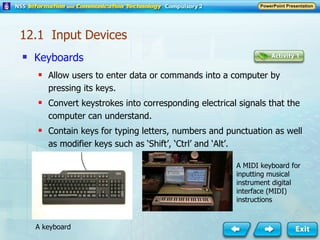
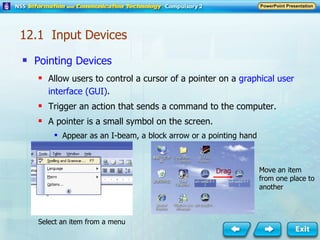
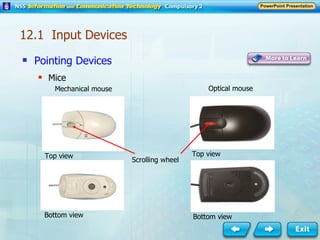
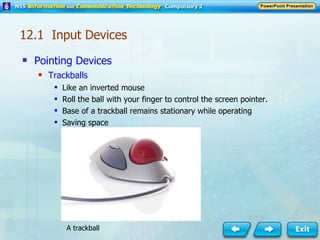
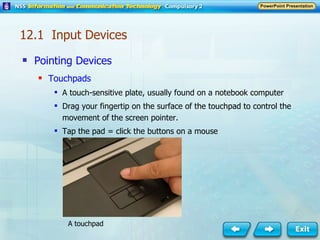
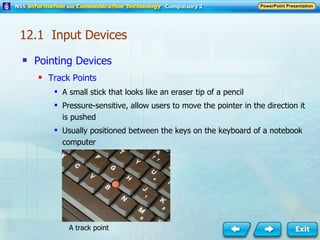
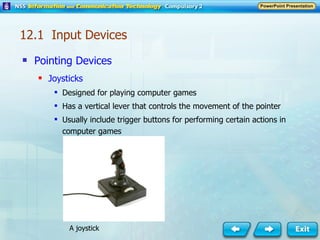
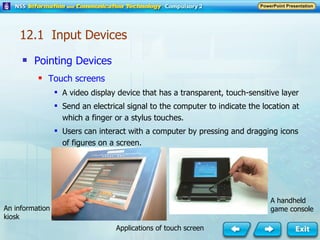
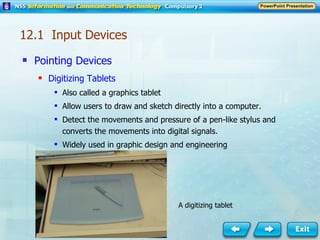
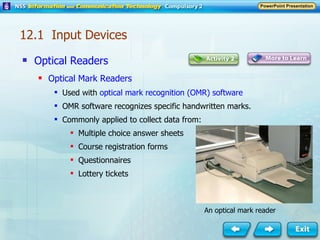
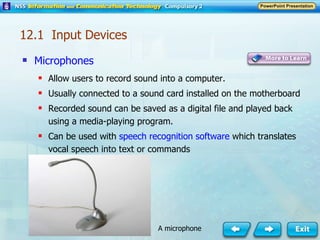
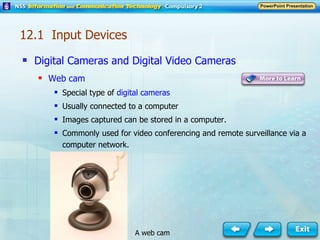
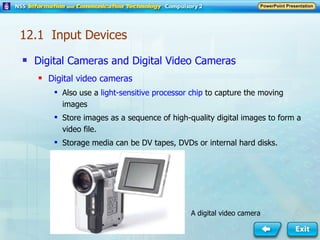
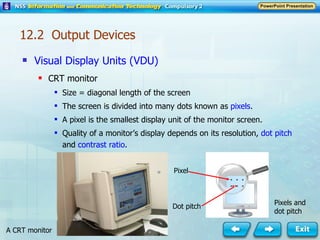
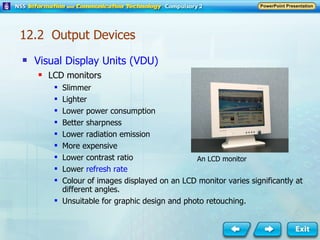
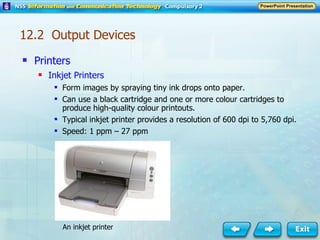
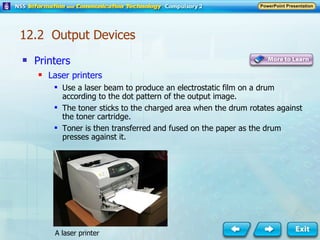
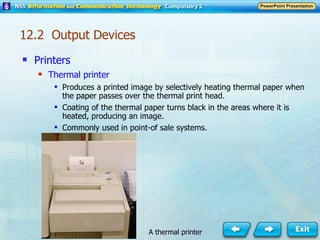
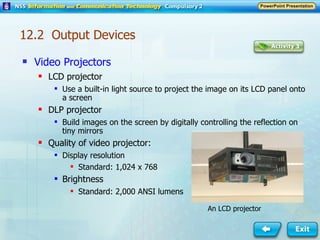
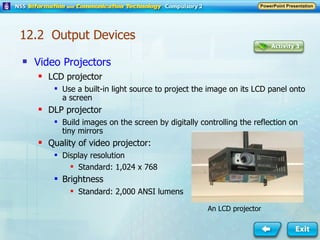
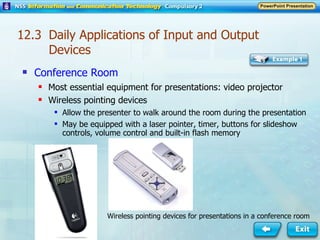
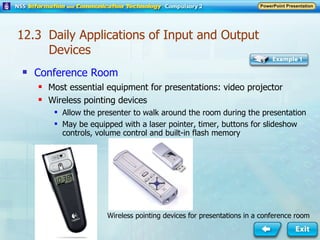
Input and output devices allow users to interact with computers. Common input devices include keyboards, mice, scanners, microphones, and digital cameras which allow data to be entered. Common output devices include monitors, printers, speakers, and video projectors which allow the computer to display information in visual or audio form. These devices are used in various applications such as point-of-sale systems, banking machines, small offices, and presentations.