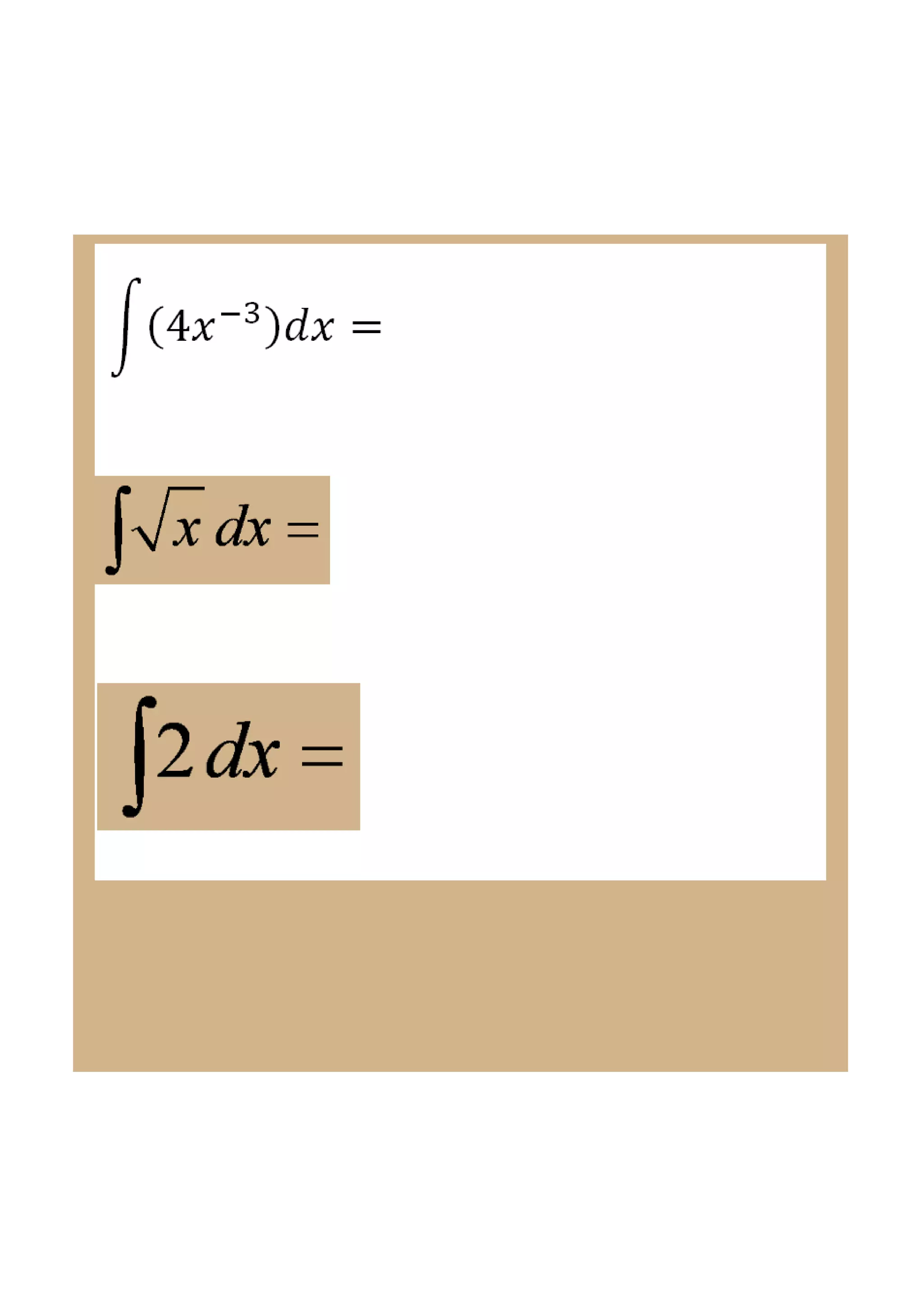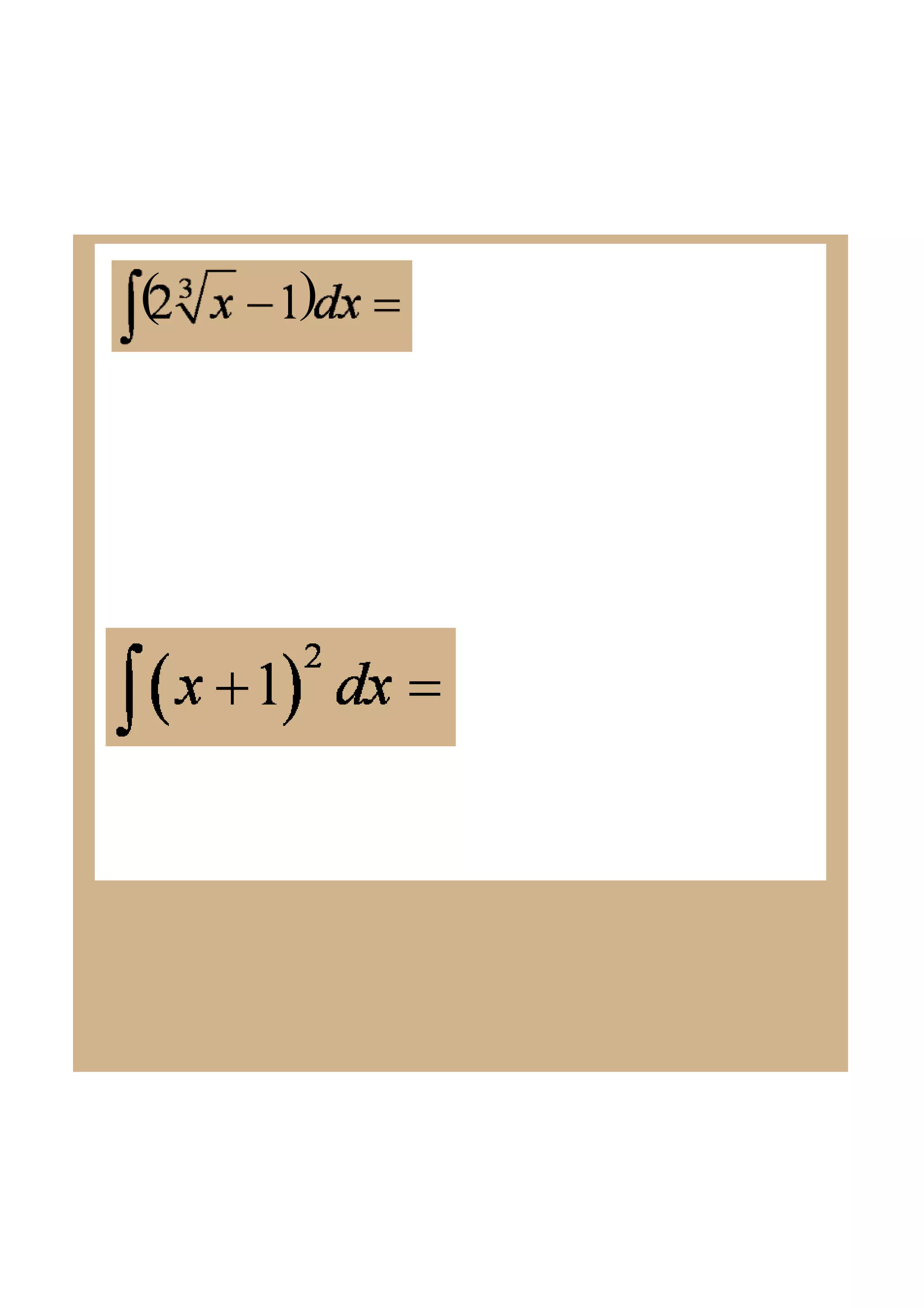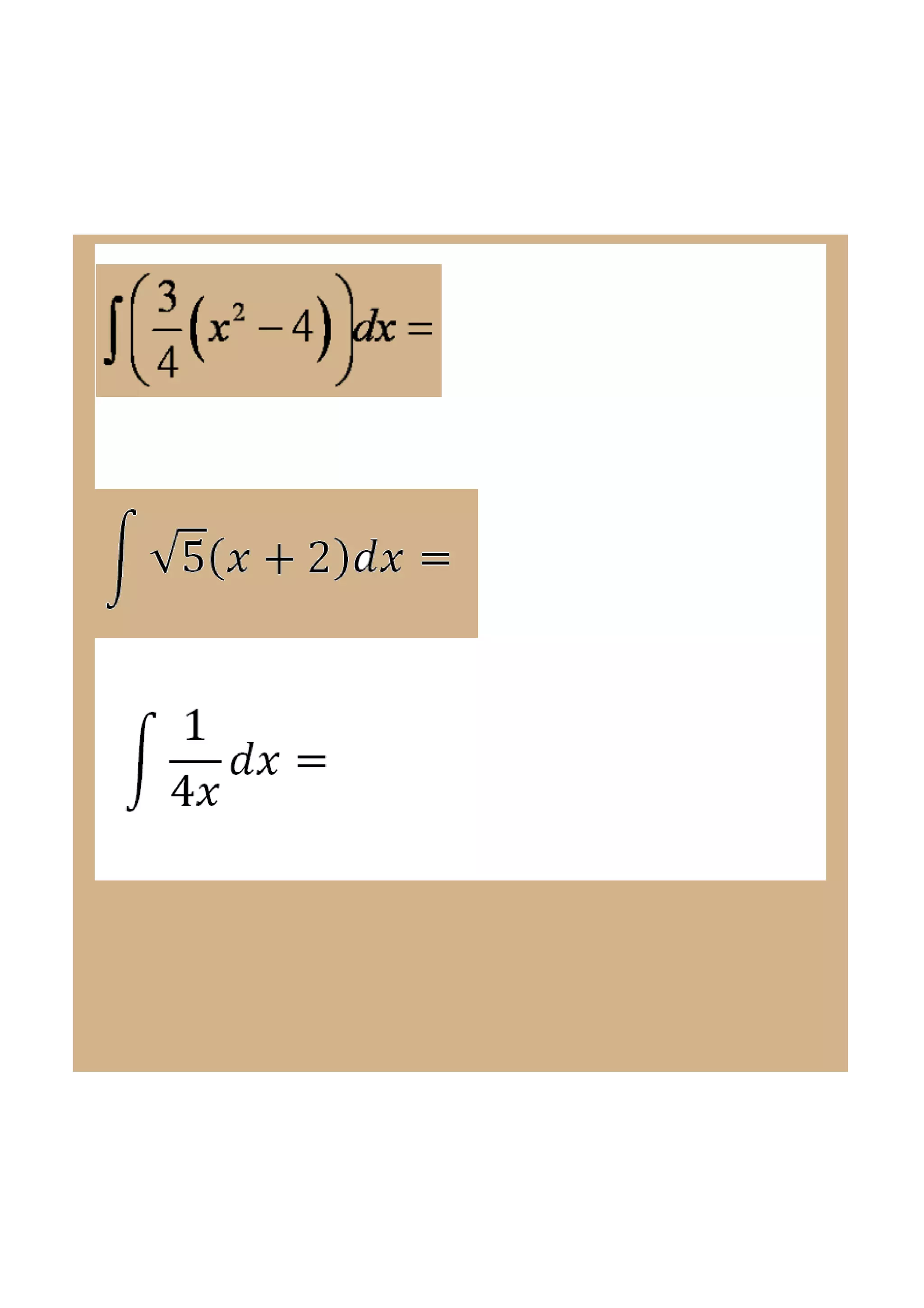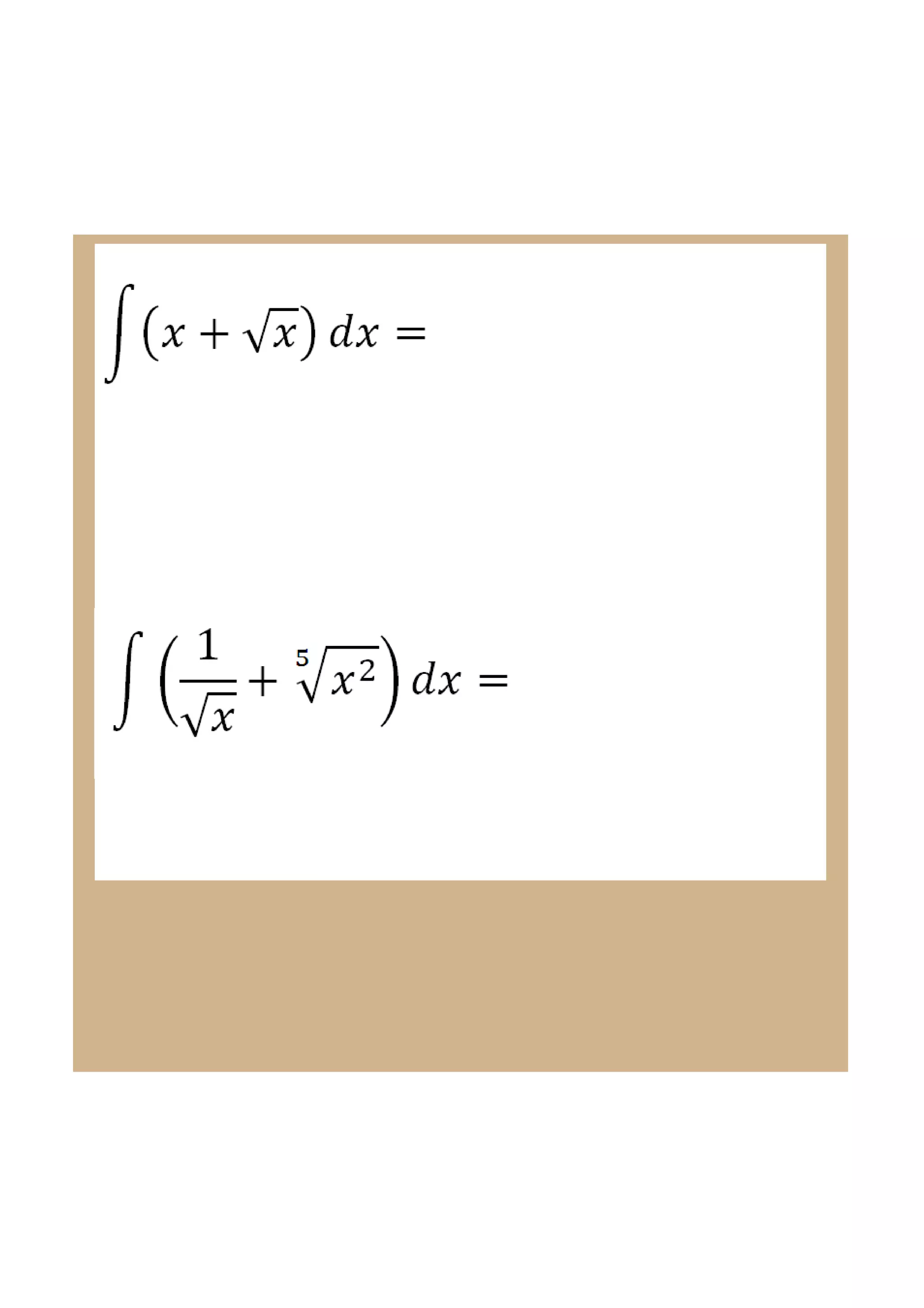