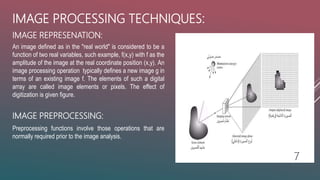
1. Image processing involves modifying digital images using various techniques. It is used to check for presence, detect and localize objects, and identify and verify objects from images.
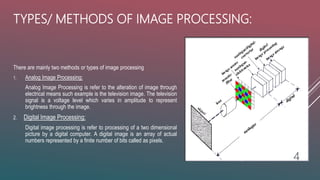
2. There are two main types of image processing: analog image processing which alters images through electrical means like TV, and digital image processing which processes 2D images using computers by representing images as arrays of pixels.
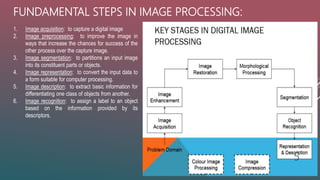
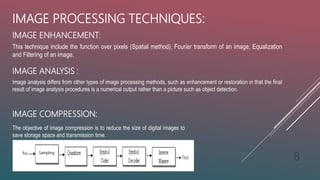
3. Key steps in image processing include image acquisition, preprocessing, segmentation, representation, description, and recognition. Techniques include representation, preprocessing, enhancement, analysis, and data compression. Applications are in remote sensing, medicine, forensics, military, film, documents, graphics, printing, and more.