers identify plant diseases without needing to contact experts, reducing time and costs. However, the method may not be applicable to all types of plants.