Embed presentation
Downloaded 21 times


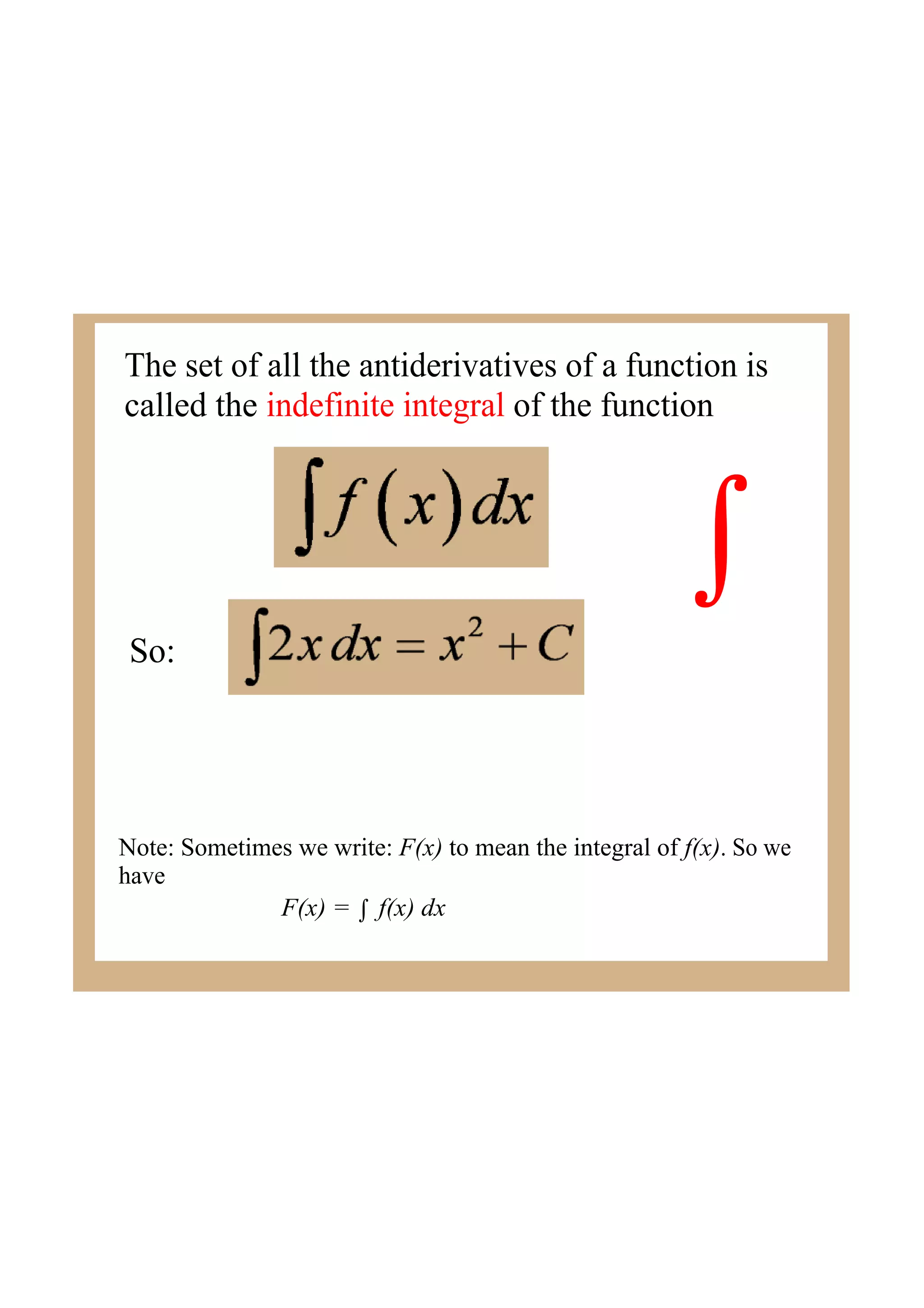
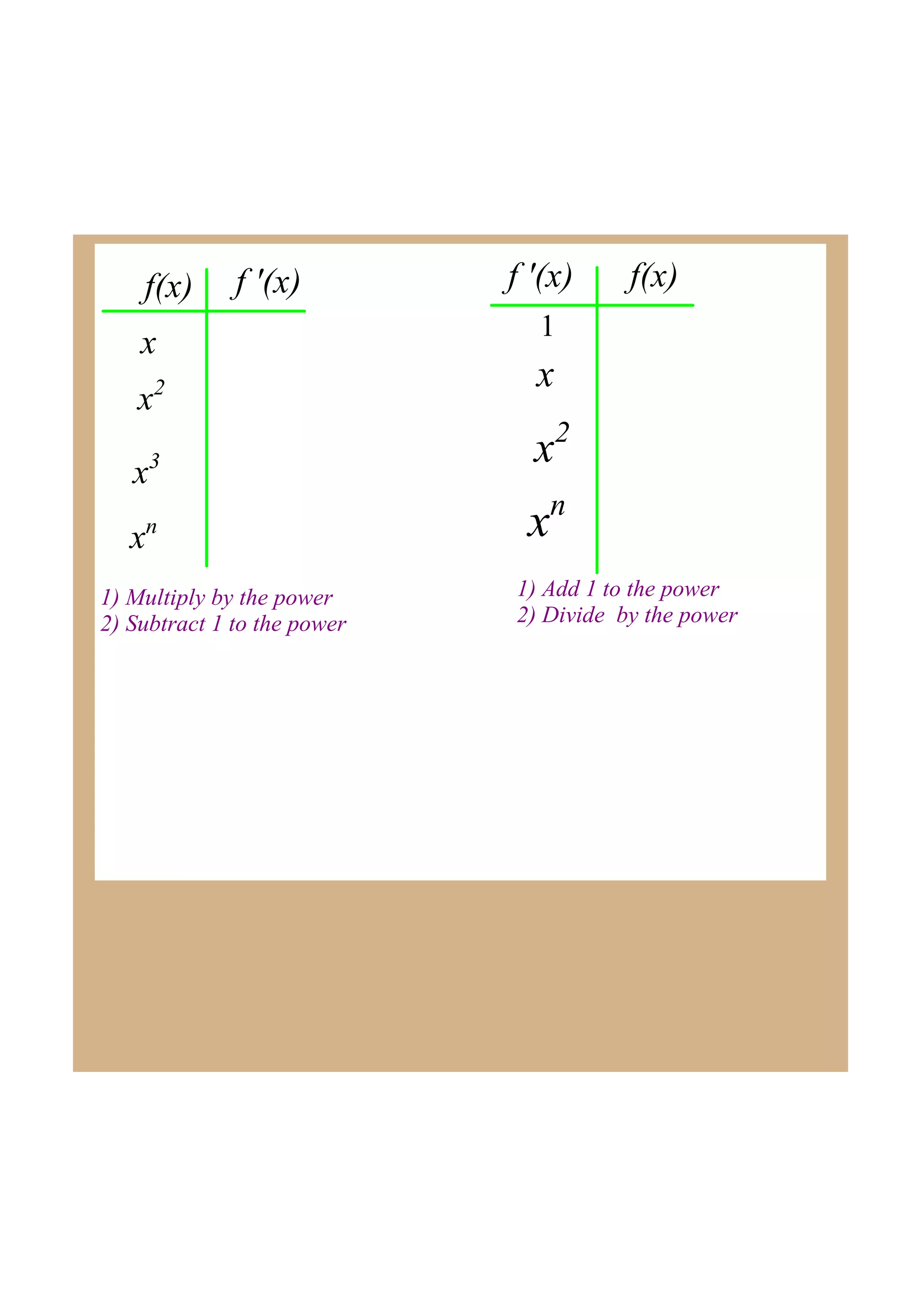
