This document discusses output capacitor selection for low voltage, high current power supplies used in applications like microprocessors. It derives an equation to calculate the minimum number of capacitors needed to meet transient voltage regulation requirements during load current steps. Different capacitor types are compared based on this calculation, including electrolytic, tantalum, ceramic, and polymer capacitors. Simulation and experimental results are presented to verify the theoretical analysis. The analysis shows that the minimum capacitors required depends on factors like equivalent series resistance, capacitance, current step size, and whether the system frequency is higher or lower than the capacitor's zero frequency. This methodology allows engineers to optimize capacitor selection for cost and performance.
![2004 351h Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen. Germany. 2004
Output Capacitor Comparison for Low Voltage High Current Applications
Chongming Qiao, Jason Zhang, Parviz Parto and David Jauregui
International Rectifier
Email: mqiaol@,irf.com
Abstract: The digital IC such as microprocessor requires low
voltage, high current as well as very tight transient regulation.
This imposes strict requirement for the power supply -
typically a step down PWM converters with single phase or
multi-phase. The output capacitors play an important role in
the transient response. Many types of capacitors are available
in the market such as Aluminum electrolytic, Tantalum,
POSCAP, OSCON cap, Specialty polymer, as well as large
value of multi-layer ceramic capacitors. This paper derives a
basic equation to calculate the minimum number of capacitors
in order to meet the transient requirement. Based on this
information, a compromise between cost and performance can
be decided by engineers.
1. INTRODUCTION
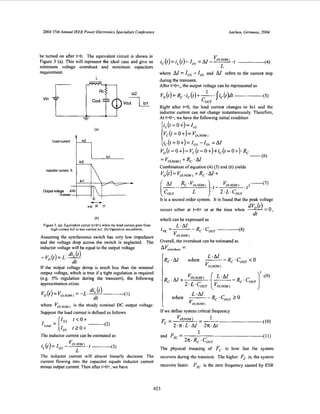
r---------:
f----iL&PWMm n M W
Vdtaae
can- j m
Fiourc 1. A diagram of single-phasesynchmnous buck convertei
The trend of power supply for digital world such as
microprocessor, DSP is that the supply voltage keeps
decreasing and the supply current keeps increasing. The
voltage regulation window becomes much smaller as the
voltage goes down. In the meantime, the slew rate of load
transient current can go as fast as IOOOA/us. All these
requirements impose a challenge for power supply
designers.
Typically, a single-phase or multi-phase synchronous buck
converter is employed to supply the current for
microprocessor or other high-speed digital system such as
memory application [I]. A general diagram is shown in
Figure 1 and typical transient response for synchronous
buck converter is shown in Figure 2. For current
microprocessor, the voltage droop and overshoot
specification during the transient is very tight and it is
typically i5% of nominal output voltage with a IOOA step
load amd 100A/us slew rate. In order to meet the transient
requirement, the selection of inductor [2] and capacitors is
very critical. Suppose the inductor is chosen such that the
inductor current ripple is about 20%-40% of nominal
current, the voltage droop during the transient will be highly
dependent on the output capacitor performance. This paper
will discuss the impact of capacitor on the output voltage
performance during the load transient. Section 111. derives a
simple equation to illustrate the relationship among voltage
droop, output inductor, output capacitor capacitance and
ESR (equivalent series resistor). Section 111 calculates the
minimum number of capacitors to meet the voltage transient
requirement. Section IV. summarizes a comparison among
different capacitors. Section V. discusses “body brake”
technology proposed by International Rectifier to reduce the
overshoot. Simulation and experiment verification was
described in Section VI. and VII. . Finally a conclusion is
given in Section VIII. .
Figure 2. Typicaltransient responsewaveforms.
