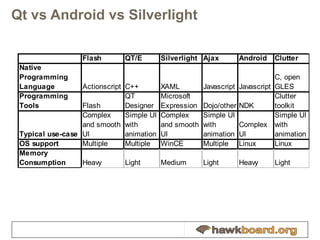
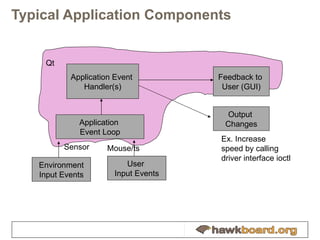
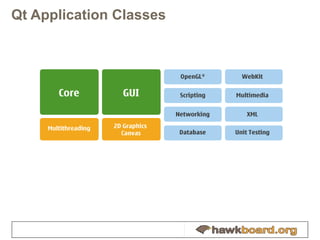
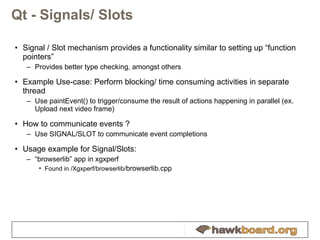
The document provides an overview of developing Qt applications specifically for the Hawkboard platform, outlining Qt's history, licensing options, and fundamental concepts such as application structure, the signal/slot mechanism, and UI development using widgets and graphics views. It includes practical tips for creating efficient applications with the Qt framework and introduces the XGXPerf toolkit for benchmarking and profiling Qt applications. The content is intended for developers looking to build and optimize Qt applications on embedded systems like Hawkboard.
![Developing Qt applications on HawkBoard Prabindh Sundareson [email_address] July 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hawktawk2qthawkfinal-100725100741-phpapp01/75/Developing-and-Benchmarking-Qt-applications-on-Hawkboard-with-Xgxperf-1-2048.jpg)










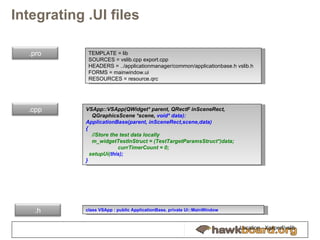

![XgxPerf Usage SVN access: svn checkout http:// gforge.ti.com/svn/gleslayer Username = anonymous, password= (blank) (or) Download and extract source tarball Non-OpenEmbedded users https://gforge.ti.com/gf/download/docmanfileversion/192/3696/xgxperf_1.1.0.tar.gz (check SVN for latest) Update path of framework (ex. QTDIR =) in Rules.make Build - “make && make install” Open Embedded-users For Angstrom setup, use the recipes for Angstrom at https://gforge.ti.com/gf/download/docmanfileversion/195/3699/ti-xgxperf.tar Build any image that provides Qt - X11 or Qt – Embedded package Choose the appropriate Xgxperf recipe: ti-xgxperf-qt-x11 for X11 build, or ti-xgxperf-qt-embedded. X11 build is shown below. Q^oe] sh oebb.sh bitbake ti-xgxperf-qt-x11 Q^oe] ls -l build/tmp-angstrom_2008_1/deploy/glibc/ipk/armv7a/ti-xgxperf-qt-x11_1.0.0.0-r0+svnr54.5_armv7a.ipk -rw-r--r-- 1 prabindh prabindh 4873428 2010-07-19 20:18 build/tmp-angstrom_2008_1/deploy/glibc/ipk/armv7a/ti-xgxperf-qt-x11_1.0.0.0-r0+svnr54.5_armv7a.ipk XgxPerf is now ready to use on local HW EVM ./xgxperf_app [–qws] <cookie> <fps> …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hawktawk2qthawkfinal-100725100741-phpapp01/85/Developing-and-Benchmarking-Qt-applications-on-Hawkboard-with-Xgxperf-25-320.jpg)

![2 minute Qt Application Development [live demo] Create new Xgxperf subproject from template Add items Build project Use xgxperf_app to invoke “ ./xgxperf_app –qws <args>”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hawktawk2qthawkfinal-100725100741-phpapp01/85/Developing-and-Benchmarking-Qt-applications-on-Hawkboard-with-Xgxperf-28-320.jpg)