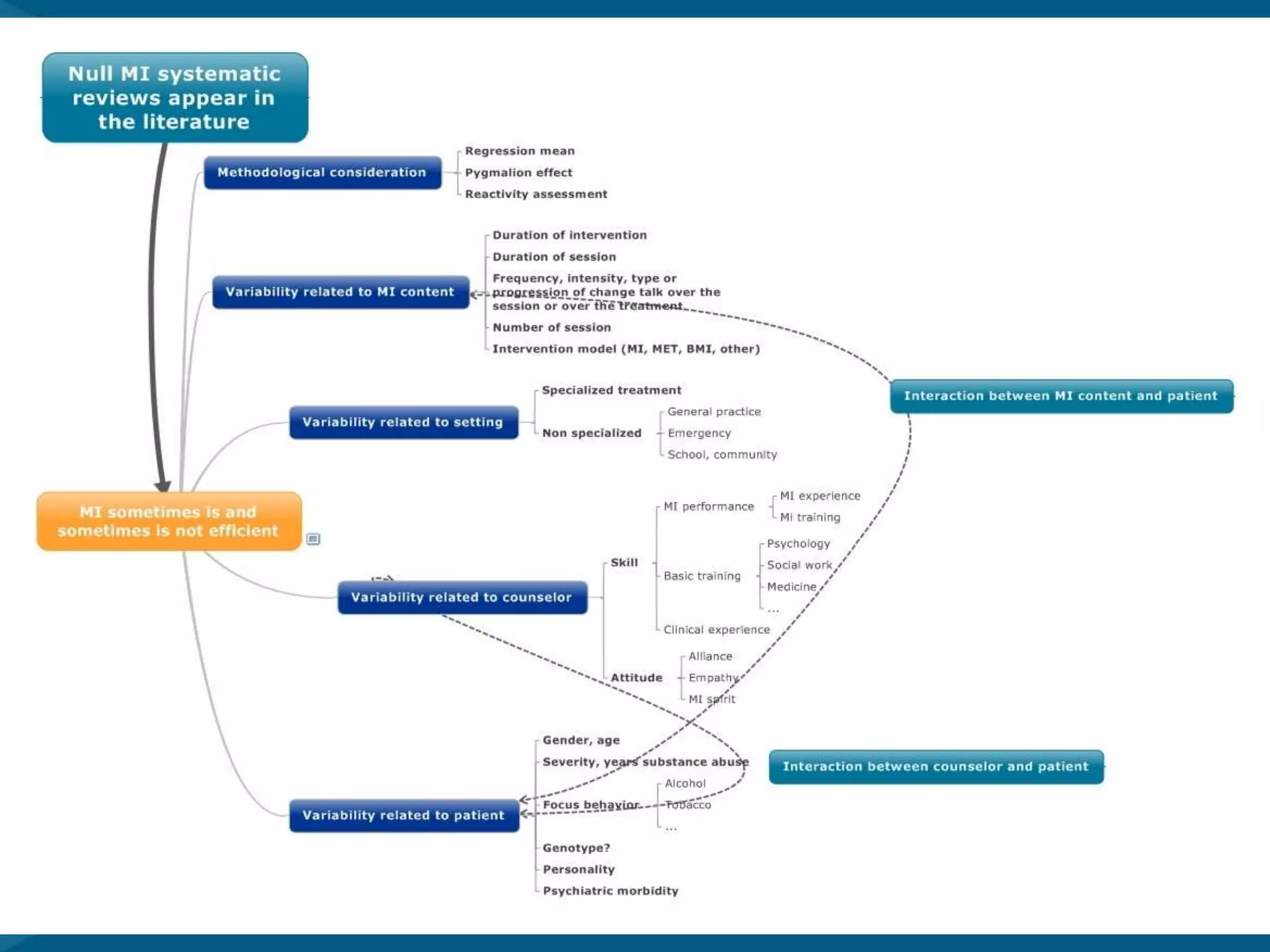
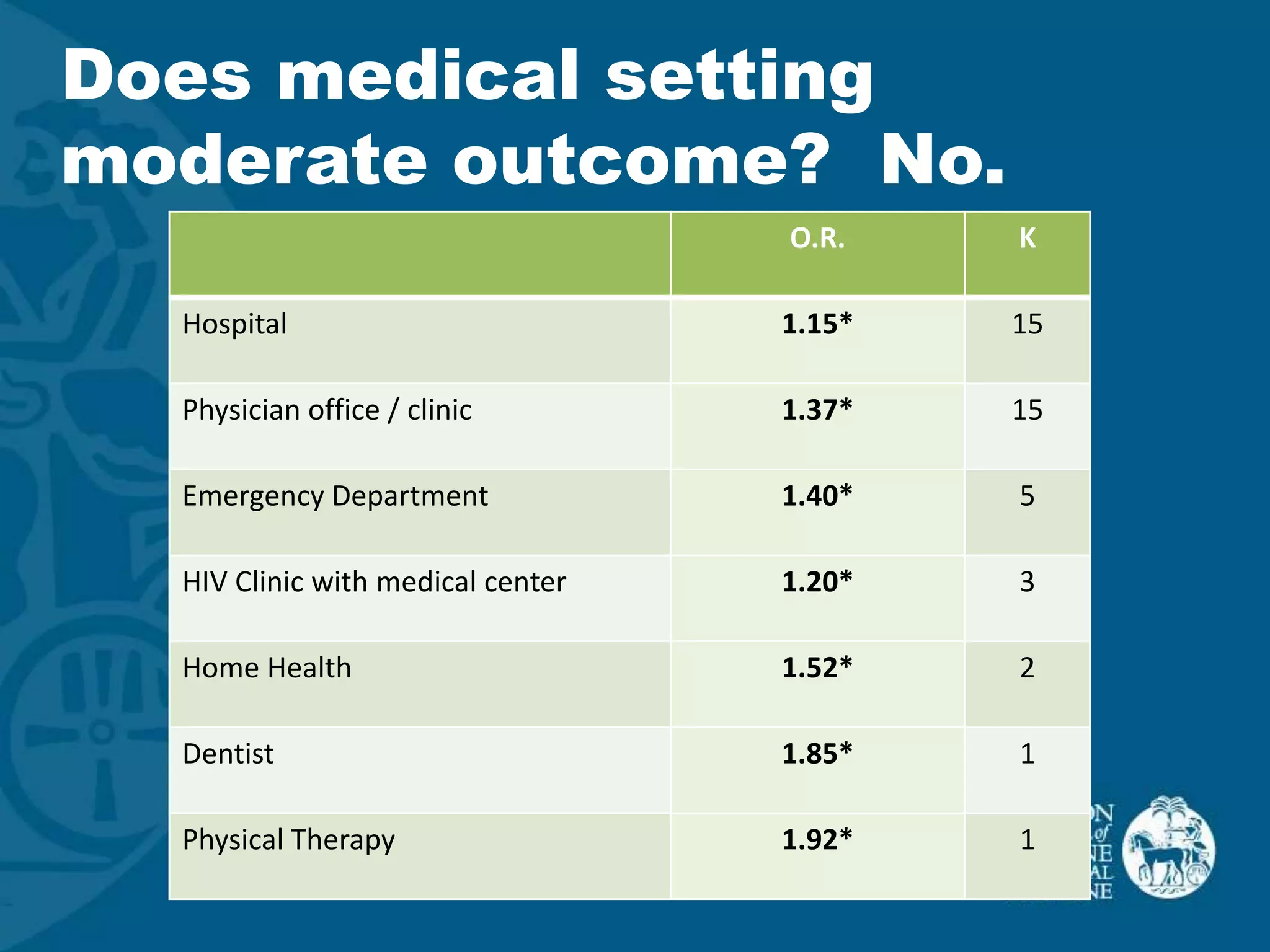
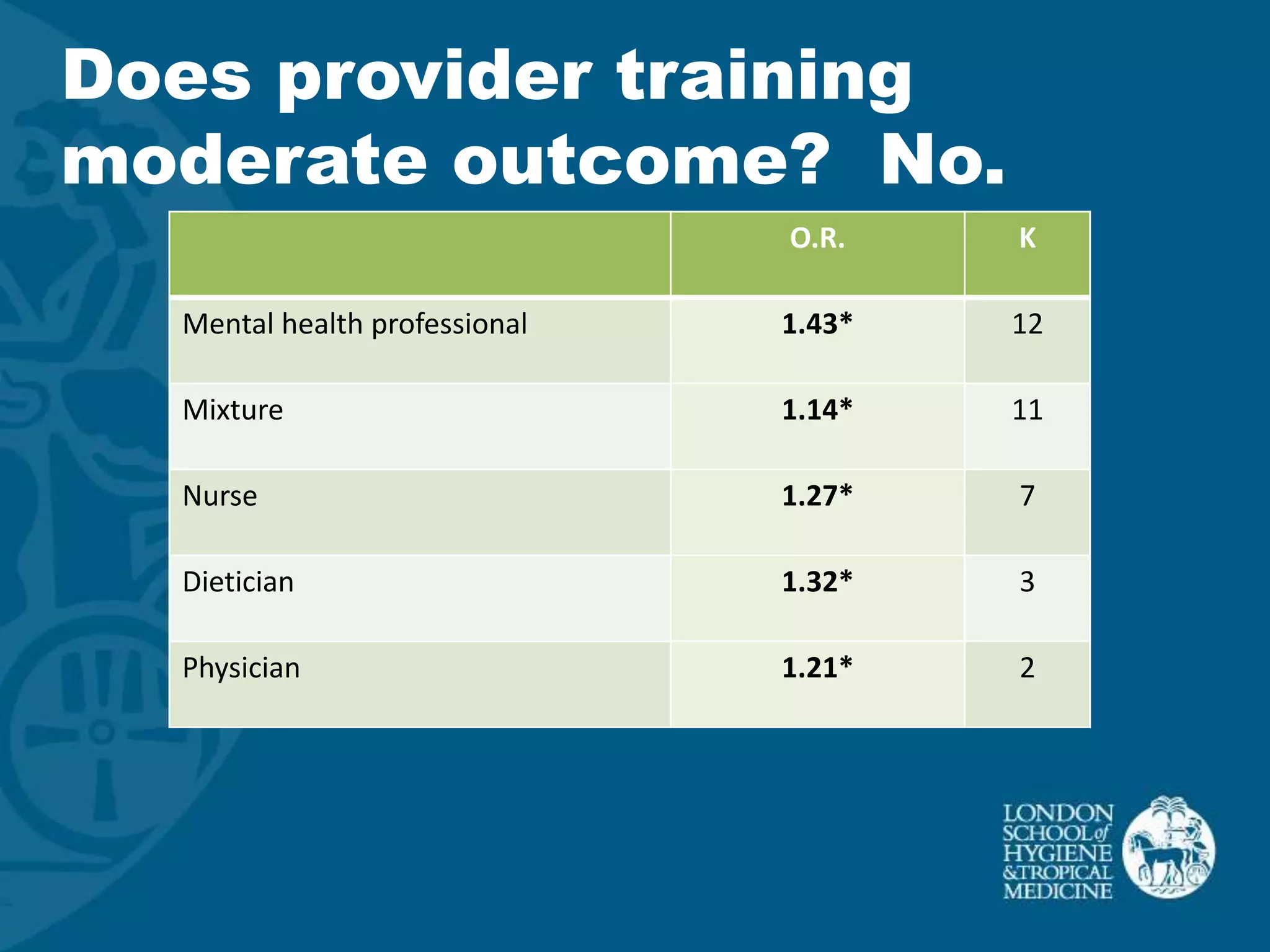
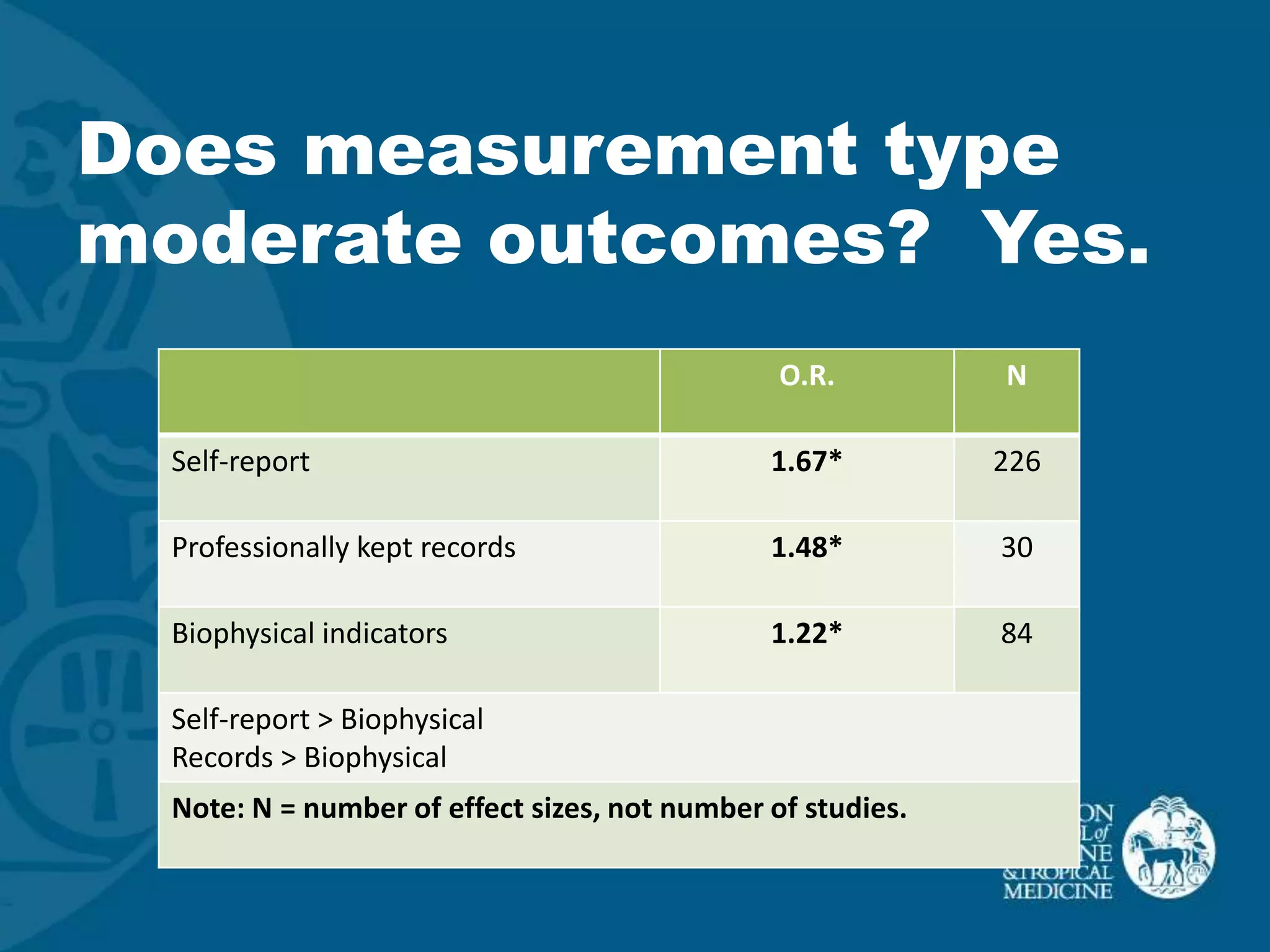
This document discusses motivational interviewing (MI) as a complex intervention and proposes applying a complex interventions perspective to better understand MI. It suggests that thinking of MI as a complex intervention and using systematic reviews and studies of heterogeneity can help address the large variability seen in MI's effectiveness between studies. The document provides some examples of meta-analyses looking at whether certain factors like medical setting, provider training, or measurement type moderate MI outcomes. It argues that more systematic reviews and methods are needed to better understand MI when implemented in real-world settings.