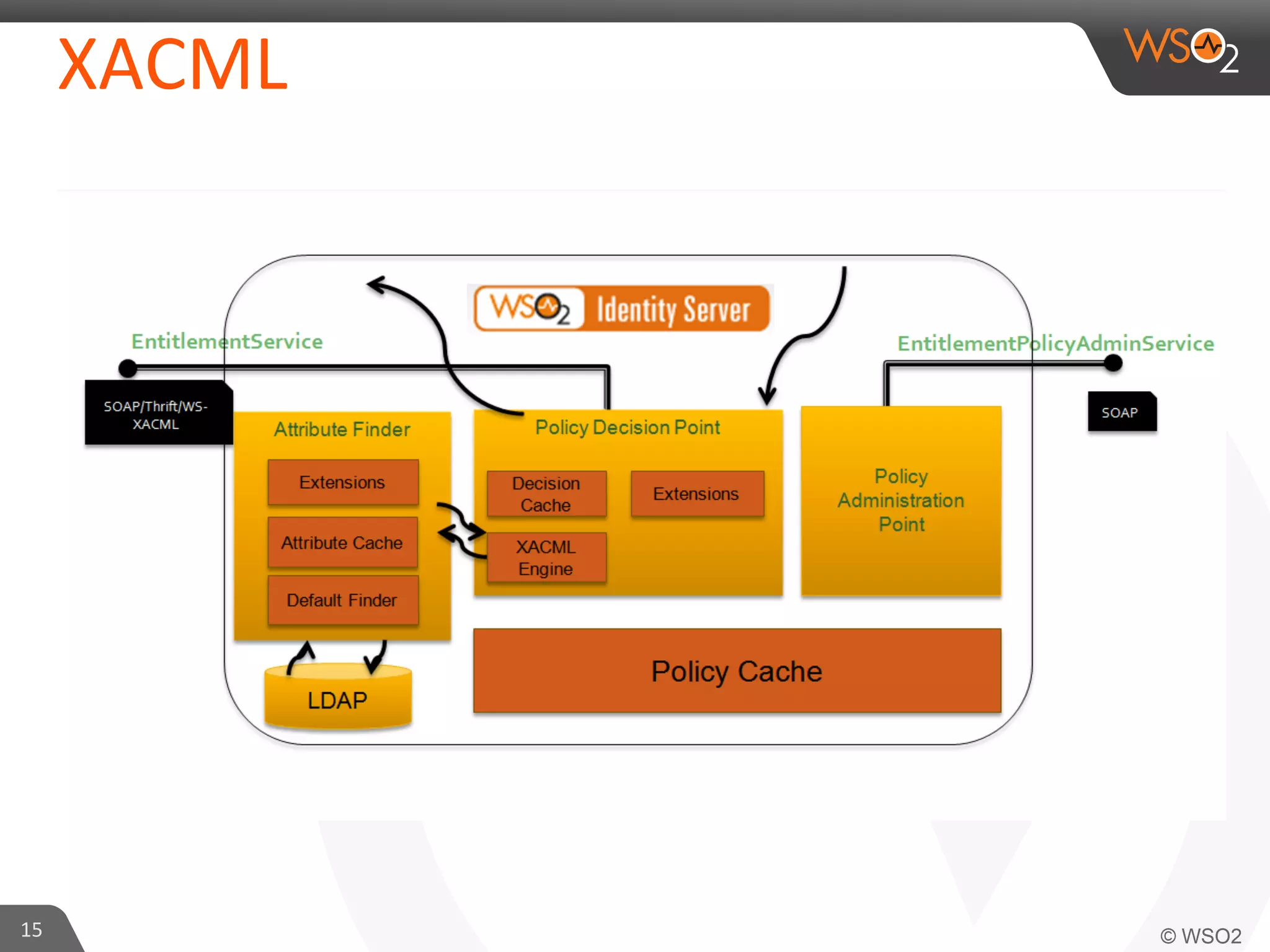
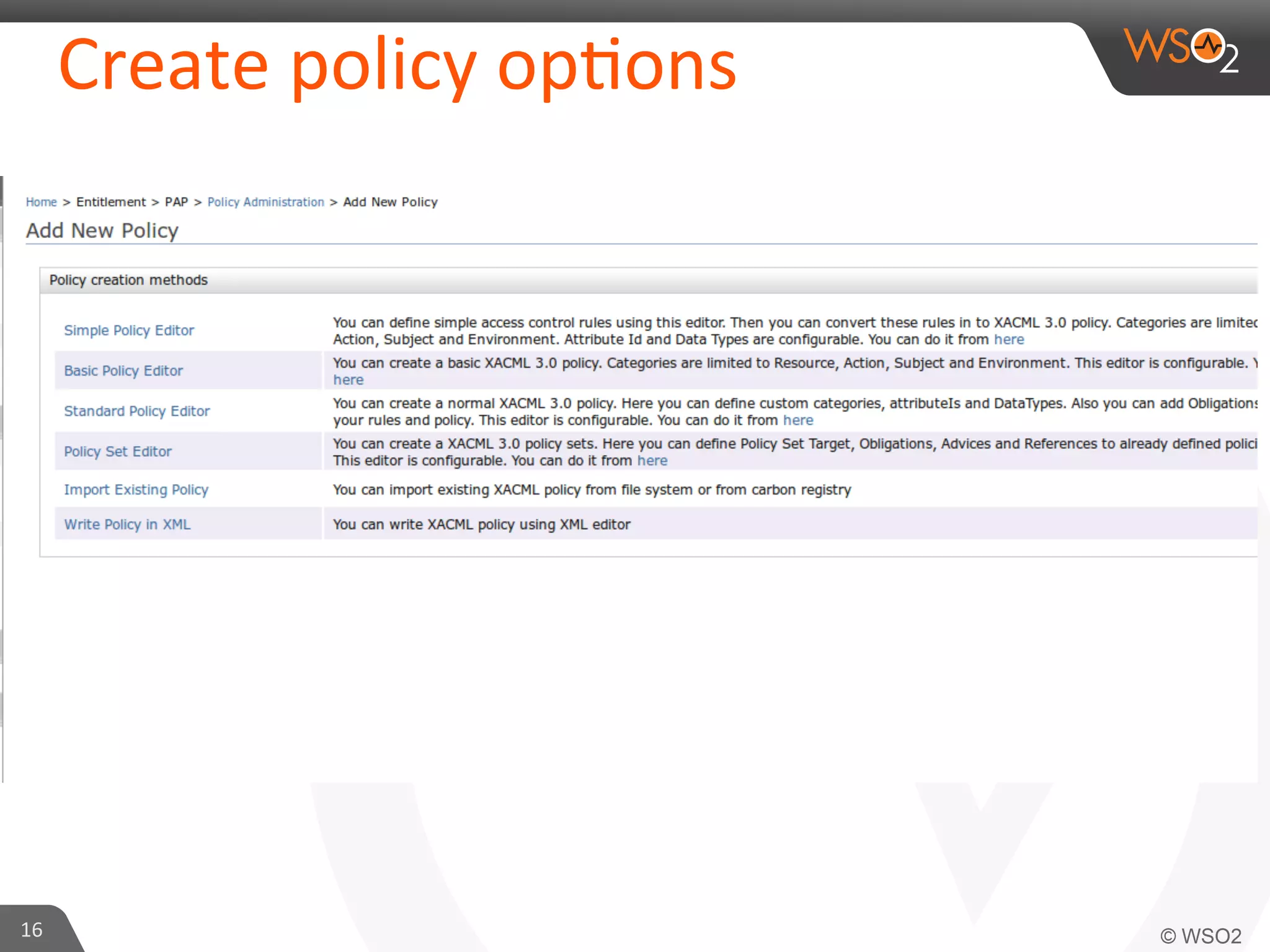
