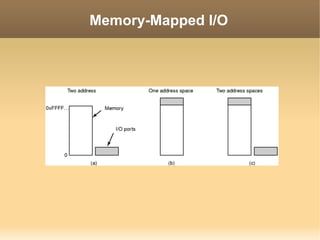
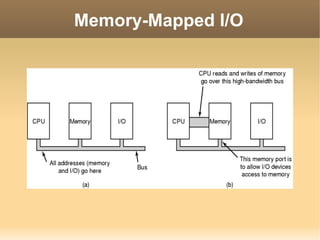
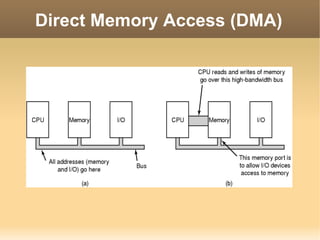
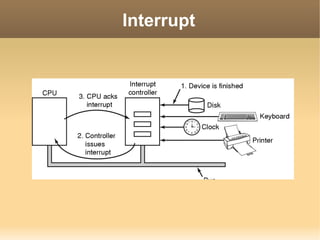
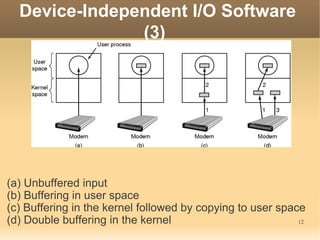
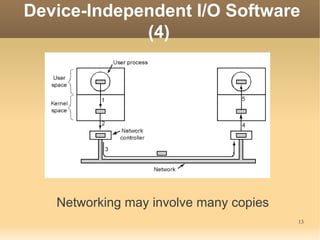
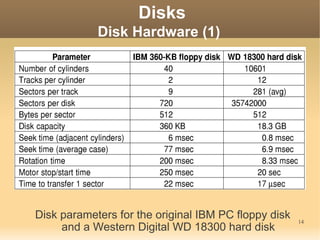
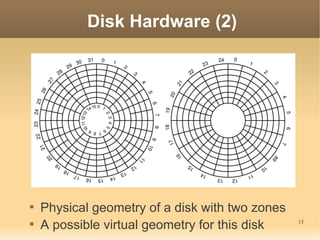
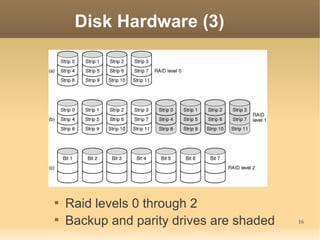
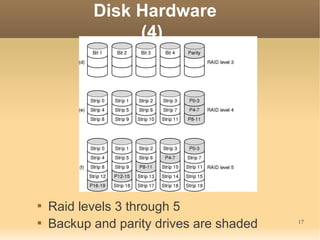
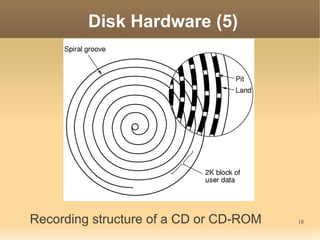
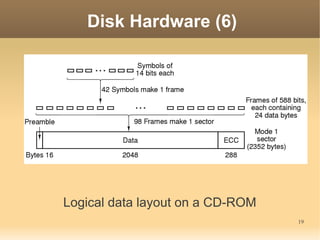
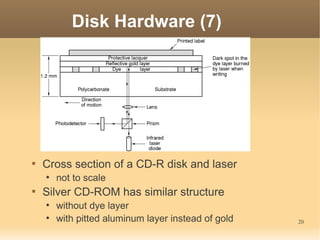
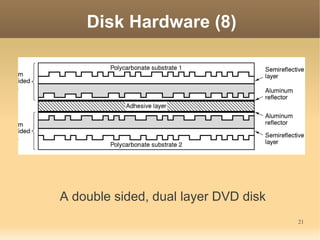
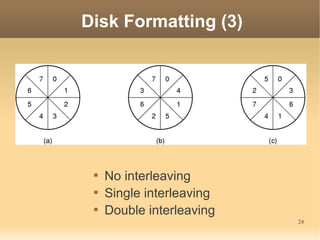
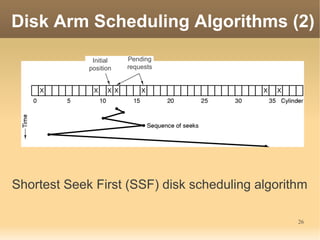
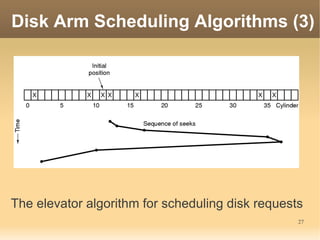
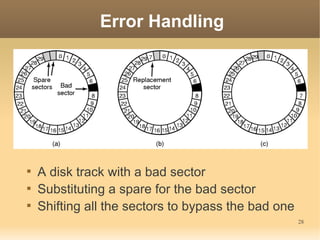
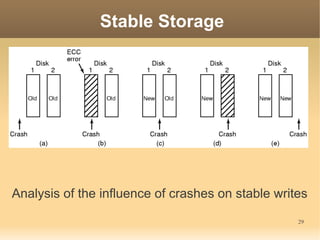
This document discusses input/output (I/O) concepts in operating systems. It covers I/O devices and controllers, principles of I/O software including device independence and uniform naming. Memory-mapped I/O, direct memory access, and interrupts are described. Page replacement algorithms like not recently used and first-in first-out are introduced. The document also examines disk hardware components, formatting, and scheduling algorithms. Error handling and stable storage concepts for disks are summarized. References for further reading on operating system concepts are provided.