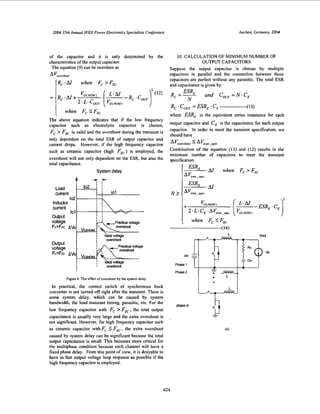
11. CALCULATION OF VOLTAGE OVERHSHOOT
DURING THE TRANSIENT
In Figure 2, at most of application, the input voltage is much
higher than the output and the typical duty ratio of PWM
converter is much less than 50%. The voltage droop or
overshoot is typically unsymmetrical. Voltage AV,,,,,, is
usually higher than AVdrmp.Therefore, this paper will
emphasize the analysis based on However, the
analysis approach can be applied to AVdrmp as well.
Suppose the load current changes from 102 to 101 at time
t=O, if we assume the bandwidth of the PWM controller
feedback loop is high enough, the synchronous switch will
07803-8399-0/04/$20.M) 02004 IEEE. 622](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0ee88220-29e2-4850-ba59-54da2482f1bf-151110185021-lva1-app6892/75/IEEE-2004-1-2048.jpg)

![2004 35rhAnnual IEEE Power Elecironics Specialisis Conference Aachen, Germany, 2004
P
pBom
V. REDUCE THE OVERSHOOT WITH BODY BRAKE
International Rectifier Inc. has a trademark “body brake”
concept [3], which can significantly reduce the overshoot for
a step load from high current to low current. The concepj is
to turn off the synchronous FET as soon as the transient load
current starts from high to low. The equivalent diagram is
shown in Figure 7.
f-mw?%Bodydiodeo ~
synchrorous FET
Figure 7. The equivalent diagramwith body brake during the load transient
(current fmm high to low).
During the time period before inductor current goes to 101,
the voltage across the inductor is given as
di
L.-- -V,,,,, +V, (Body diode voltage drop)-(17)
dt
Since at low voltage application (e.g. Iv), the body diode
voltage drop is similar scale as output voltage, the inductor
current decreases almost as two times fast as the case
without body brake concept as shown in Figure 3 (a). As a
result, the voltage overshoot is greatly reduced. Replacing
the V,,,,,, with V,,,,,, cV, in equation (12) will give the
estimated overshoot with body brake concept as shown in
equation (1 8).
A VuVe”hmr
(R,.Al when Fc >Fzc
....... :I .......... :.......;........:_.......
i i j ii jijiiiiiii::::::::::::::::::;:::::::...........................
Figure 8. Operation waveform of the body brake concept implementation.
The implementation of body brake concept is simple. One
comparator is added to compare the output of voltage error
amplifier output and the body brake threshold, which is set
to be slightly lower than the minimum voltage of oscillator
ramp. During the load transient, when the load current
changes from high to low, the output voltage will start to
increase, the voltage feedback loop will respond and the
output of voltage compensator or error amplifier will start to
decrease rapidly. Once the output voltage of voltage
compensator is certain voltage lower than the minimum
voltage of PWM oscillator ramp, the comparator will disable
the synchronous FET driver and allow the output inductor
current flowing through the body diode of synchronous
FET. Assuming the body diode voltage drop is 0.7V, for the
case in.Section IV, 124 IOOuF ceramic capacitor, with body
brake concept, the overshoot when load current from IOOA
to OA will result in 30mV according to equation (IS), which
is about 40% improved comparing with 50mV result shown
in Table 3. The simulation verification is shown in Figure 9.
Loadcurrent
.....;........;........;........4........
::::::::::::::::I::::::::::::::::::::::::
.......................,......................_ L ........ _........_,.................
%re 1 SynchronousFE1driver
._ ~~ .,D. ........L ........C... .....,..................
. ......... .....,m
<m ........................................
n s
..,.........*.......I . ,
.’.
.,e (.?,I‘“. 3,s 11. 1 1 1
nnrln.,
Figure 9. Simulationresults for transient response with body brake forthe
case in Section IV.
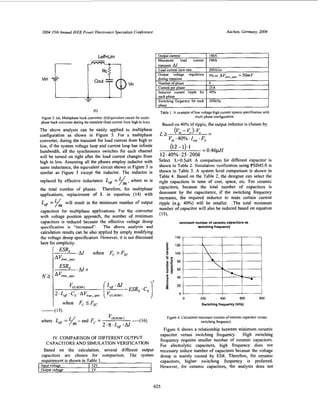
VI. CASE OF MIXED OUTPUT CAPACITORS
If the output capacitors are more than one type, such as
combination of ceramic and OSCON capacitors, the analysis
is slightly difficult. One of possible solutions is to do a
simple simulation as shown in Figure IO.The set up for the
two current sources are defined in Figure 11. The voltage
shown in the output will give a good estimate of the voltage
overshoot during the transient.
