Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times





![Rule 7:
All predefined java class names and interface names we use as identifiers.
Example1:
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args){
int String=10;
System.out.println(String);
}}
Output:
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/identifier-170110102205/75/Identifier-6-2048.jpg)
![Example 2:
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args){
int Runnable=10;
System.out.println(Runnable);
}}
Output:
10
Even though it is legal to use class names and interface names as identifiers but
it is not a good programming practice.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/identifier-170110102205/75/Identifier-7-2048.jpg)
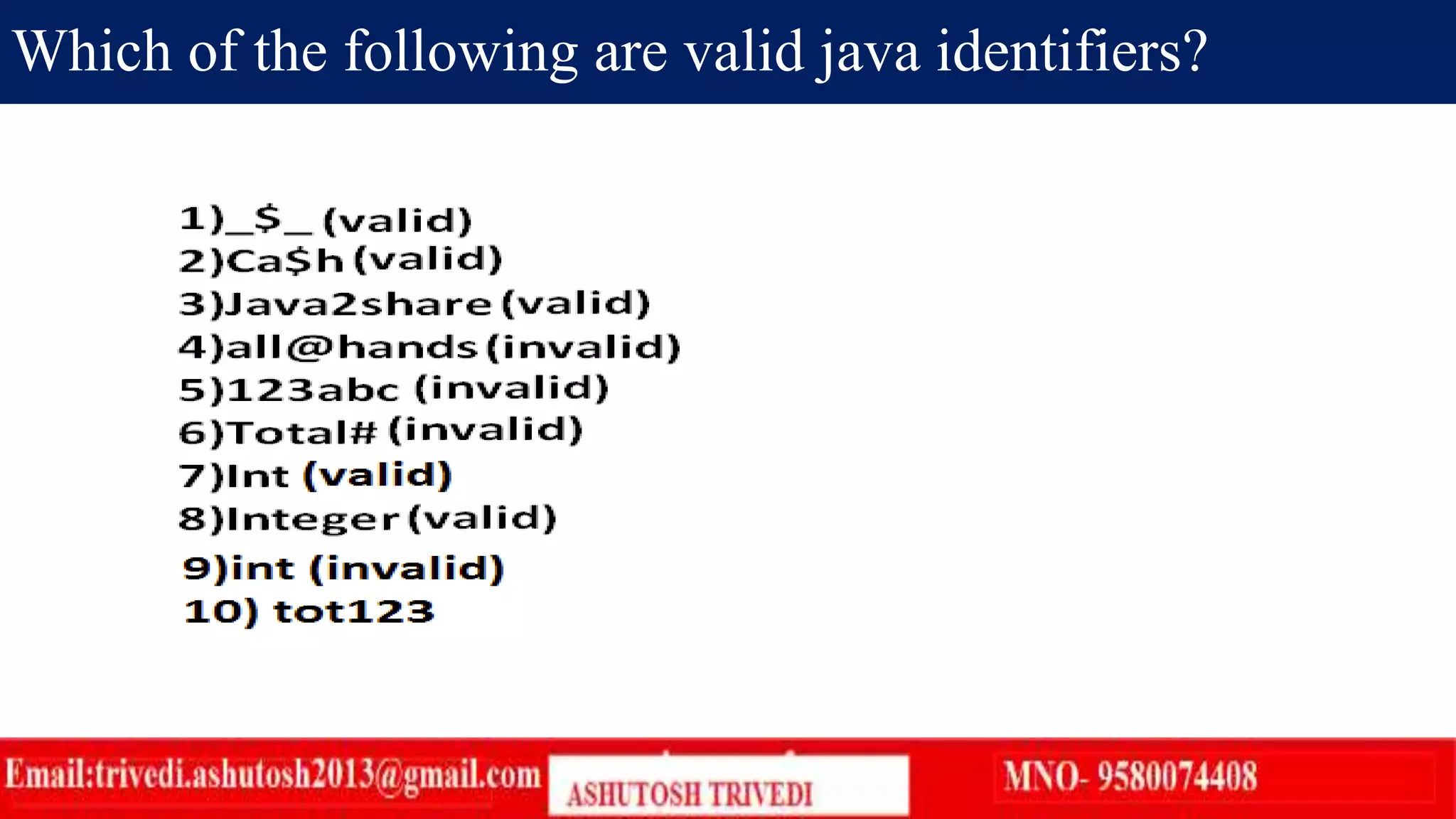

An identifier in Java is a name given to classes, methods, variables, and labels. There are 7 rules for defining valid Java identifiers: 1) They can contain letters, numbers, underscores, and dollar signs. 2) They cannot start with a number. 3) Java is case sensitive so identifiers like number and Number are different. 4) There is no length limit but more than 15 characters is not recommended. 5) Reserved words like if cannot be used. 6) Predefined class and interface names can be used but it is not good practice.





![Rule 7:
All predefined java class names and interface names we use as identifiers.
Example1:
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args){
int String=10;
System.out.println(String);
}}
Output:
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/identifier-170110102205/75/Identifier-6-2048.jpg)
![Example 2:
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args){
int Runnable=10;
System.out.println(Runnable);
}}
Output:
10
Even though it is legal to use class names and interface names as identifiers but
it is not a good programming practice.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/identifier-170110102205/75/Identifier-7-2048.jpg)