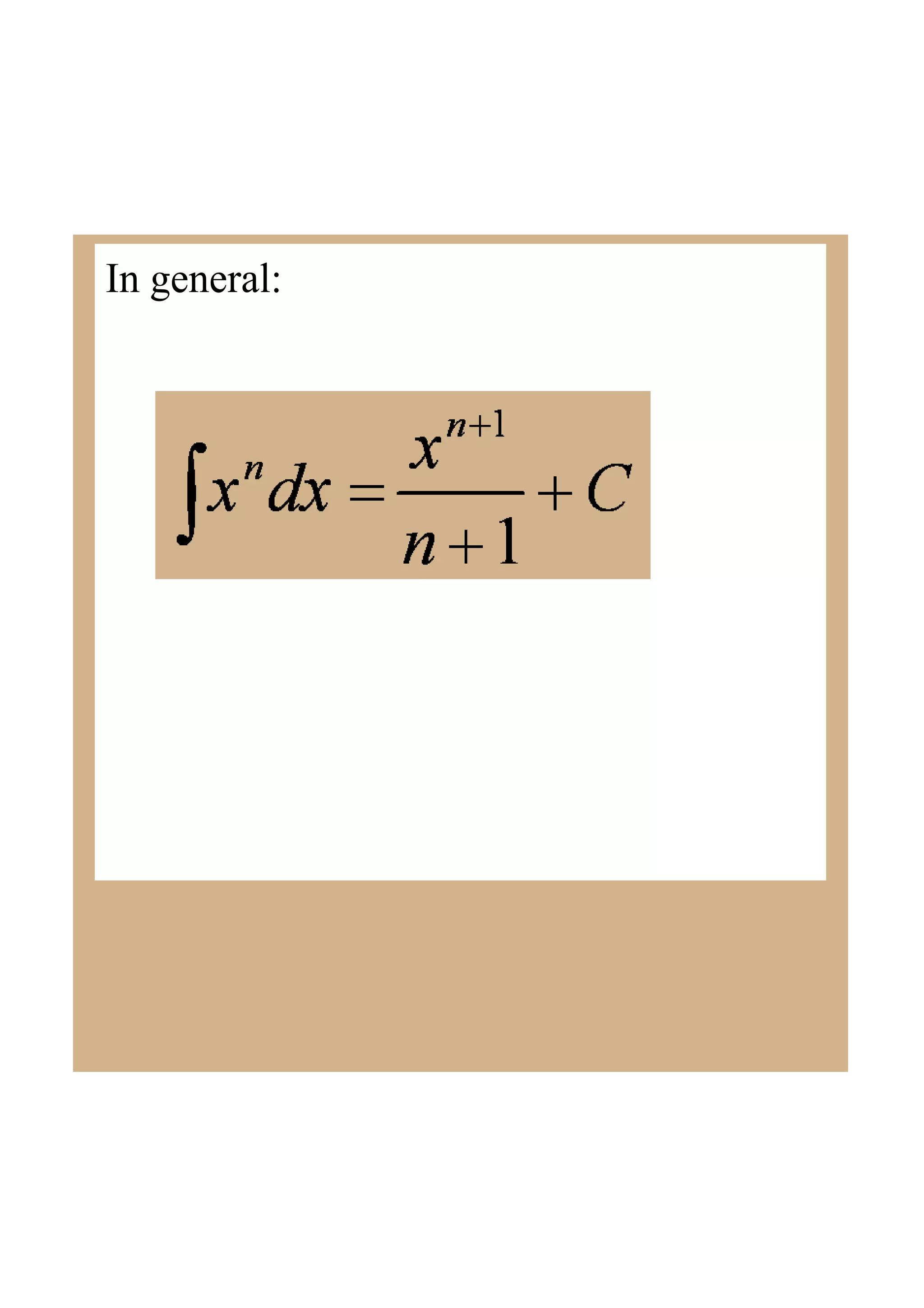
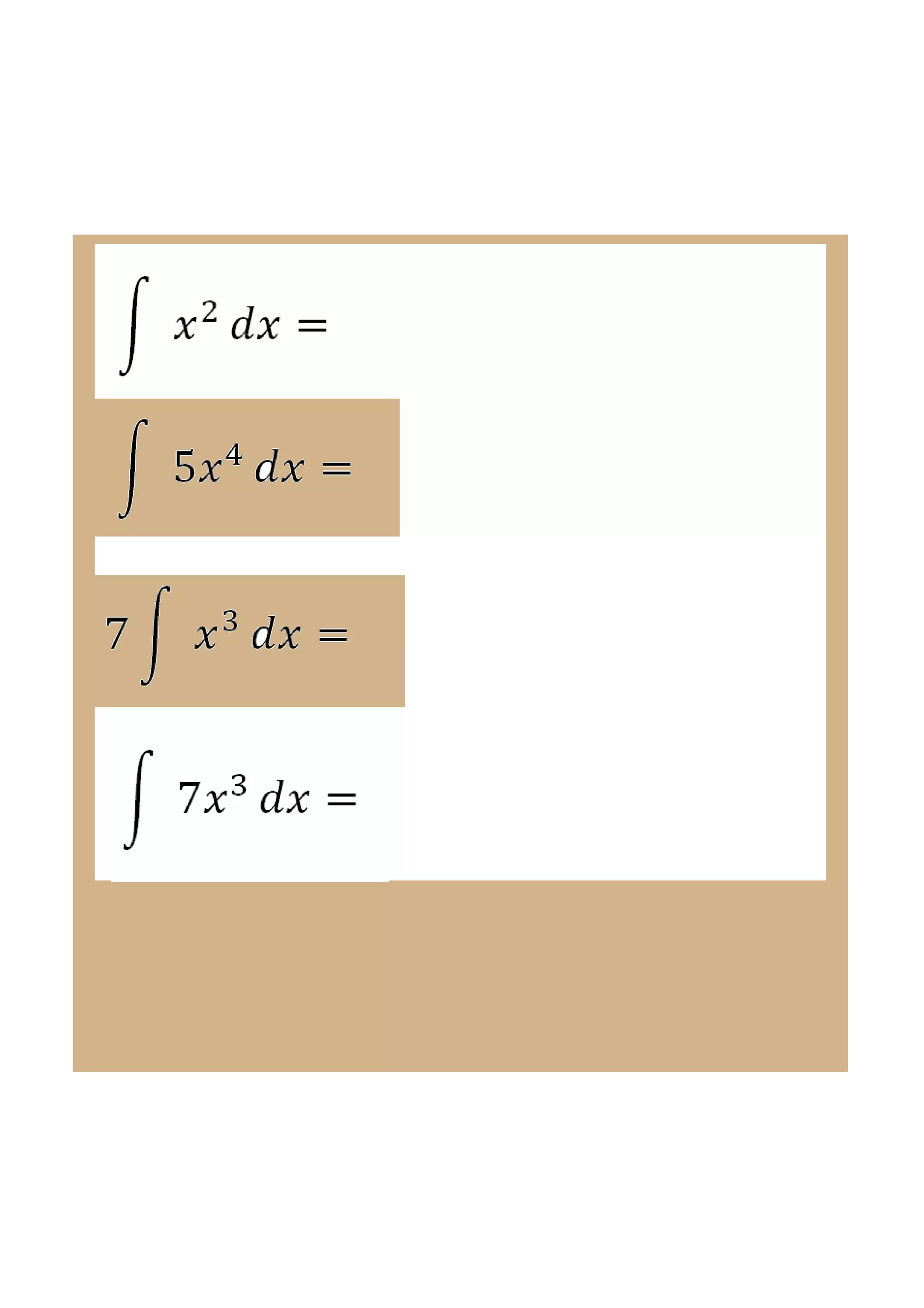
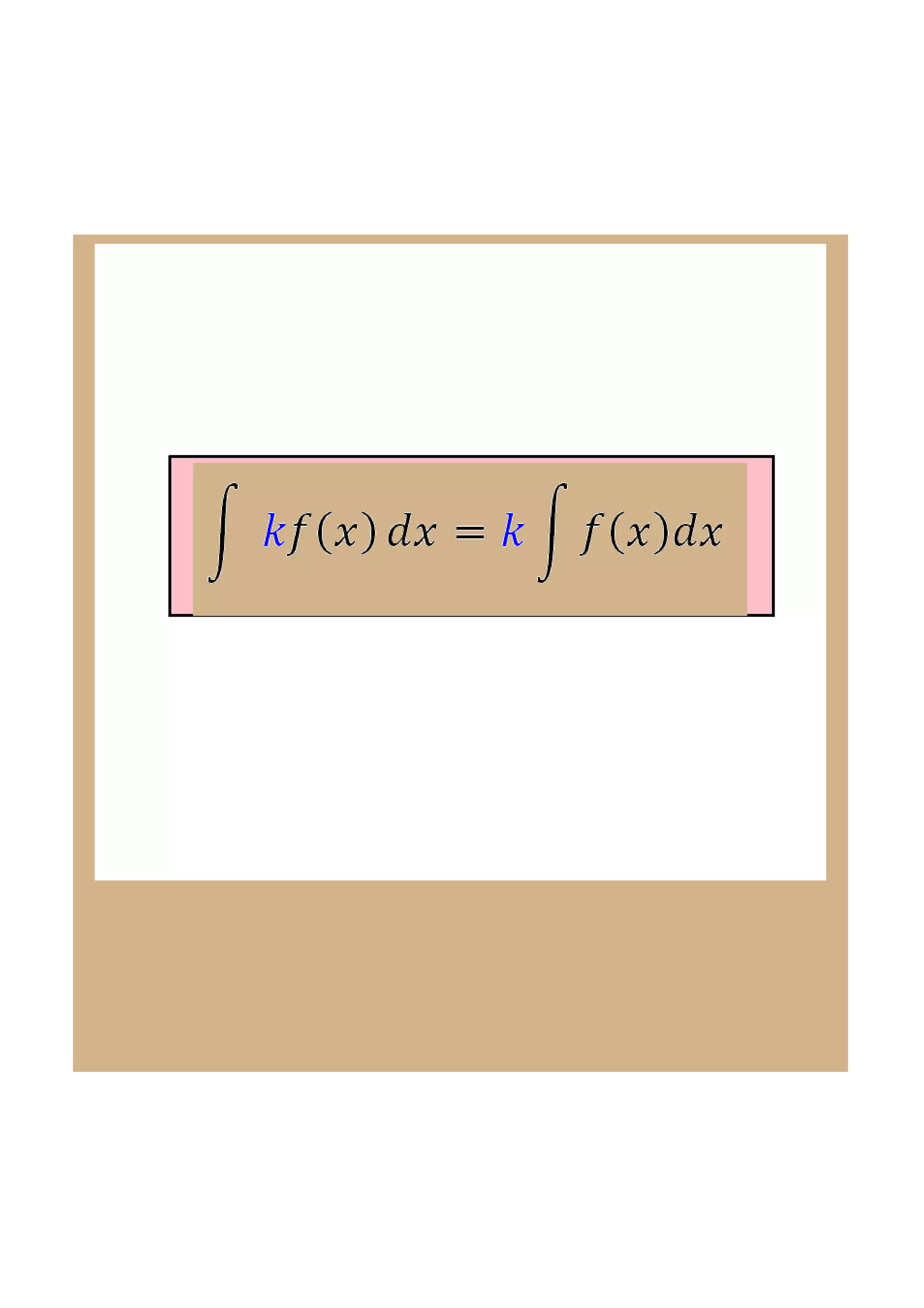
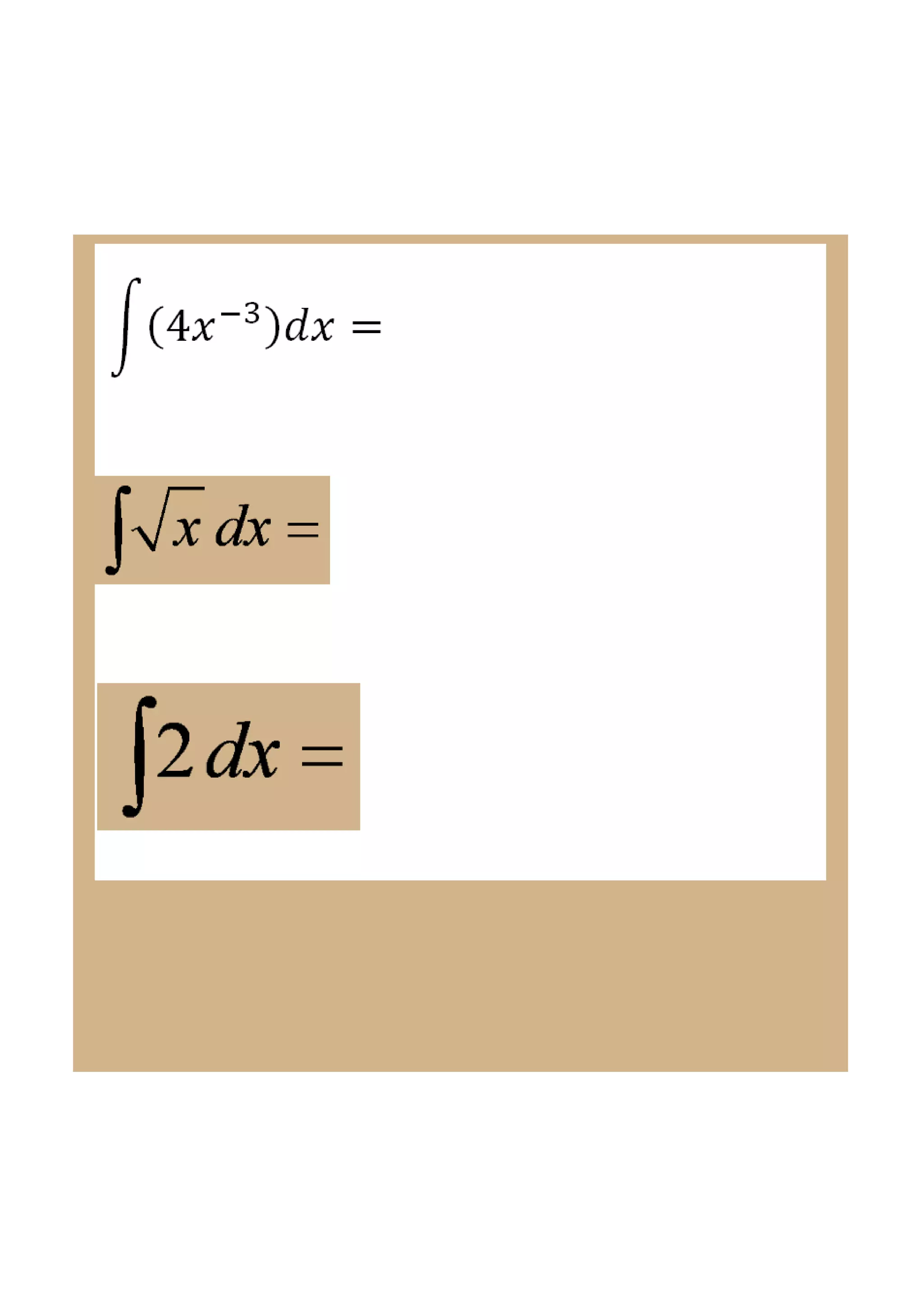