Output voltage
Figure IO. Simple simulation schematic for transient load with mixed
output capacitors.
627](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0ee88220-29e2-4850-ba59-54da2482f1bf-151110185021-lva1-app6892/85/IEEE-2004-6-320.jpg)
![2004 3.5rh Annual IEEE Power Elecrronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Germany, 2004
Output currentsource
(Load current )
lo1
lnp"tcurrentso102
(Inductor current)
wt=O At t l
At=Len*AlNarm
Figure II.Simulation setup for two currentsources.
VU. EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION
International Rectifier introduced iPOWlR technology
which is a breakthrough in power density, efficiency and
simplicity for power conversion. The following experiment
shows a 4-phase application using IP2001 devices. The
'stem requirement is summarized in the following table.
........I..... .................................................................................................
imWtfhlemslEkkfMqriim
!
i...,........................
Figure 12. Internal Blockdiagram oflPZ00I.
Table 5. System specification
In reality, the ceramic capacitor is not ideal; the resistance
caused by layout is not negligible compare with the ESR of
ceramic. In addition, the previous analysis neglects the
output voltage ripple. In fact, the ripple ofthe output voltage
can contribute to the overall the voltage regulation
specification. More important, for multiphase application,
each channel has a phase delay referring to the other
channel. During the transient, it is impossible that all the
control switches will be turned off at same time. This delay
will cause more voltage droop or overshoot during the
transient. Therefore, the selected output ceramic capacitors
are more than the minimum capacitance. In this application,
the total capacitors are about 2000uF.
T s k m 1.00MSfs 33 Aces
r - 4
A:27.6mV
. . . .
. . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+ . . . . . . . . . . . . .
i . . . :. .
. .
: i : : :. .
i
. . . . . . I . . . . . .. . . .
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . : . . T . . : . . . . . . . . . . .
. . .
. .
. . .
. ., , . ~: : i
M 5 0 . 0 ~ 1chl I I .35 9 Mar2002
10:04:56
Figure 13. Expenmental waveforms for output voltage ai 54A load current
transient.
VIII. CONCLUSION
The high-speed digital processor requires strict
requirement on the voltage regulator. In this paper, based on
a simplified circuit diagram, the relationship between
voltage overshoot, output inductor and output capacitors are
derived. Furthermore, an equation is derived to calculate the
minimum number of capacitors in order to meet the transient
specification. It shows that the minimum number of
capacitors is not only dependent on the ESR of capacitor,
but also the total capacitance. A comparison among
aluminum electrolytic, OSCON, polymer and ceramic
capacitors is given in details. Analysis along with
simulation verification is provided. This paper provides a
general guideline to choose the output capacitors based on
the system requirement.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The author would like to thank for the advise of professors
Keyue Smedley, Franco Maddaleno and the help of
colleagues Mark Yabut, Veng Tang, etc.
REFERENCES:
[I] Peng Xu; Jia Wei; Kaiwei Yao; Yu Meng; Lee, F.C.;
Investigation of candidate topologies for 12 V VRM Applied
Power Electronics Conference and Exposition. 2002. APEC
2002. Seventeenth Annual IEEE , Volume: 2 , 10-14 March
2002 Pa&): 686 -692 vol.
Pit-Leong Wong; Lee, F.C.; Peng Xu; Kaiwei Yao. Critical
inductance in voltage regulator modules; Applied Power
Electronics Conference and Exposition, 2002. APEC 2002.
Seventeenth Annual IEEE , Volume: 1 , 10-14 March 2002
Page($): 203 -209 v0l.l
[2]
131 1133086datasheet..
628](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0ee88220-29e2-4850-ba59-54da2482f1bf-151110185021-lva1-app6892/85/IEEE-2004-7-320.jpg)