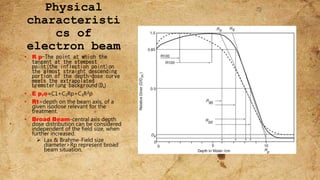
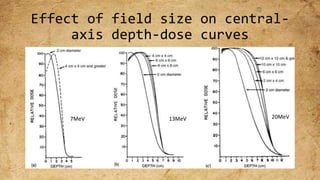
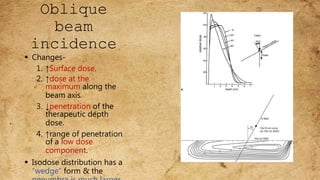
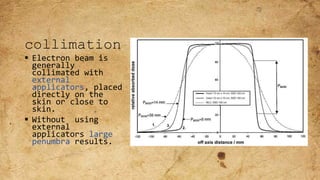
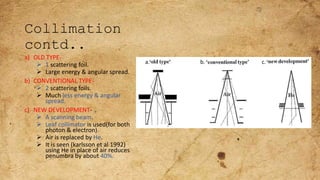
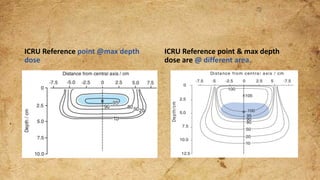
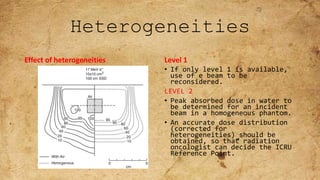
ICRU Report 71 outlines the procedures for prescribing, recording, and reporting electron beam therapy, highlighting key benefits such as dose uniformity for superficial tumors and minimal collateral damage to deeper tissues. The report also details methods for reporting dose information, recommendations for quality assurance, and addresses the challenges associated with irregular field shapes and dose determination in heterogeneous tissues. Additionally, it discusses critical parameters for effective treatment such as isodose distributions and collimation techniques.