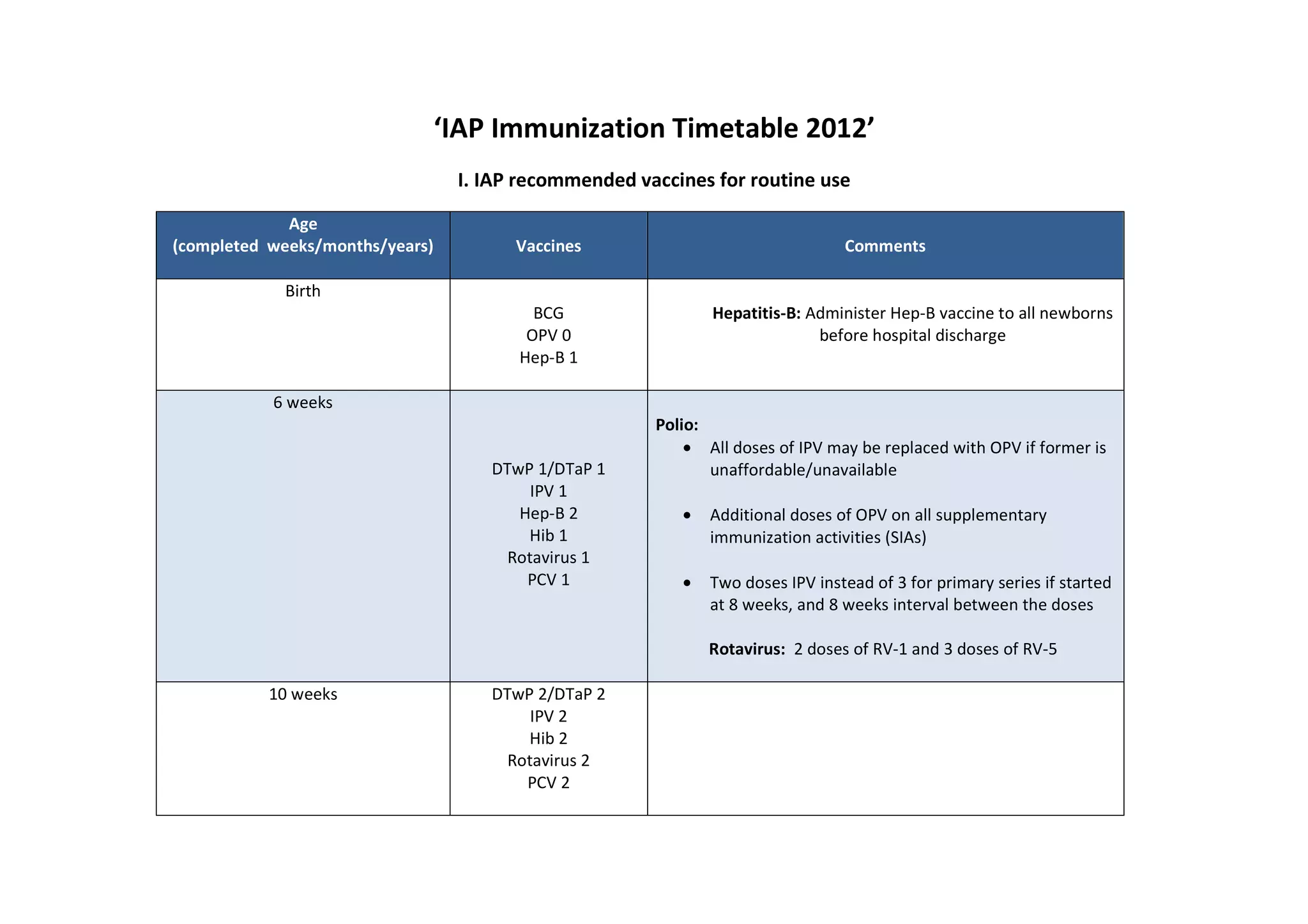
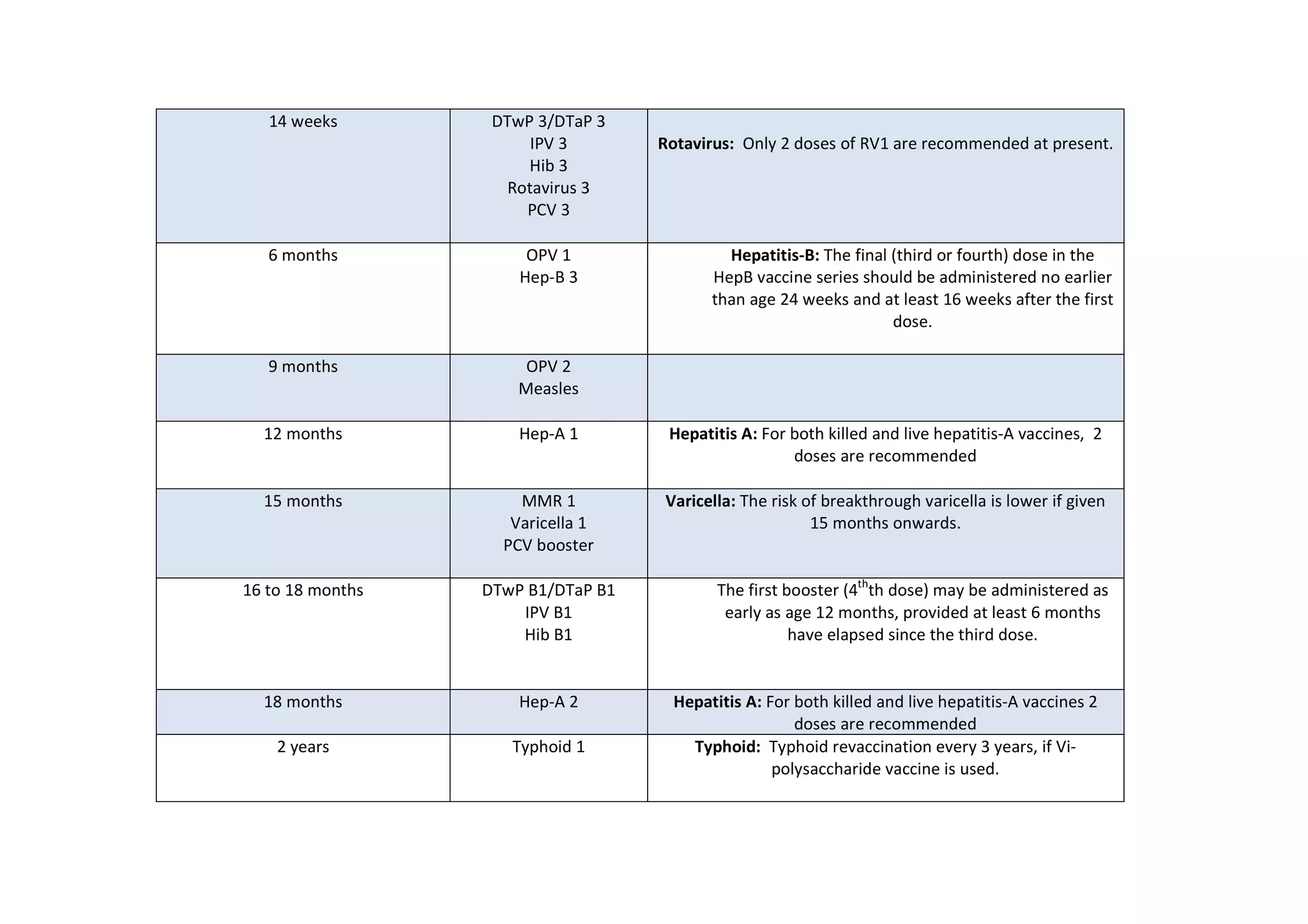
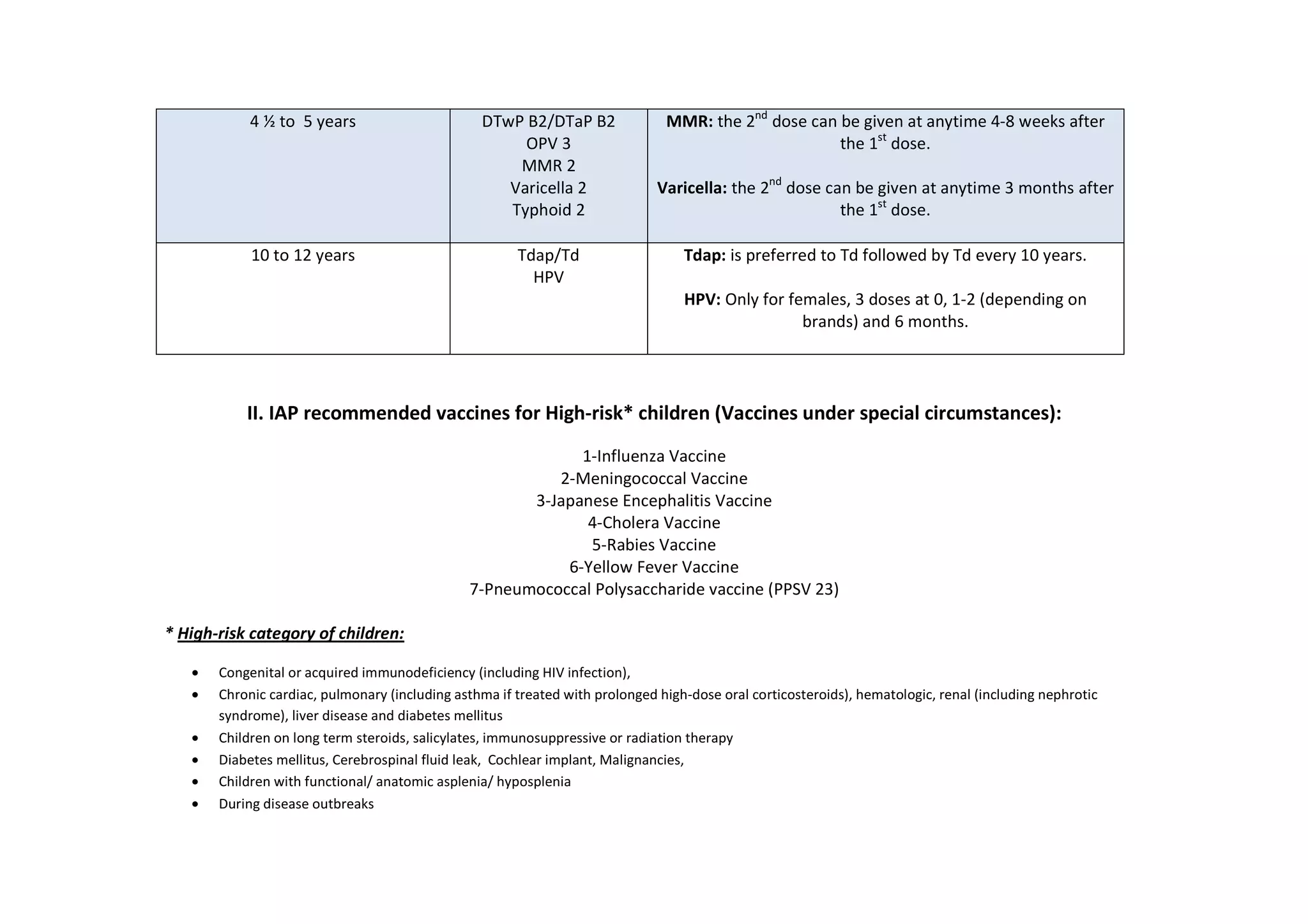
The document outlines the IAP's recommended immunization timetable for routine vaccines in India. It recommends vaccines including BCG, hepatitis B, polio, DTwP/DTaP, IPV, Hib, rotavirus, PCV, measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, hepatitis A, HPV, typhoid, influenza and meningococcal at various ages from birth through adolescence. It also lists additional vaccines recommended for high-risk children including influenza, meningococcal, Japanese encephalitis, cholera, rabies, yellow fever and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine.