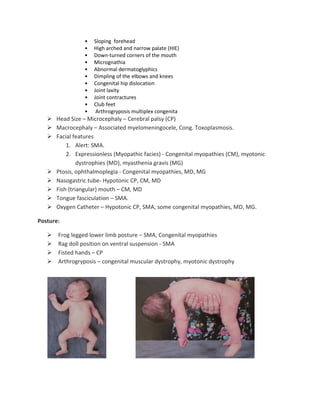
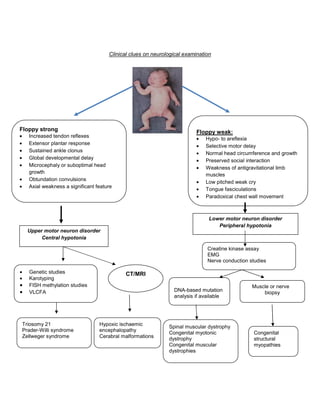
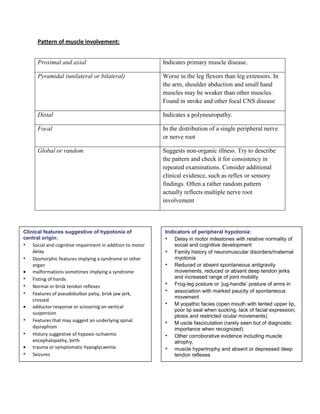
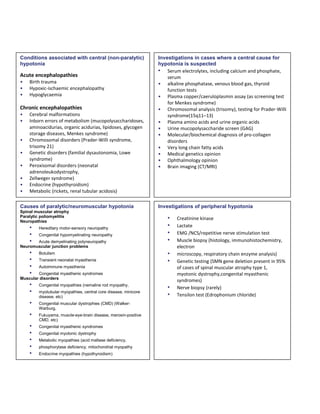
The document discusses hypotonia in infants, which is a decreased resistance of muscles to stretch. It can be caused by central nervous system issues or peripheral motor neuron/muscle disorders. Key signs of central hypotonia include normal or brisk reflexes and cognitive/social impairment. Peripheral hypotonia is suggested by reduced reflexes, facial weakness, and relatively normal cognition. Differential diagnosis involves assessing patterns of weakness, family history, and specialized tests. Thorough neurological exam and investigations are needed to identify the specific cause.