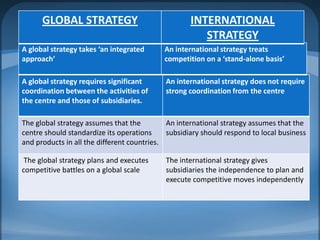
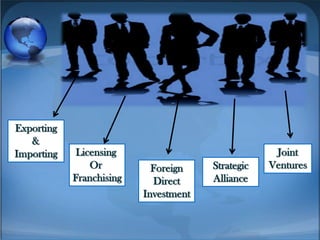
International business strategies are necessary for companies to compete globally. There are two main types of international strategies - global strategies which standardize operations worldwide, and international strategies which allow local subsidiaries more independence. Companies go international to expand customer base, reduce seasonal impacts, and lower costs. Globalization has increased opportunities for international collaboration but also presents challenges around coordination and responding to local conditions that companies must address in their strategies.