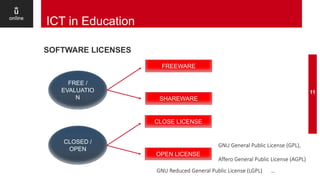
The document discusses the role of digital content in education, emphasizing the distinction between analog and digital forms of information. It covers intellectual property rights, copyright, and various software licenses, including Creative Commons licenses that govern the use and distribution of digital content. Additionally, it includes practical guidelines and resources for students to explore digital content creation and licensing.