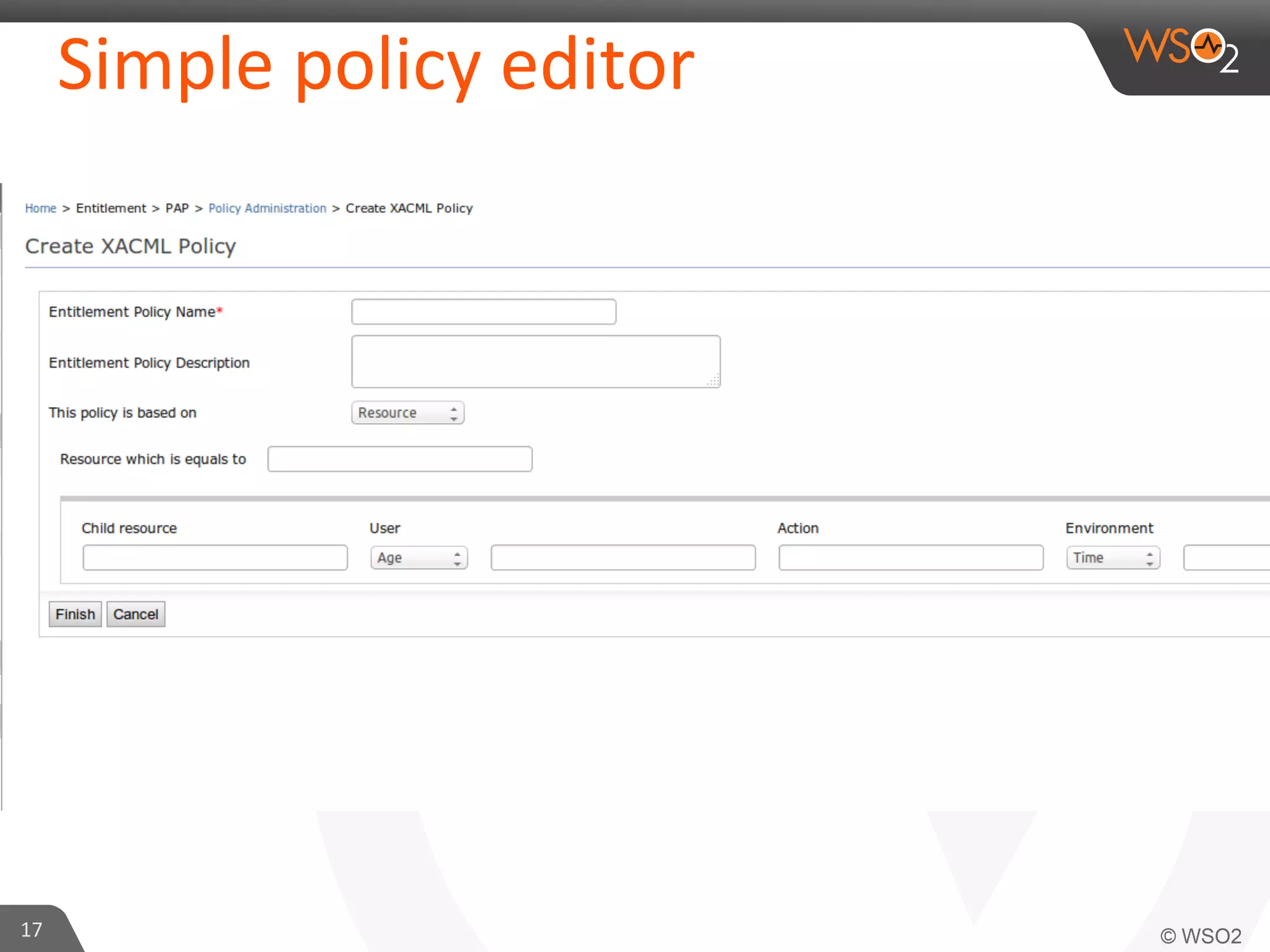
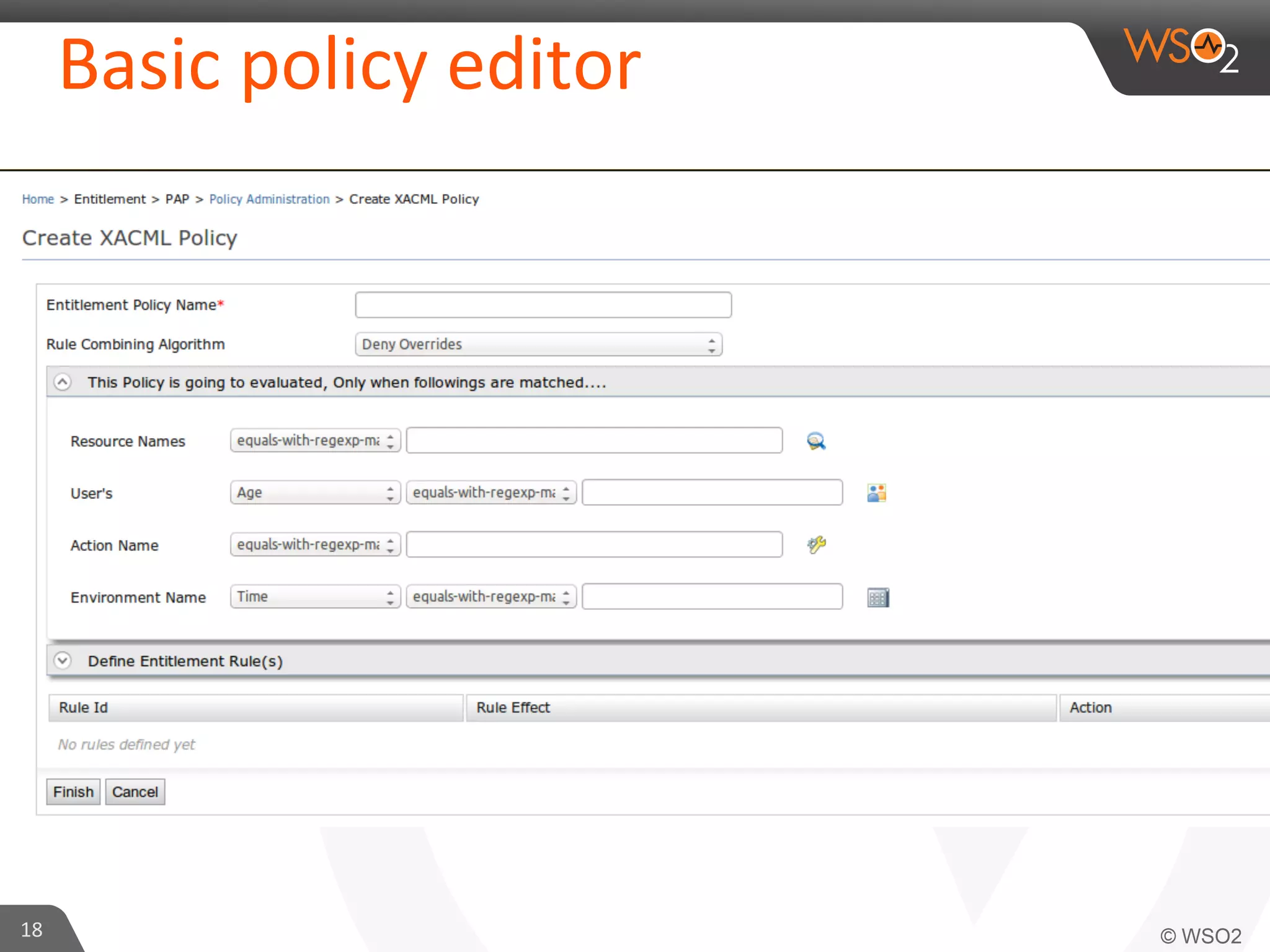
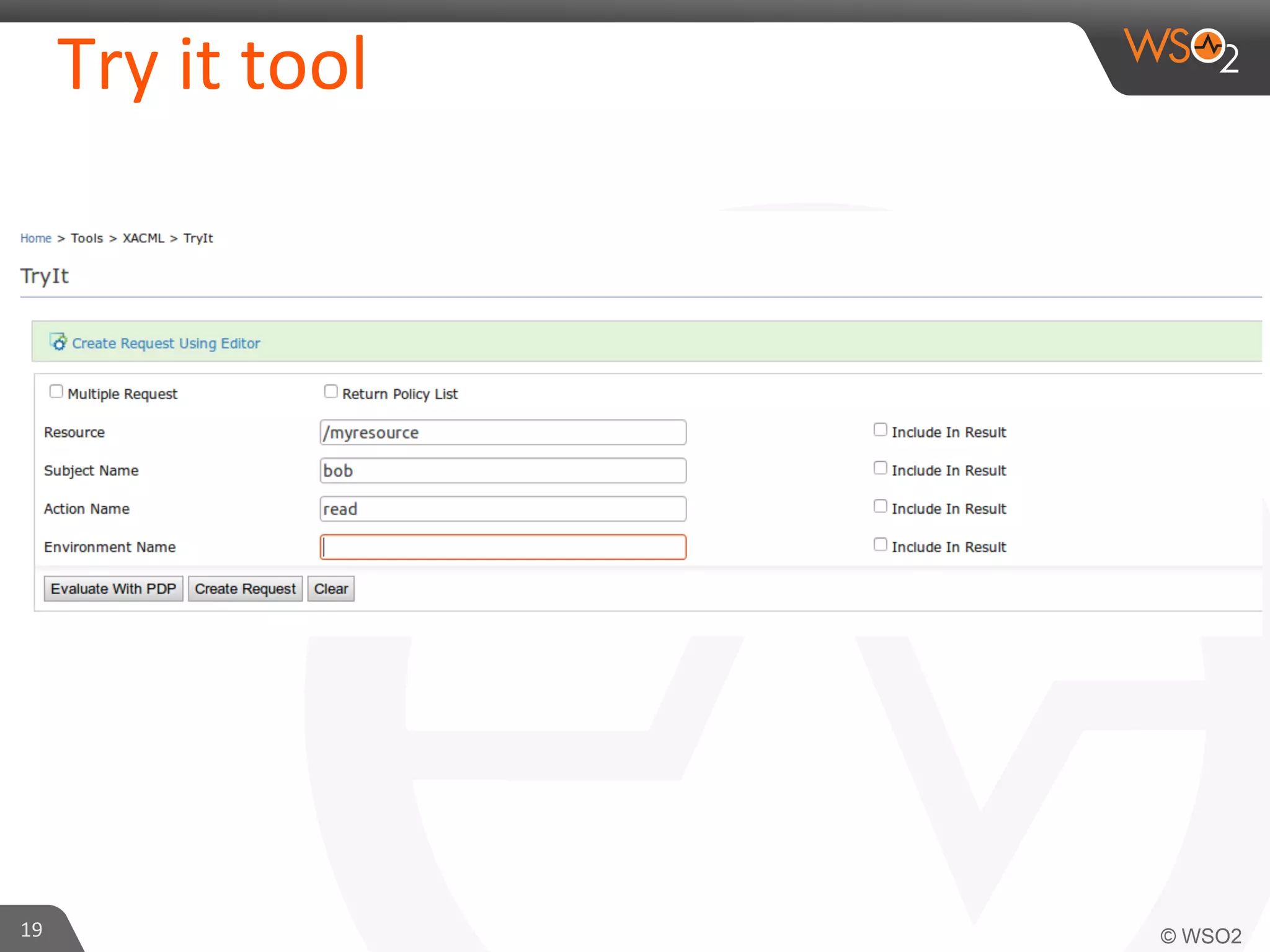
