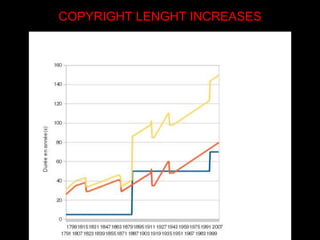
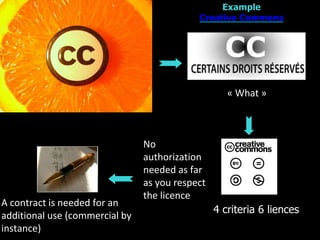
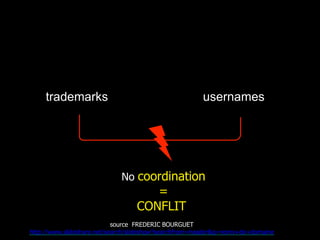
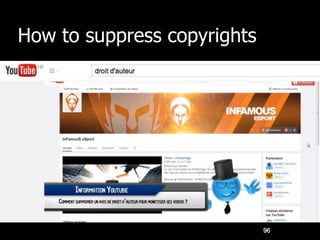
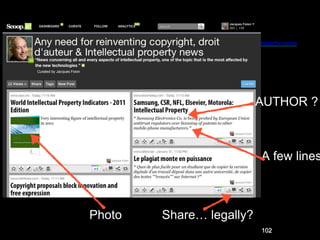
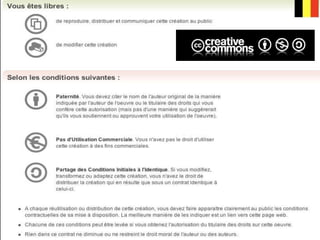
IPR as an important part of business strategy in the digital age. The document discusses criticisms of IPR, including that 80% of French internet users do not consider piracy to be theft. It also discusses whether IPR is outdated and examines limitations IPR places on research and art. The purpose of IPR is outlined as allowing authors to live off their works and providing various types of legal protections.