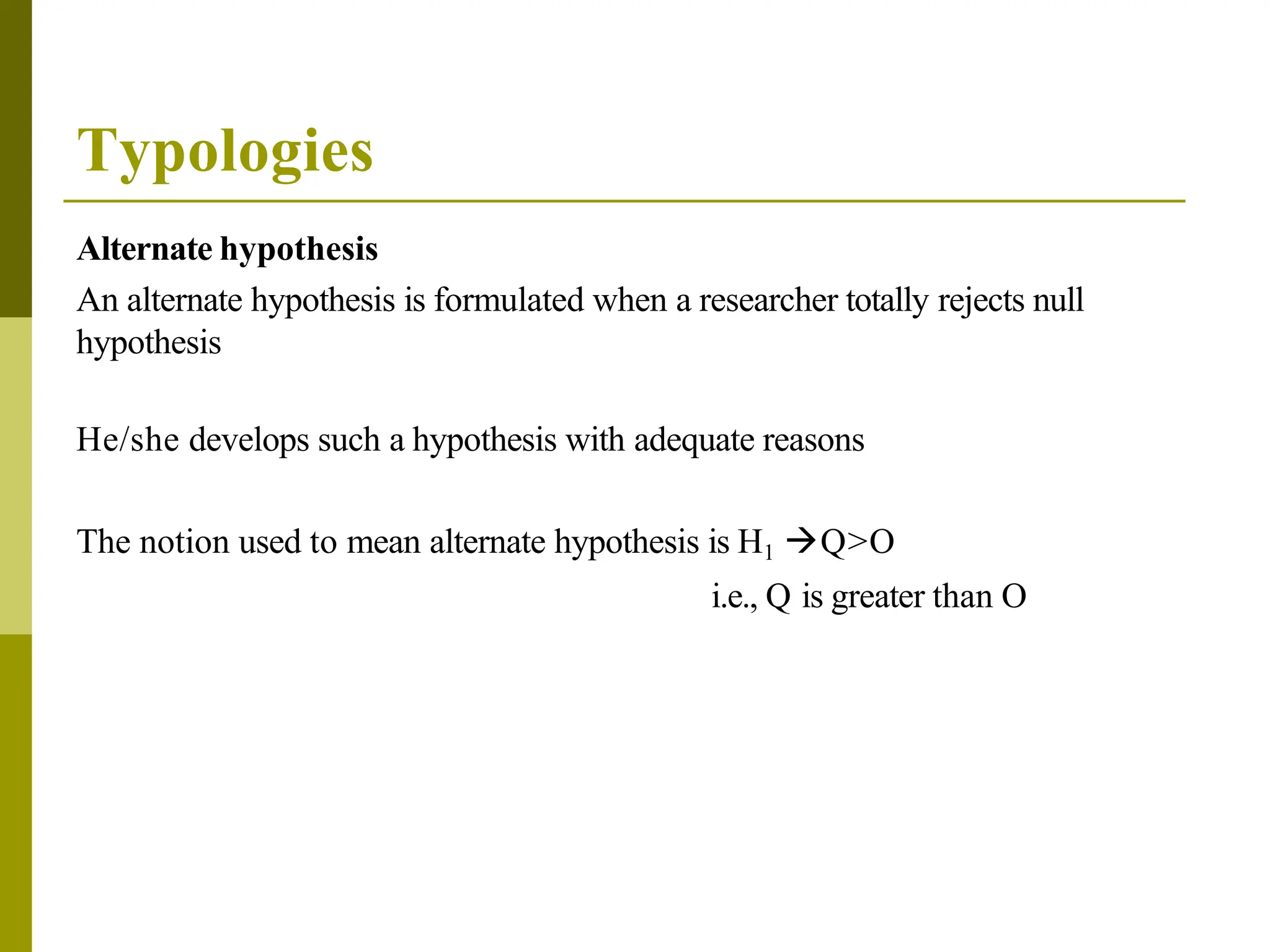
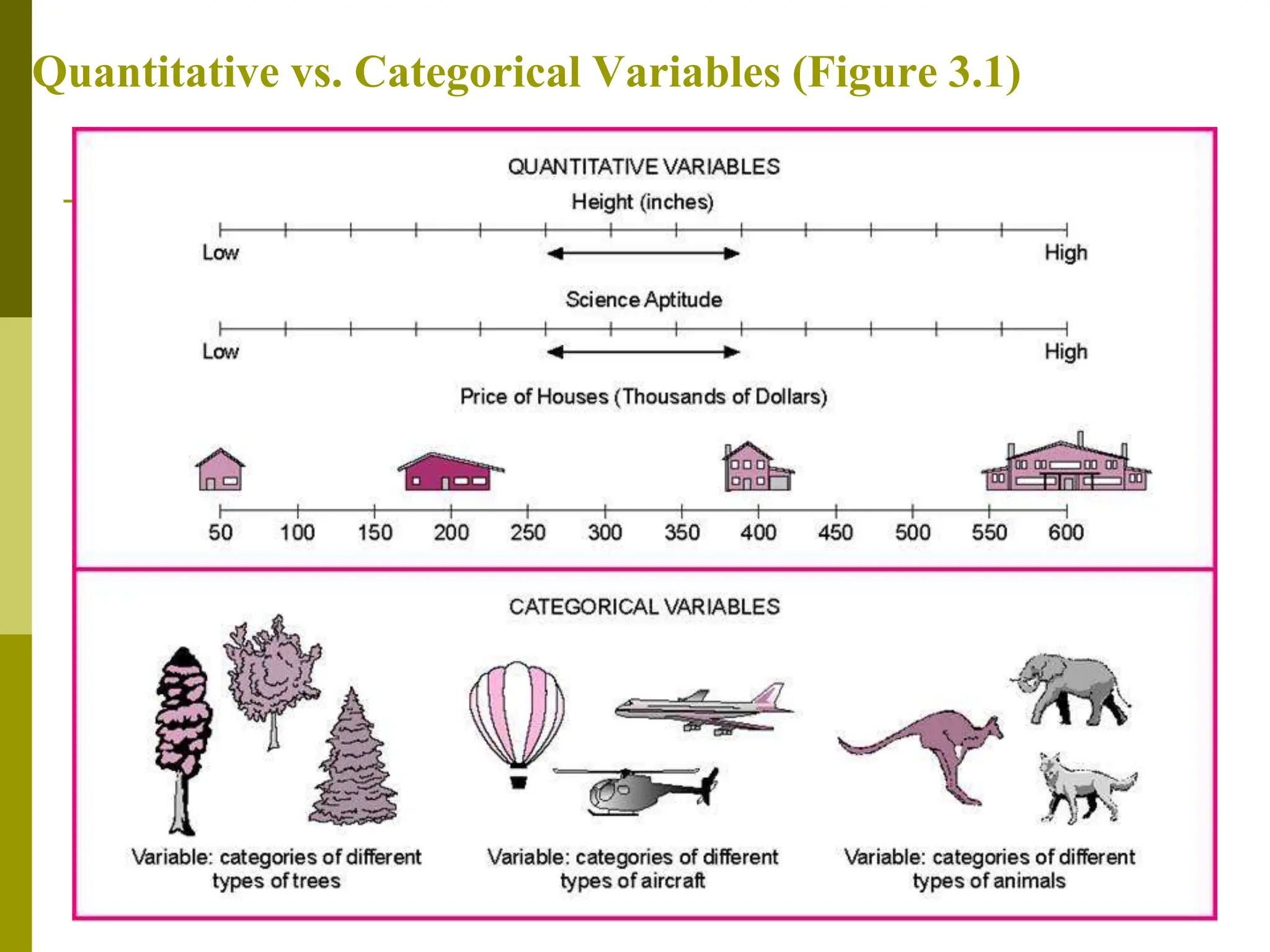
The document defines a hypothesis as a tentative statement about a relationship between two or more variables that can be tested. A hypothesis should be specific, testable, and able to be proven or disproven based on data. There are three main types of hypotheses: a working hypothesis, which provisionally explains an observed relationship; a null hypothesis, which opposes the working hypothesis; and an alternate hypothesis, which is formulated if the null hypothesis is rejected. The document also discusses variables, distinguishing between independent and dependent variables, and categorical and quantitative variables.