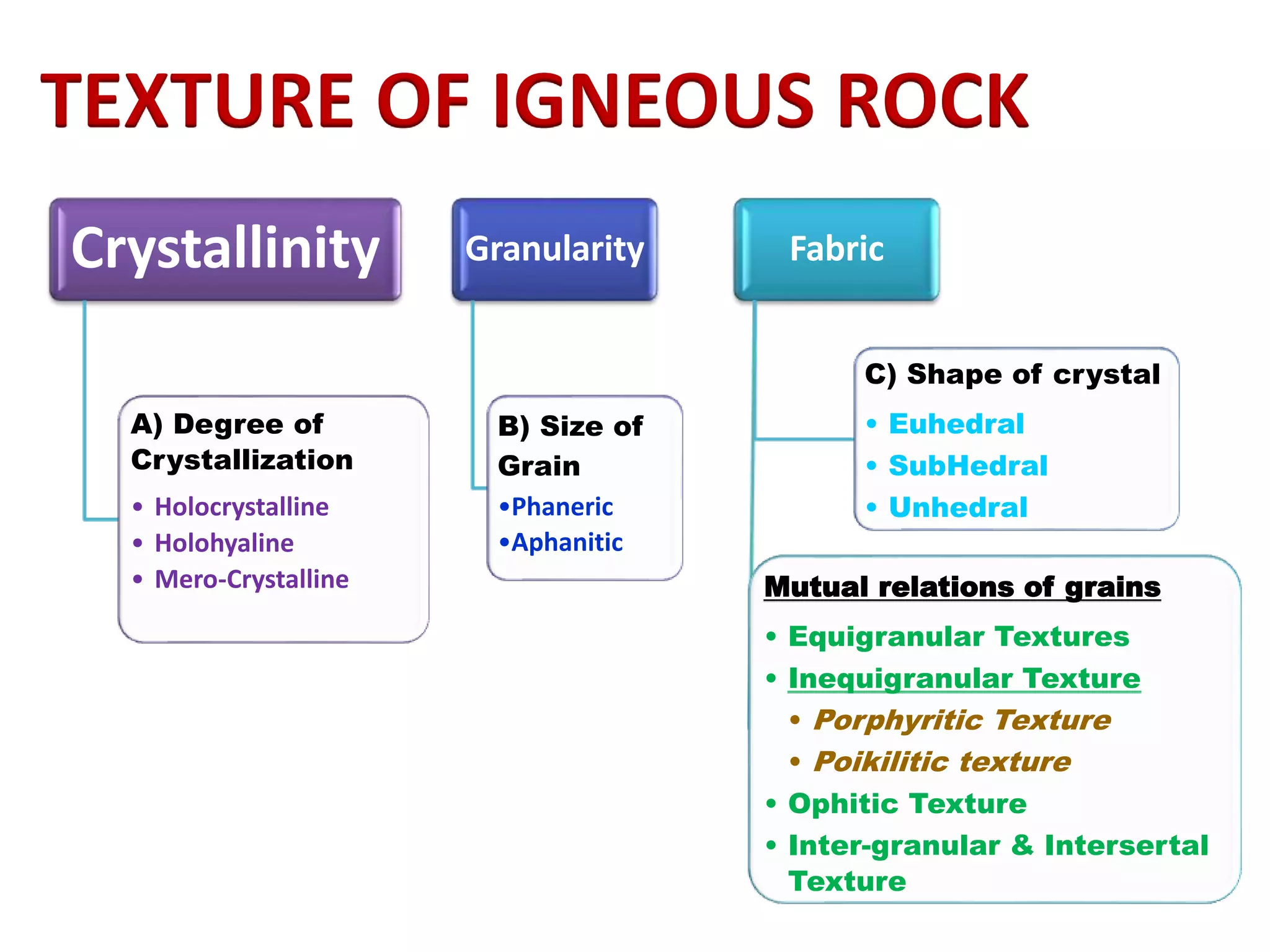
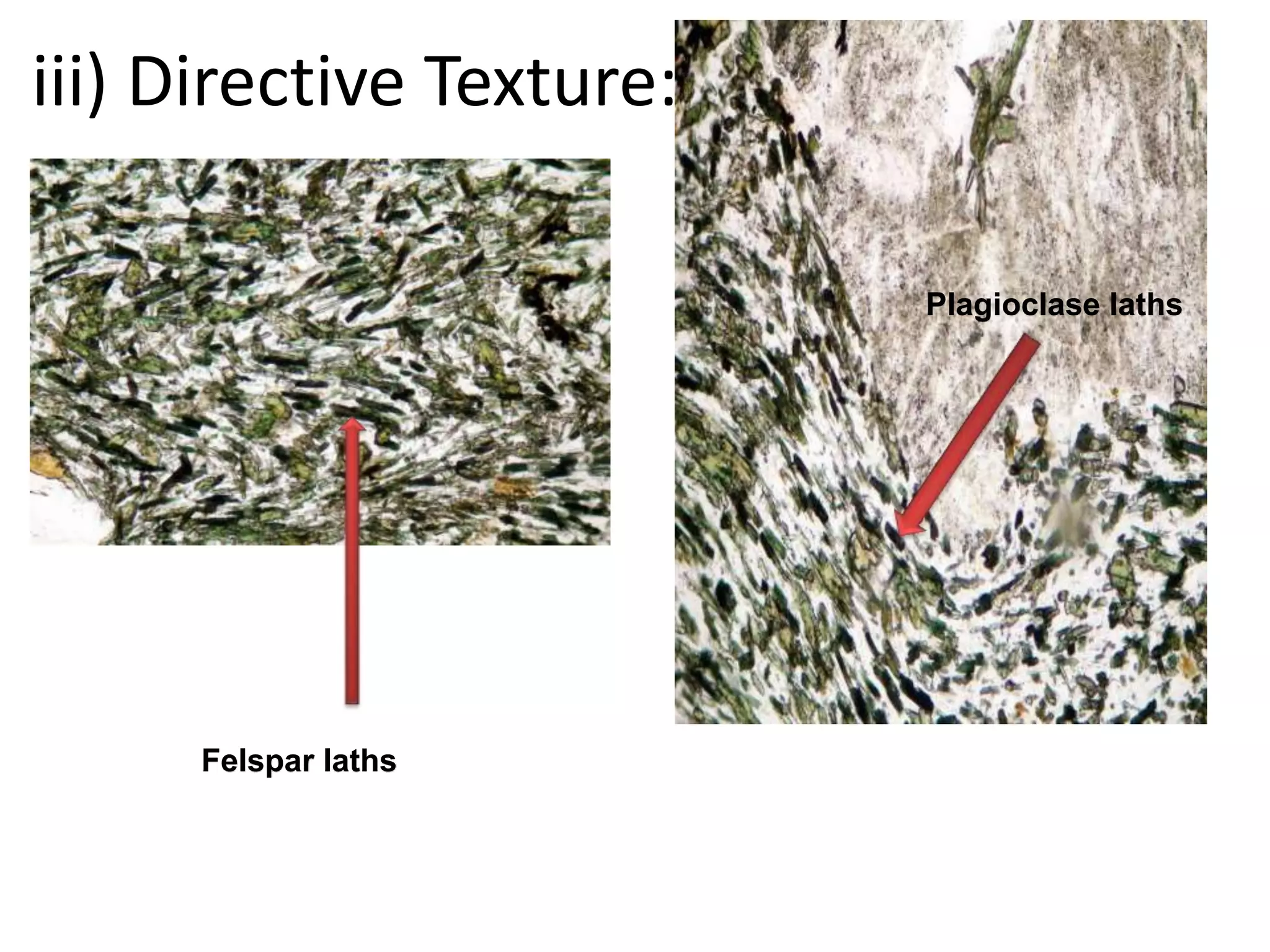
The document discusses petrology, focusing on the classification, origin, and texture of igneous rocks. It outlines the types of igneous rocks based on silica content and their crystallization characteristics, including granularity and fabric. Key concepts include the effects of cooling rates on texture and the relationships between mineral grains within rocks.