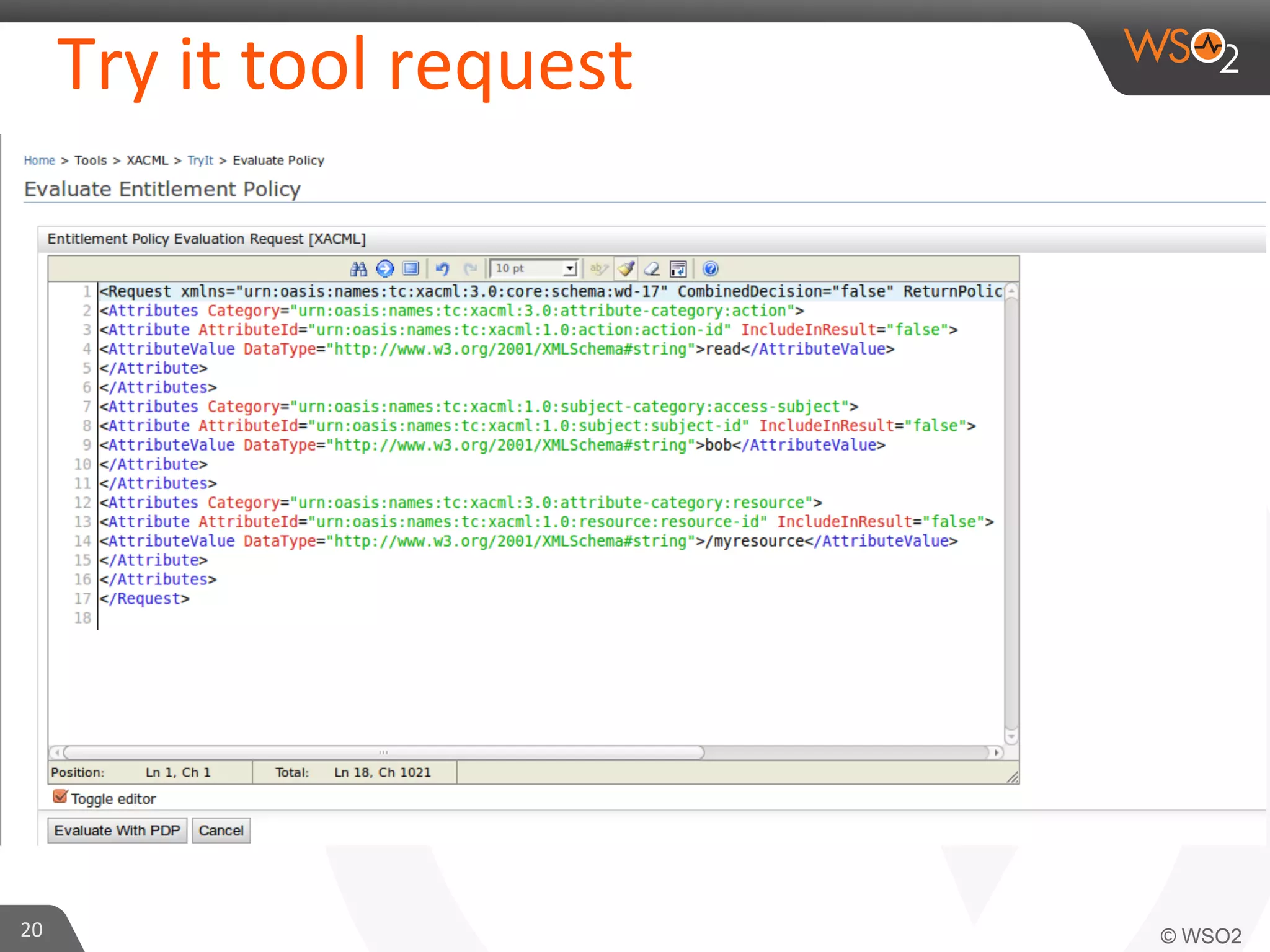
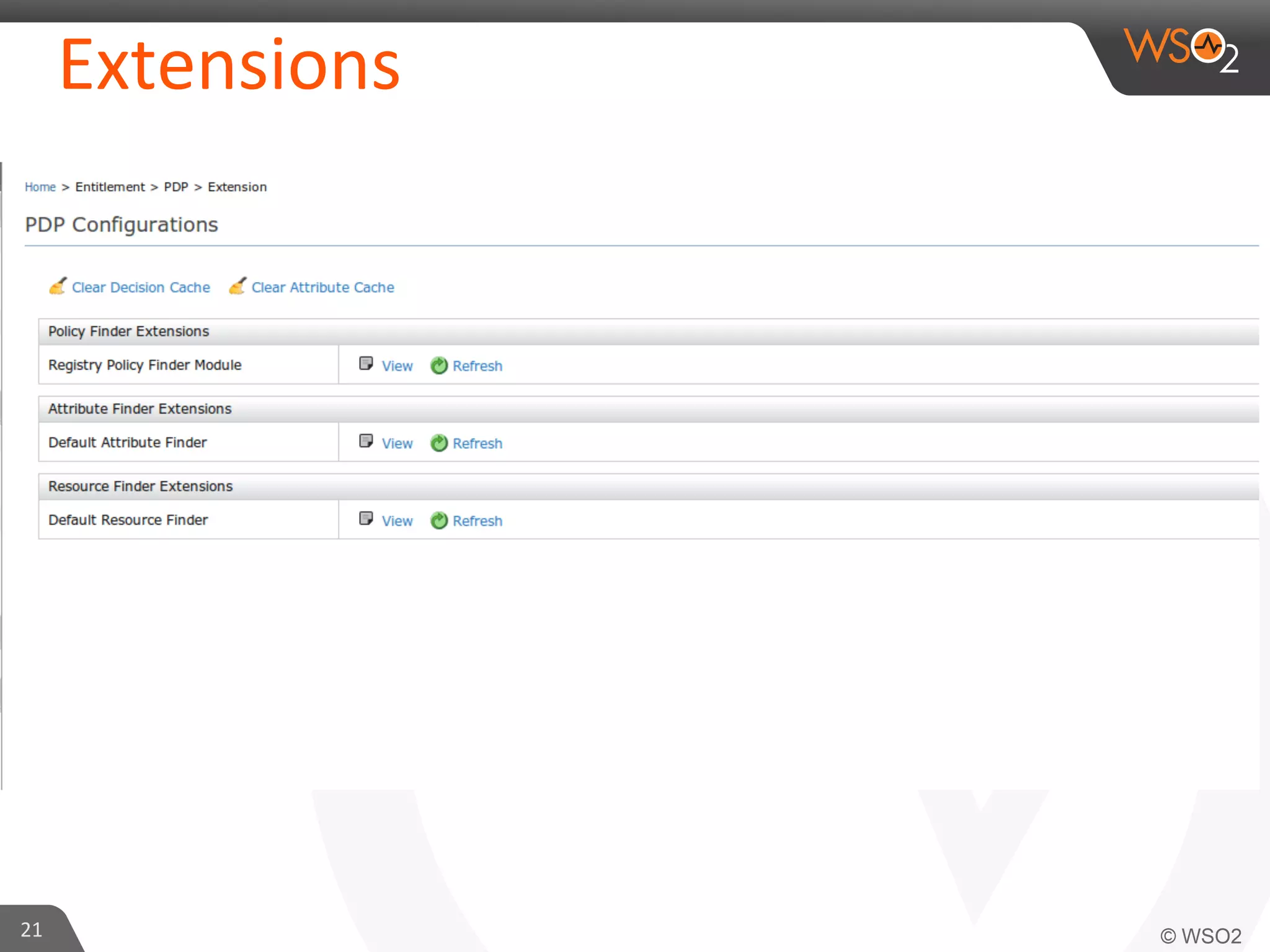