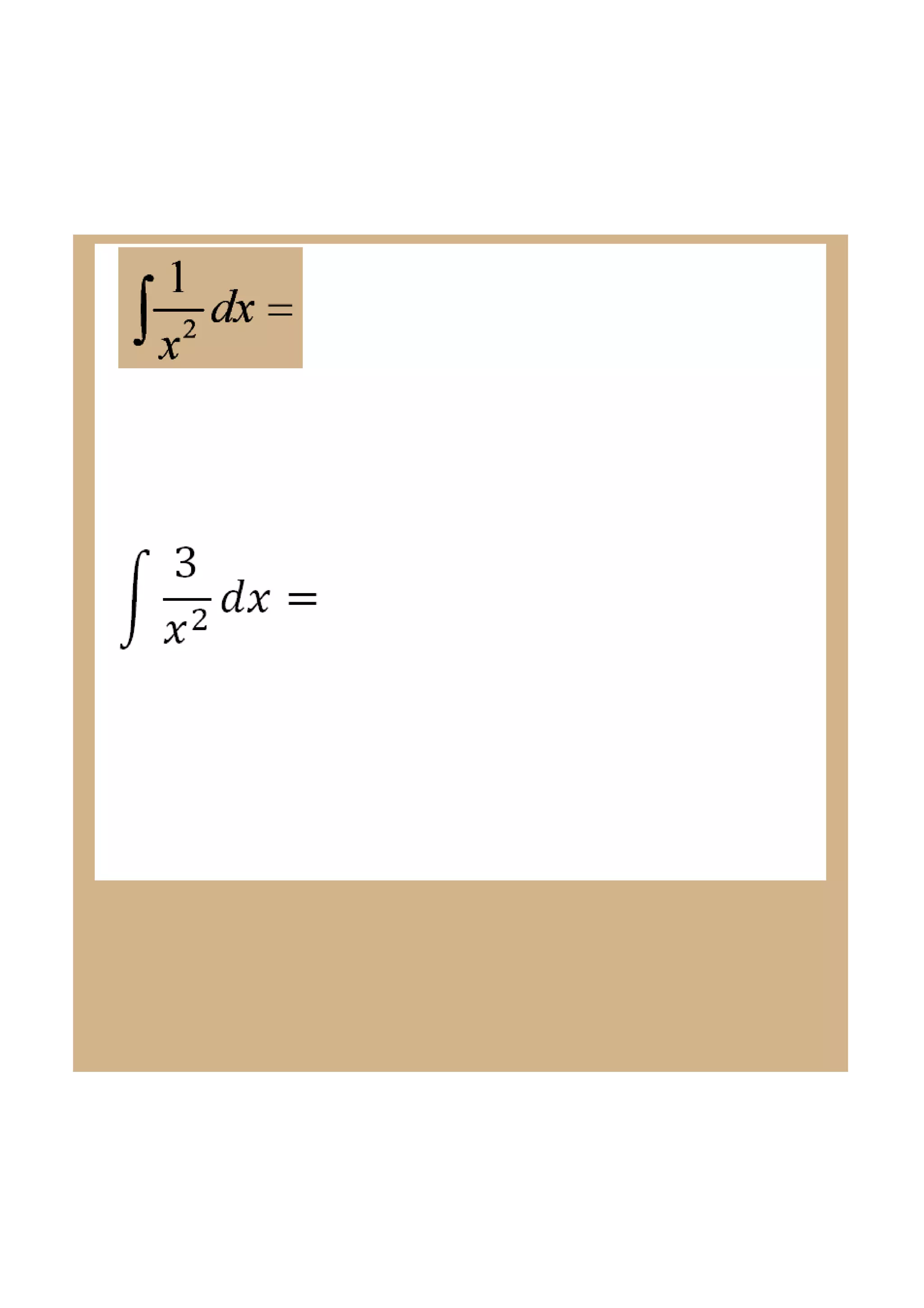
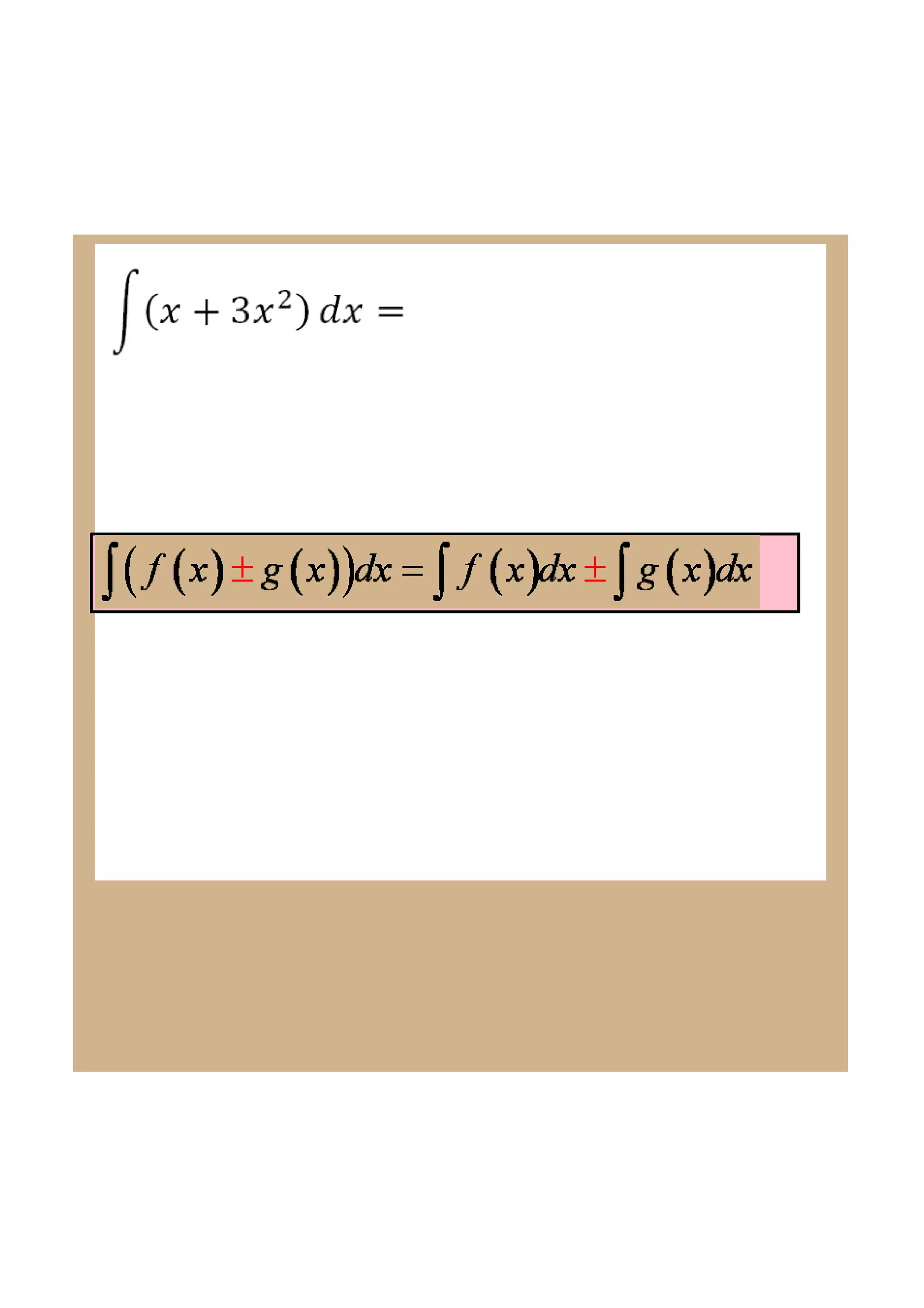
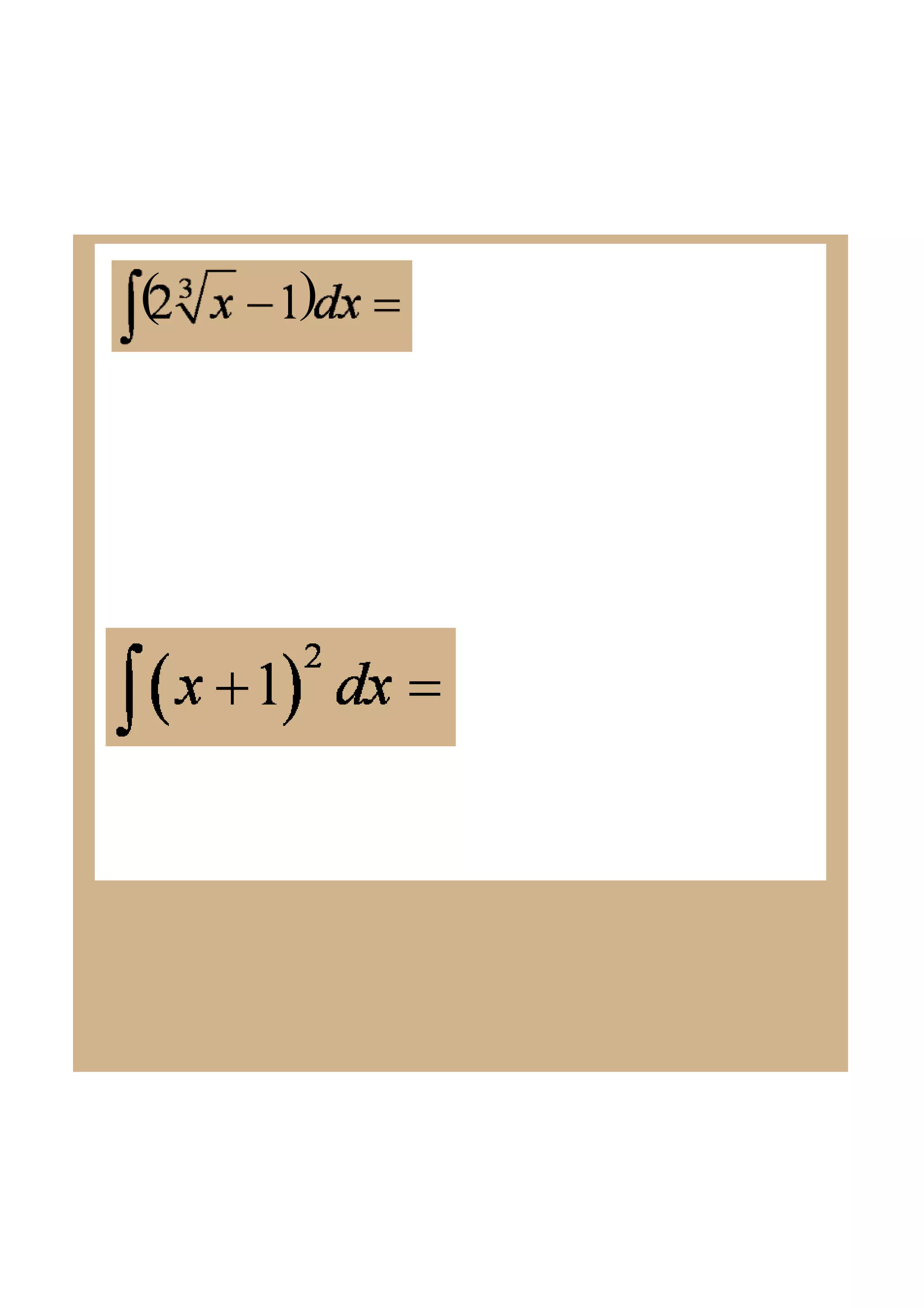
