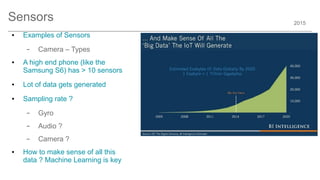
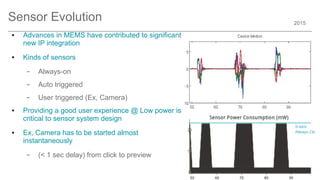
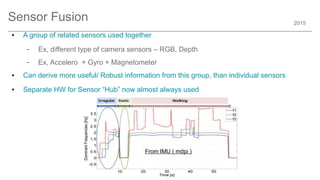
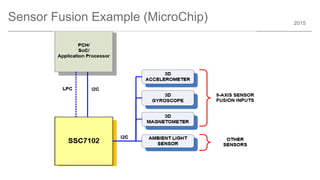
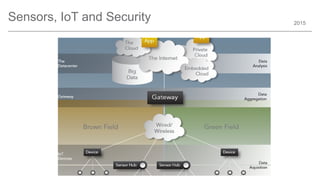
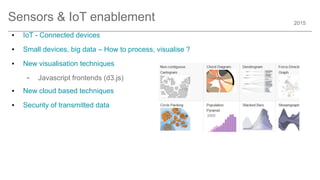
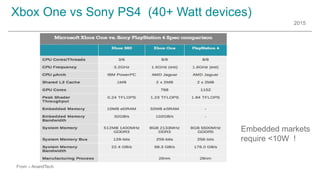
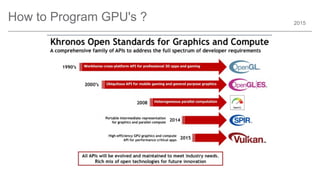
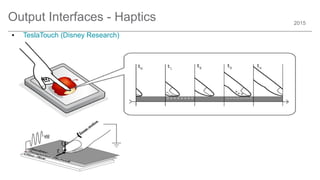
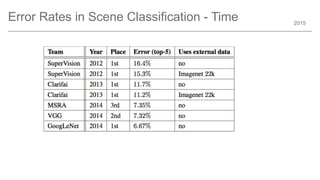
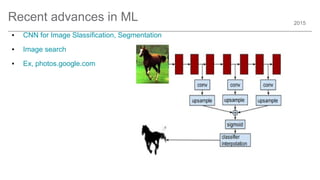
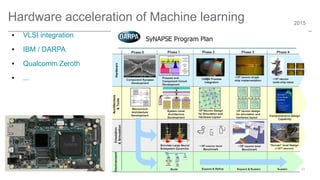
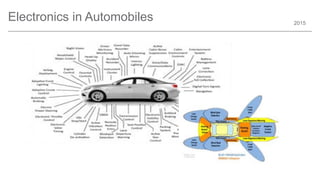
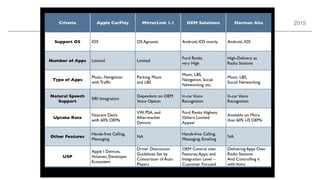
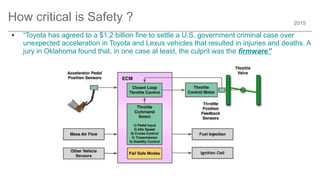
The document outlines trends and opportunities in consumer electronics, focusing on core components such as sensors, displays, user interfaces, and machine learning. It emphasizes the evolution of technology and integration in automobiles, highlighting the importance of security and safety. Additionally, it discusses future research trends and the need for advancements in low power architectures and machine learning applications.