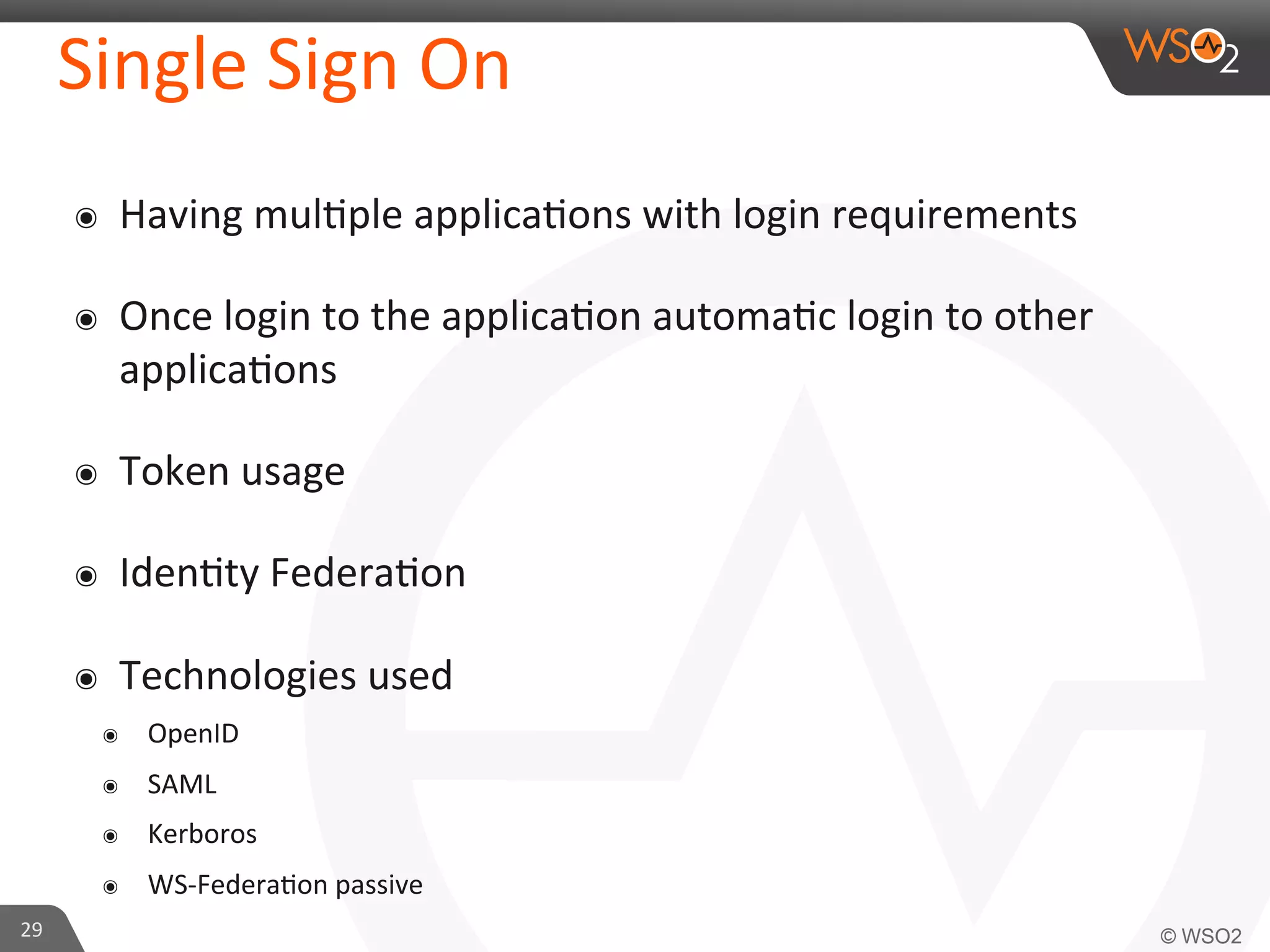
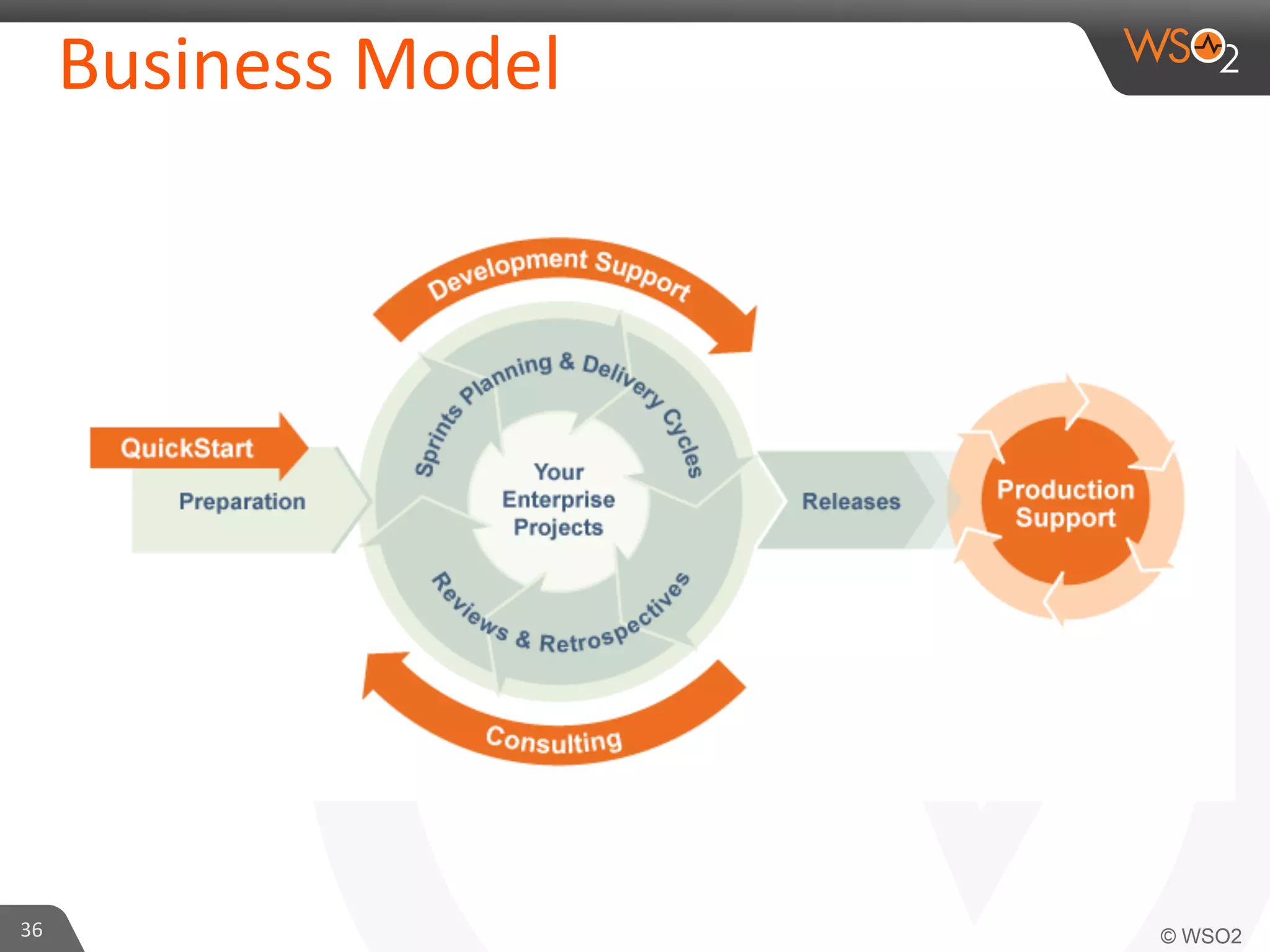
This document provides an overview of entitlement management and identity management concepts. It discusses different access control models like access control lists, role-based access control, attribute-based access control and policy-based access control using XACML. The presenter Chamath Gunawardana is a technical lead at WSO2 who works on their identity server. WSO2 provides open source identity and access management solutions.