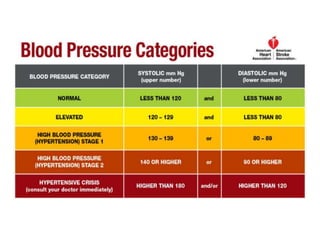
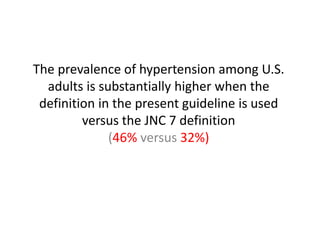
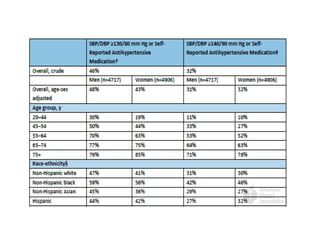
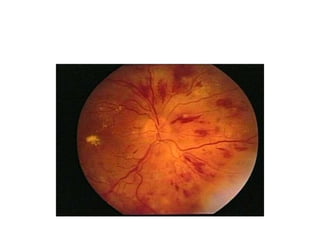
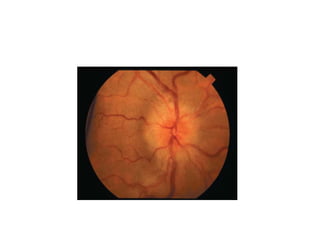
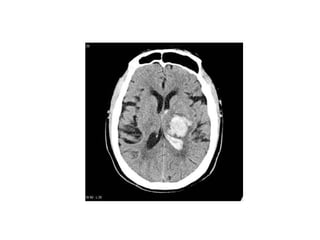
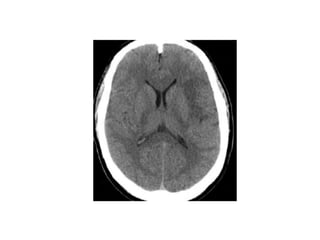
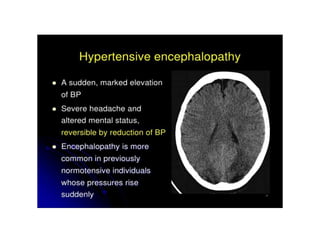
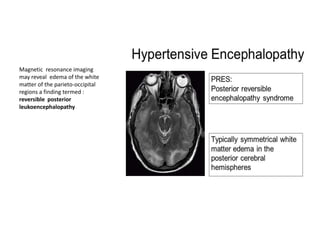
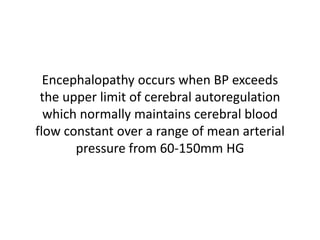
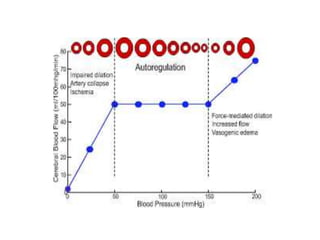
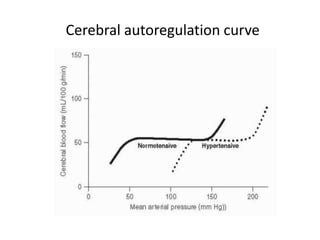
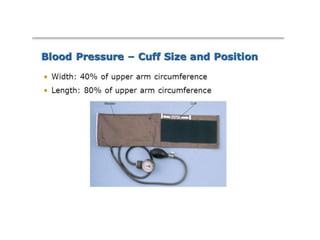
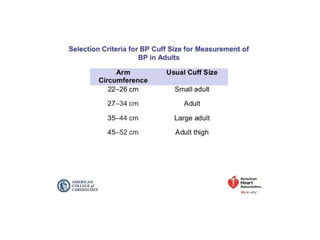
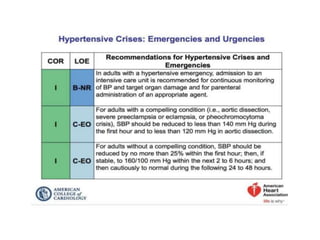
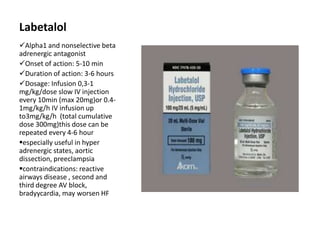
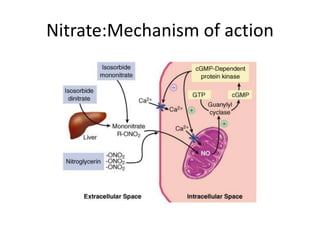
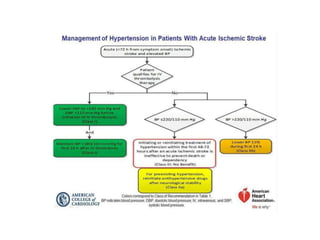
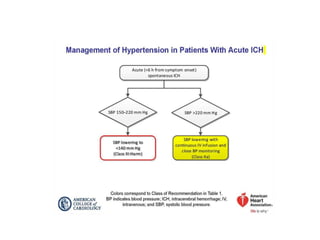
Hypertension remains a major risk factor for cardiovascular and renal disease. Hypertensive crises are classified as emergencies, with severe elevation of blood pressure and acute target organ damage, or urgencies, with severe elevation but no organ damage. Untreated emergencies have a 1-year mortality of over 79%. Causes include non-adherence to treatment, renal disease, pregnancy disorders, withdrawal of medications, pheochromocytoma, and illicit drug use. Target organ damage includes brain, heart, kidneys, eyes, and aorta. Treatment focuses on rapidly lowering blood pressure with intravenous drugs like sodium nitroprusside, labetalol, or nitroglycerine to prevent further injury. Management depends