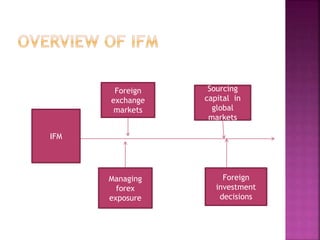
The document discusses international financial management. It covers topics such as the balance of payments, foreign exchange markets, sources of financing for foreign investment, and factors that influence international trade flows. International financial management involves managing financial resources and exposure across different countries and currencies. A key part is the balance of payments, which records a country's international transactions and provides insights into the demand and supply of its currency.