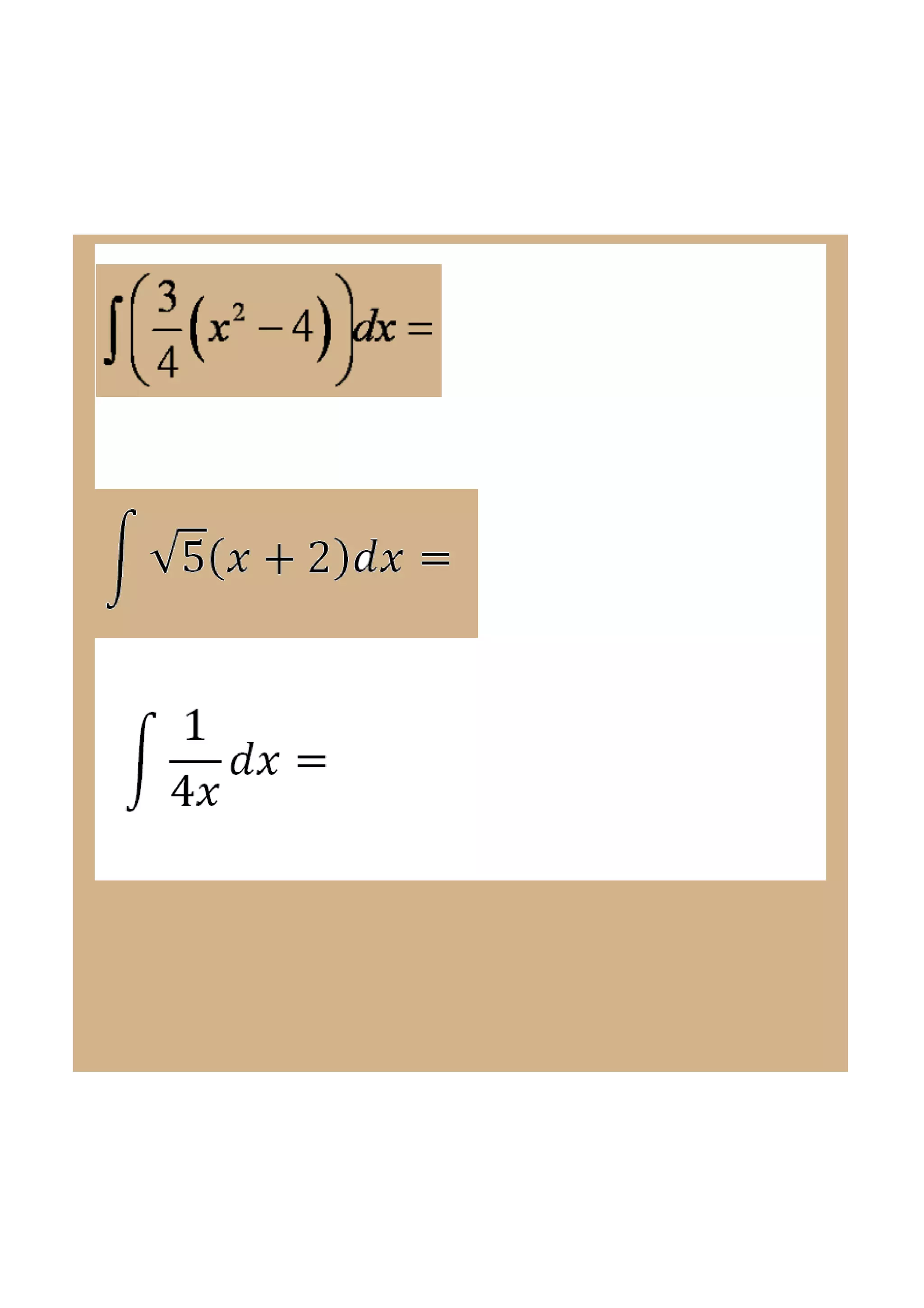
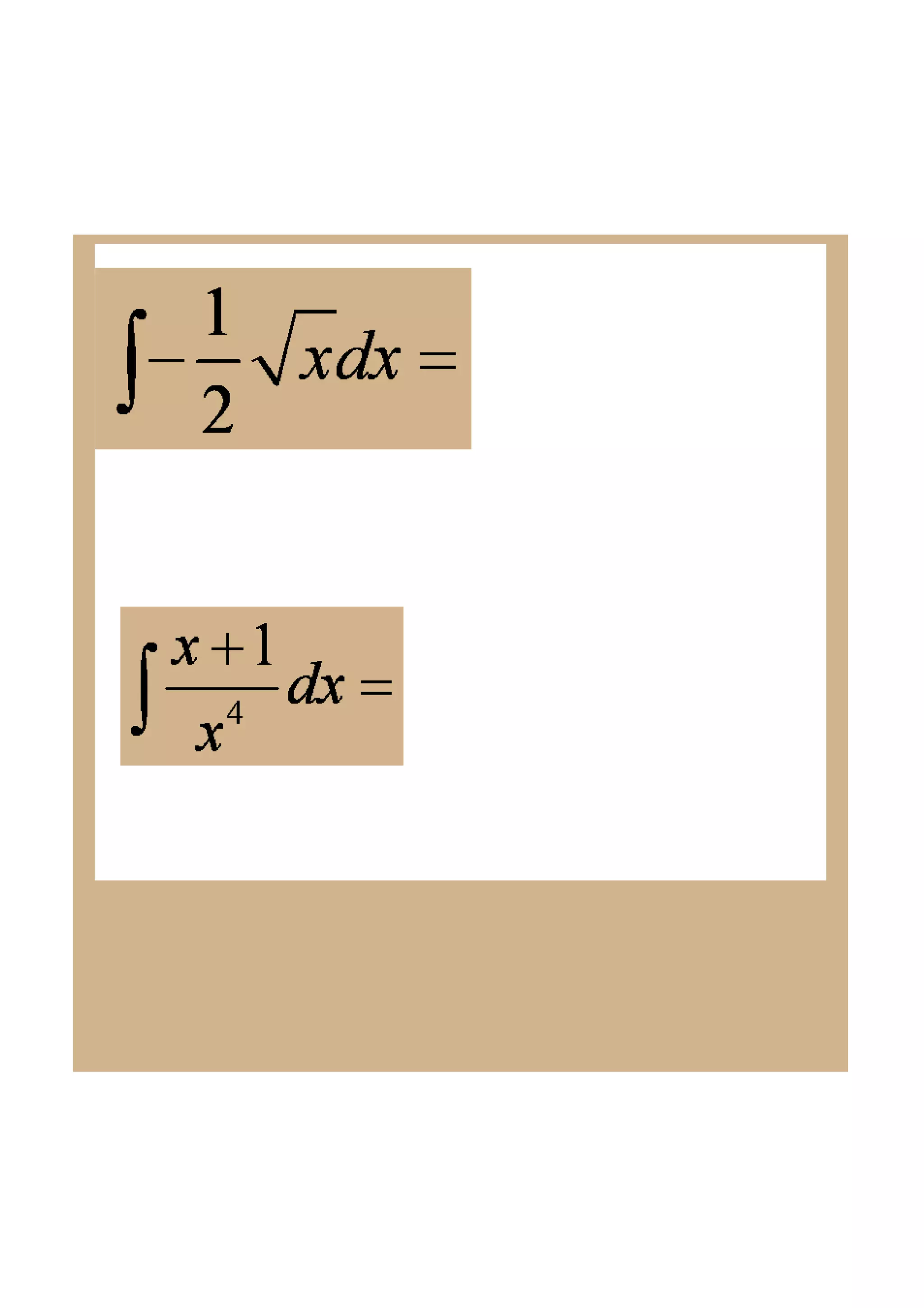
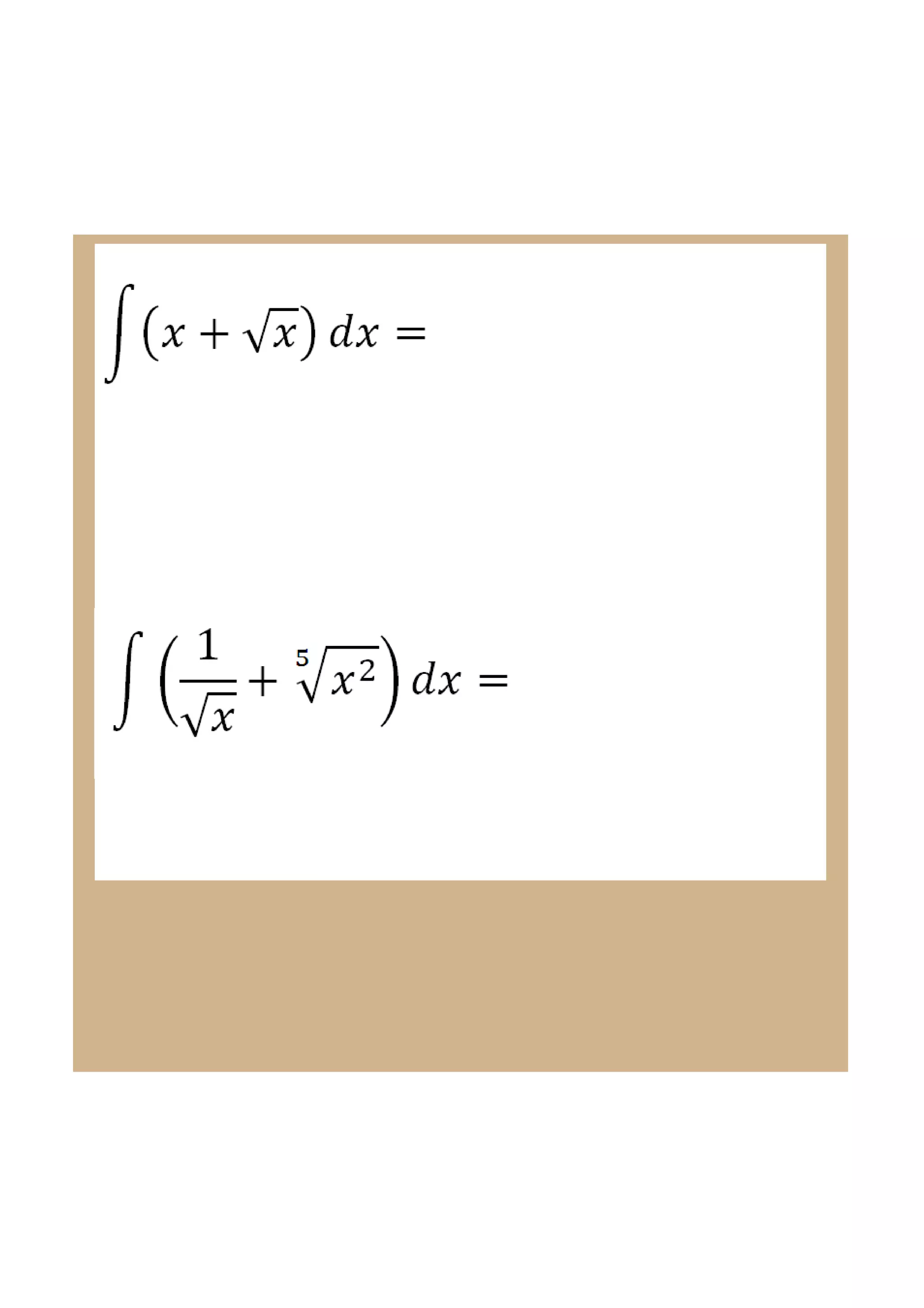


