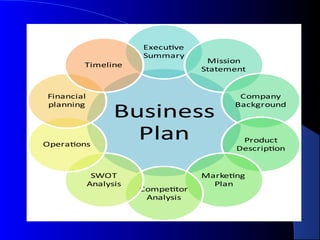
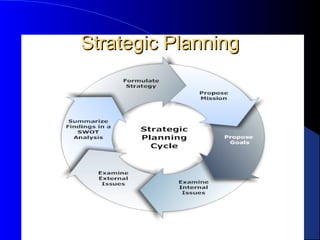
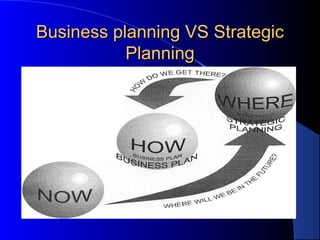
The document provides an overview of business plans and strategic planning. It explains that a business plan guides strategic direction, is needed for lenders and investors, and helps establish goals, market opportunities, costs, and profitability. A strategic plan communicates organizational direction to stakeholders. Key parts of a business plan include an executive summary, company and product descriptions, market analysis, competitors, marketing/sales plans, management, and financial projections. The document also compares business plans and strategic plans.