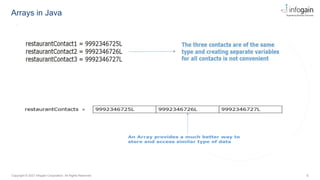
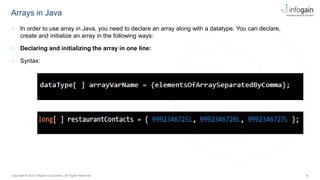
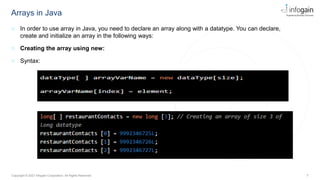
The document serves as an educational resource on arrays in Java, covering their definition, declaration, and various methods for accessing elements, including loops. It explains both one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays, illustrating their usage with examples, as well as key points about their characteristics such as fixed size and zero-based indexing. The document also briefly mentions trends in object-oriented technology and offers insights into object-oriented design principles.




![9
Copyright © 2021 Infogain Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
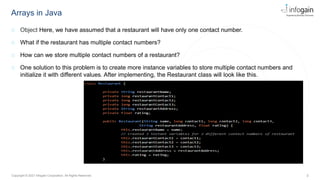
Accessing the elements of an array
◌ Each value stored in an array is called as an element. Each element in an array is accessed, stored and
retrieved using its position in the array, called index. Indexes in Java are zero-based, i.e., the valid range of
indexes for the elements of an array is from 0 to (size of Array-1).
long[] restaurantContacts = new long[3];
restaurantContacts [0] = 9992346725L; // Elements can be updated and accessed with
the help of index
restaurantContacts [1] = 9992346726L;
restaurantContacts [2] = 9992346727L;
System.out.println(restaurantContacts [1]) ;// Accessing and displaying the element
at the 1st index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-240710145114-abba60e9/85/Arrays-are-used-in-java-to-holding-more-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![10
Copyright © 2021 Infogain Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Accessing the elements of an array using for loop
◌ Instead of writing n number of lines to access n elements of an array, you can use different looping
constructs like for loop, for-each loop, etc.
◌ The below code shows how to access and display the elements of restaurantContacts with the help of for
loop.
public class Tester {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long[] restaurantContacts = { 9992346725L, 9992346726L, 9992346727L };
for (int index = 0; index < restaurantContacts.length; index++) {
// Accessing element at position index
System.out.println(restaurantContacts[index]);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-240710145114-abba60e9/85/Arrays-are-used-in-java-to-holding-more-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![11
Copyright © 2021 Infogain Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Accessing the elements of an array using for each loop
◌ Java also has another loop known as for-each loop to iterate over collections. This eliminates the use of
indexes. It displays the array elements one by one. It holds an array element in a variable and then
executes the body of the loop.
Syntax
for (dataType variable: array) {
//body of the loop
}
public class Tester {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long[] restaurantContacts = { 9992346725L, 9992346726L, 9992346727L };
for (long contactNumber : restaurantContacts) {
System.out.println(contactNumber);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-240710145114-abba60e9/85/Arrays-are-used-in-java-to-holding-more-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![12
Copyright © 2021 Infogain Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Multi-dimensional Array
◌ Multi-dimensional arrays are arrays of arrays with each element of the array holding the reference of other
arrays.
◌ A multi-dimensional array is created by appending one set of square brackets ([]) per dimension..
◌ Let's see a simple example to declare, instantiate, initialize and display a 2-dimensional (2D) array.
◌ Syntax for creating 2D array:
dataType[][] arrayVarName = new dataType[rowsize][columnsize];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-240710145114-abba60e9/85/Arrays-are-used-in-java-to-holding-more-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![13
Copyright © 2021 Infogain Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Multi-dimensional Array
//Here, the row size is 7, and the column size is 2
//The 0th index stores the Max temperature and 1st index stores the Min temperature
int[][] dayWiseTemperature = new int[7][2];
dayWiseTemperature[0][0]=29; // Initialization
dayWiseTemperature[0][1]=21;
//and so on
//Another way of creating and initializing 2D array
int[][] dayWiseTemperature = new int[][] {
{29,21},
{24,23},
{26,22},
{28,23},
{29,24},
{23,20},
{29,21}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-240710145114-abba60e9/85/Arrays-are-used-in-java-to-holding-more-pptx-13-320.jpg)