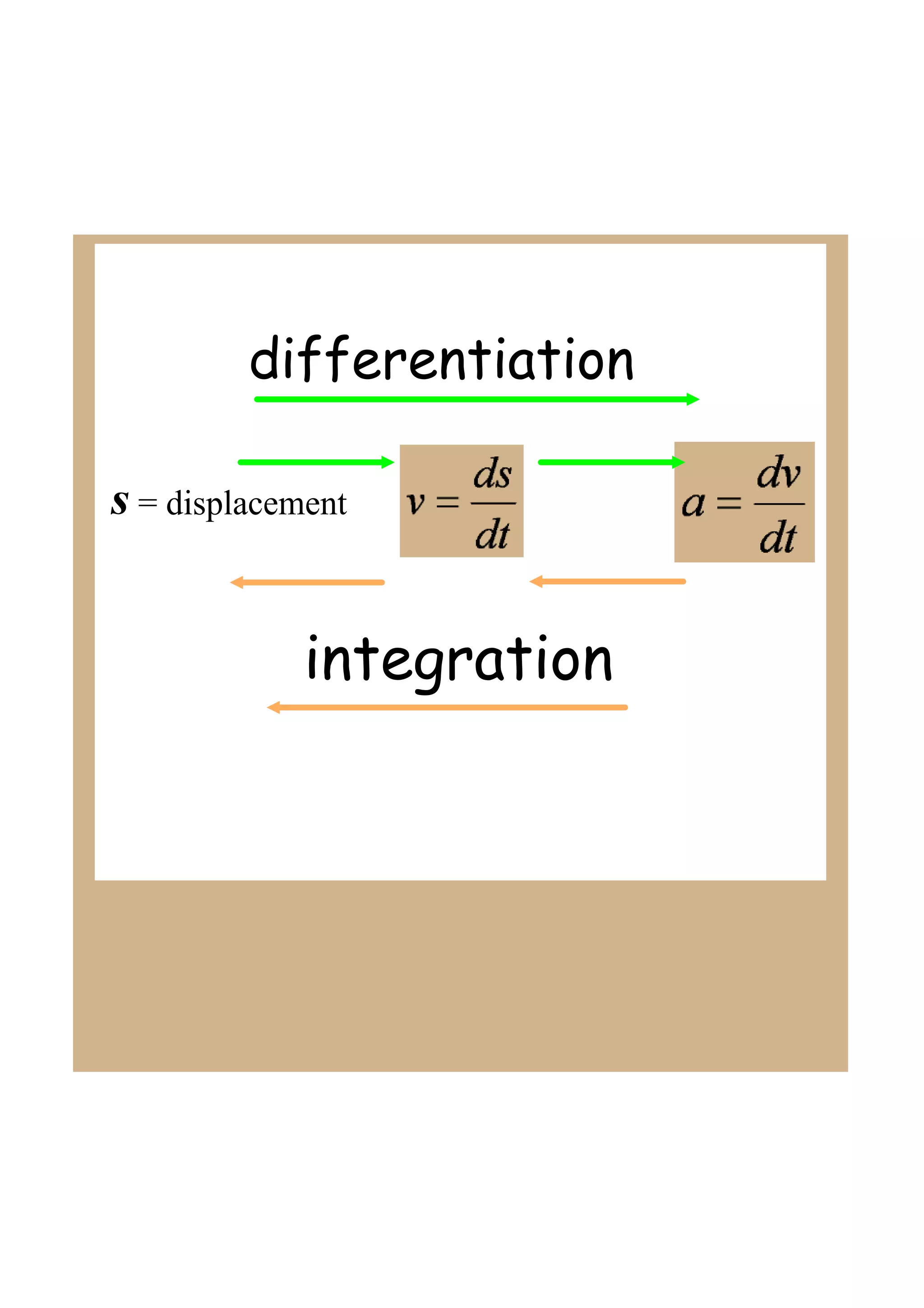


This document discusses indefinite integrals and anti-derivatives. It explains that the indefinite integral of a function is the set of all anti-derivatives of that function. It provides rules for finding the anti-derivative of a function given its derivative, such as adding 1 to the power and dividing by the new power. Examples are given of using these rules to find the function given its derivative.