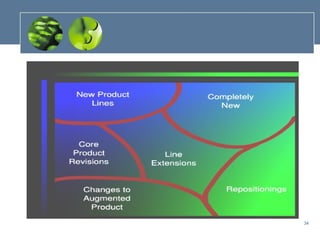
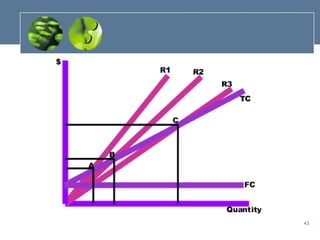
The document outlines the key components of a business plan, including describing different types of business plans, the advantages of developing a business plan, and the processes involved in business planning, marketing research, product development, financial planning, and supply chain management. It provides an overview of the various sections that should be included in a business plan and factors to consider in each business planning area.