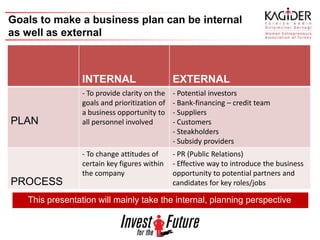
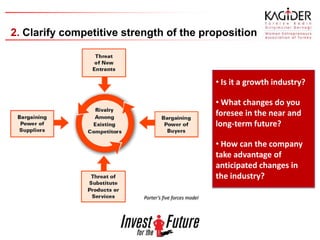
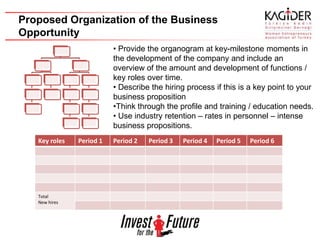
The document provides guidance on developing an effective business plan. It discusses that a business plan clarifies a company's direction, allows a company to acquire capital and financing, and identifies goals. It recommends including an executive summary, company description, products/services, marketing plan, operational plan, management overview, financial plan, capital needs, risks/opportunities, and appendices. The marketing plan should include research on the target market and competition, as well as sales forecasts. The operational plan outlines daily operations, location, inventory, legal needs, staffing, and policies.