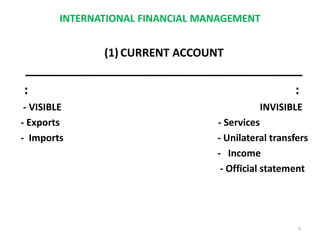
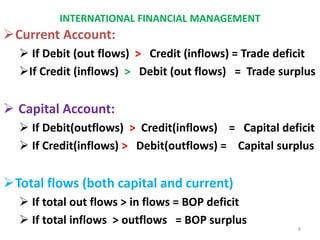
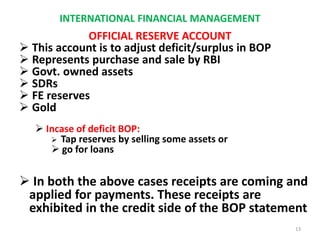
The document discusses the components of a country's balance of payments (BOP), which is a statistical record of its international transactions. It is presented as a double-entry bookkeeping statement with receipts and payments over a time period. The major components are the current account (exports, imports, services, income), capital account (investments, loans), and official reserve account (gold, foreign currency, SDRs). The current account balance is in surplus if receipts exceed payments and in deficit if payments exceed receipts. The capital account similarly shows a surplus if capital inflows exceed outflows. Overall BOP surplus or deficit depends on the combined balance of the current and capital accounts.