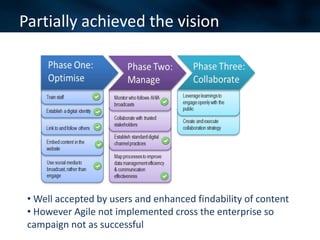
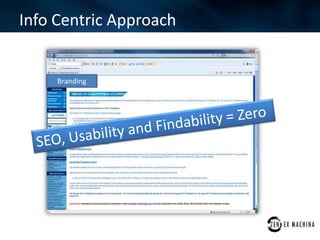
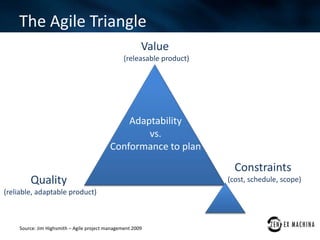
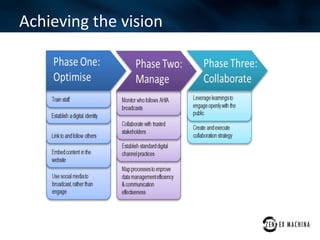
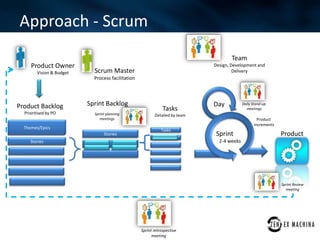
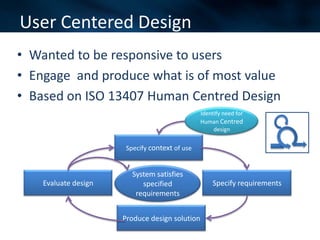
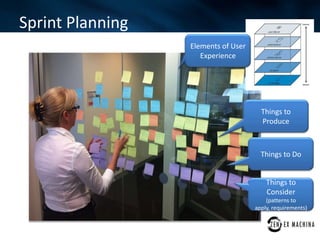
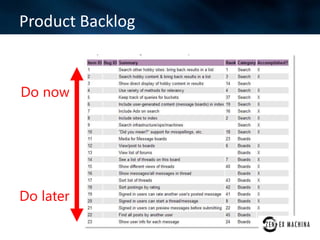
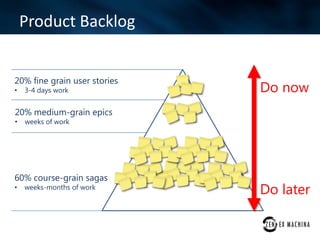
The document discusses an agile approach adopted by a health insurance company to optimize their digital strategy, emphasizing the importance of user engagement and responsiveness in a regulated and risk-averse industry. Utilizing Scrum methodology, the team delivered valuable features iteratively while adapting to evolving needs and managing multiple projects simultaneously. Despite achieving significant advancements, the implementation of agile was not fully integrated across the enterprise, limiting overall campaign success.












![Develop User Stories from Agile Personas
• As a [Role]..Gen X consumer thinking
about starting a family,
• I want to [Task]..know how much the
change to the rebate will affect me
• So that I [Goal].. can understand the
extra costs
• Generation
• Profile and background
• What they value
• Value of Info providers
• Pain points](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acs2012anagileapproachtooptimisingyourdigitalstrategyv2autosaved-120320154559-phpapp02/85/Using-Agile-to-move-from-info-centric-to-user-centric-21-320.jpg)

![Behaviour Driven Development
Title: Rebate Calculator
• Given I am a.. [Role] and.. As a consumer on a tight budget I want
to know how much the change to the
rebate will affect me. So when I input
• I Value.. [+/- Context] info into calculator via drop down
menus I will see how much extra $$$ I
•
will pay via graph and text
When I ..[User interaction]
• Then I expect.. [This]
• To achieve ..[Result/Outcome]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acs2012anagileapproachtooptimisingyourdigitalstrategyv2autosaved-120320154559-phpapp02/85/Using-Agile-to-move-from-info-centric-to-user-centric-23-320.jpg)