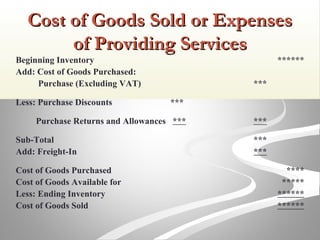
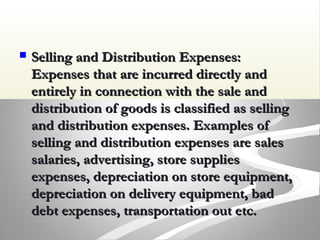
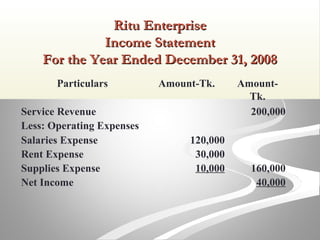
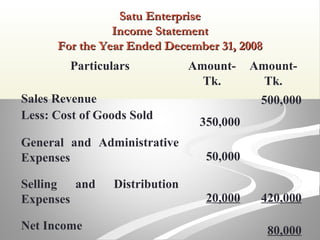
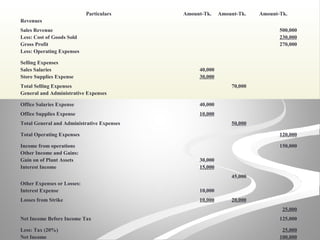
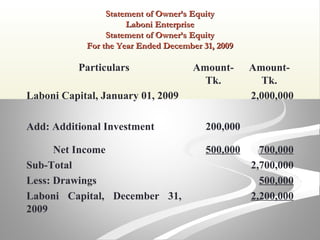
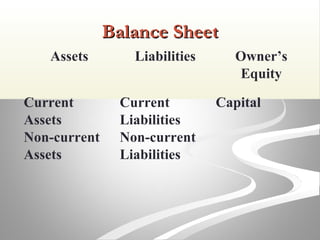
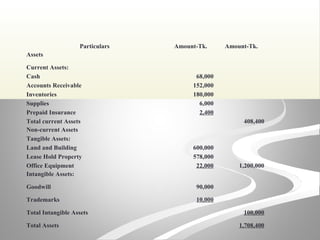
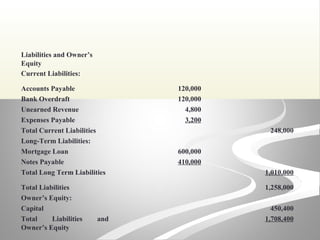
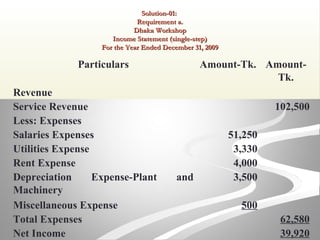
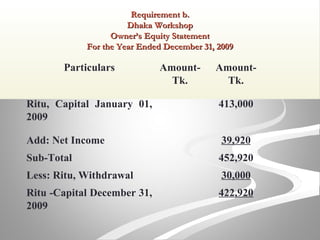
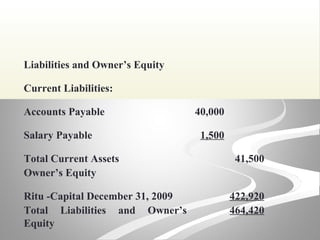
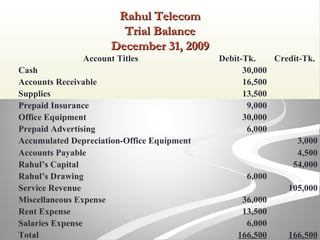
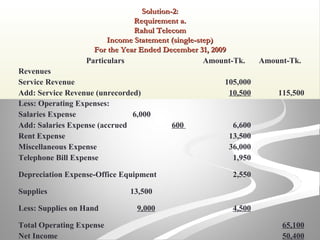
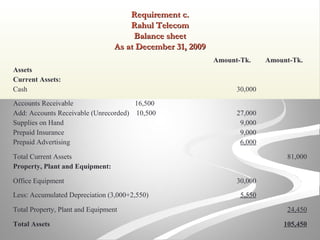
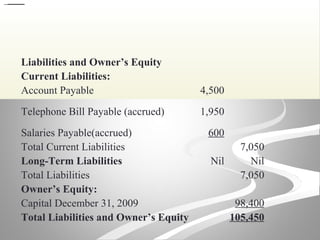
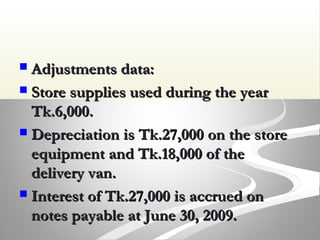
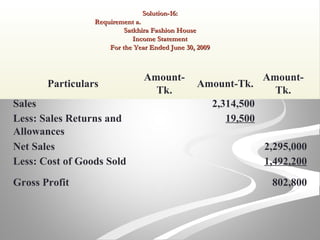
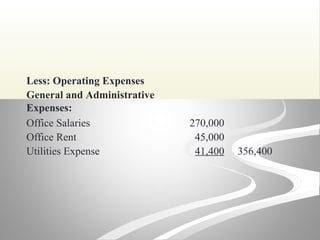
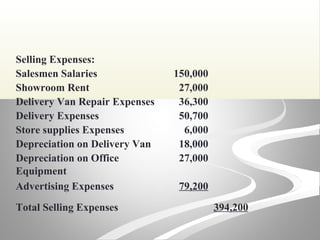
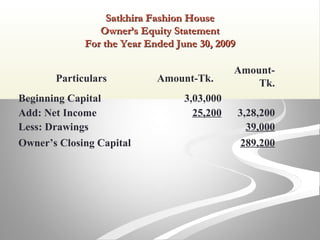
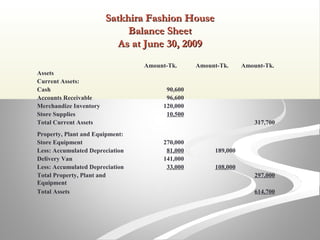
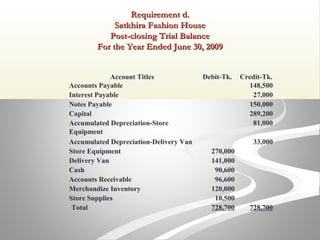
The document provides information about financial statements, including their purpose, key elements, and components. It defines income, expenses, assets, liabilities, equity, gains and losses. It describes the income statement, statement of owner's equity, and balance sheet. It includes examples of single-step and multiple-step income statements, an owner's equity statement, and a classified balance sheet. It also includes instructions for preparing financial statements from adjusted trial balance information for two companies.