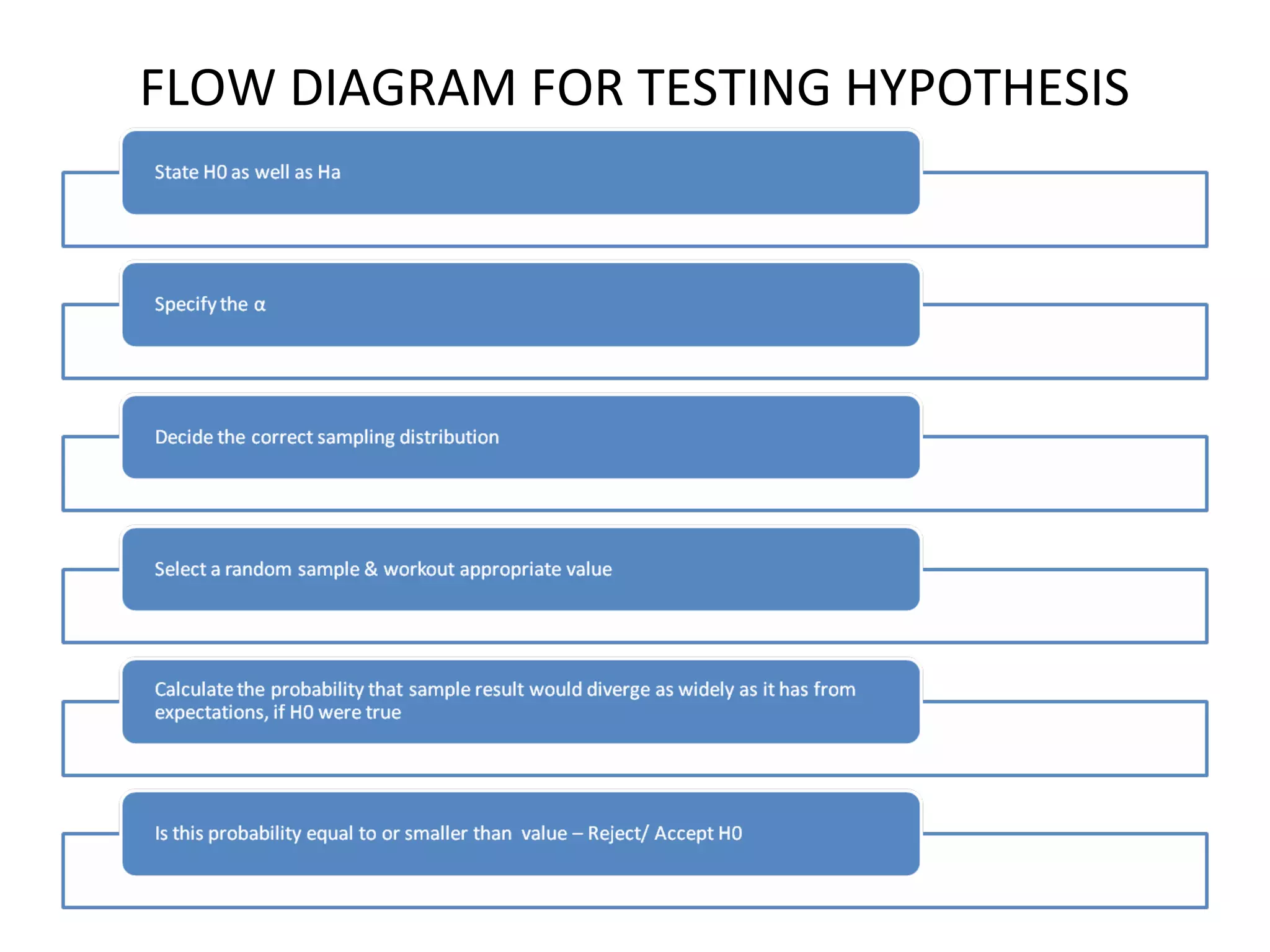
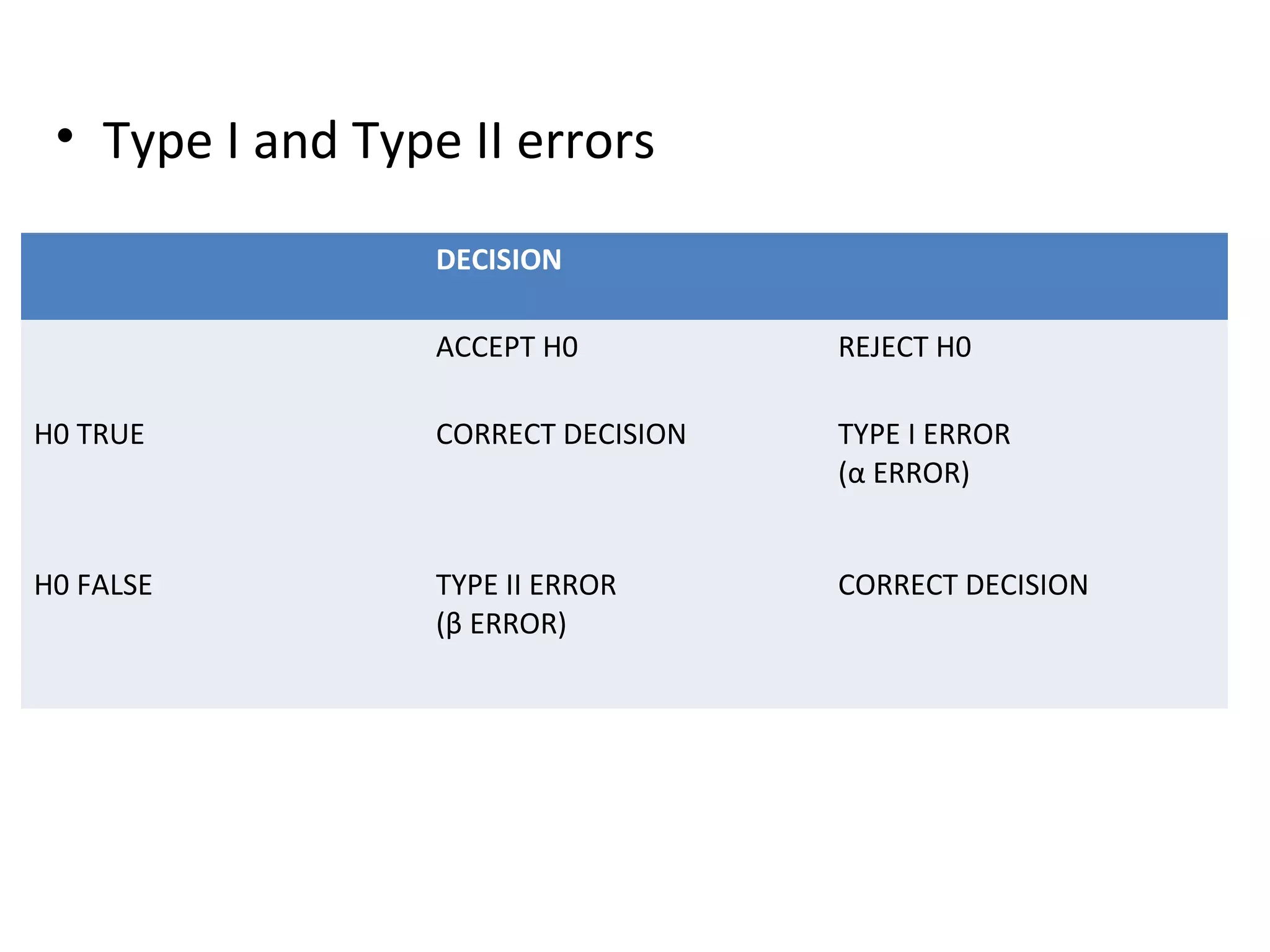
This document discusses hypothesis, including its definition, characteristics, types, formulation, and testing. A hypothesis is a tentative assumption made to explain certain facts or observations that can be tested. It should be clear, testable, relate variables, be specific and consistent. The main types are the null, prediction, declarative, and question forms. When testing a hypothesis, the researcher specifies a null hypothesis and alternative, selects a significance level like 5% typically, decides on a distribution, selects samples, computes a test statistic, and compares it to the significance level to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, avoiding type 1 and 2 errors.