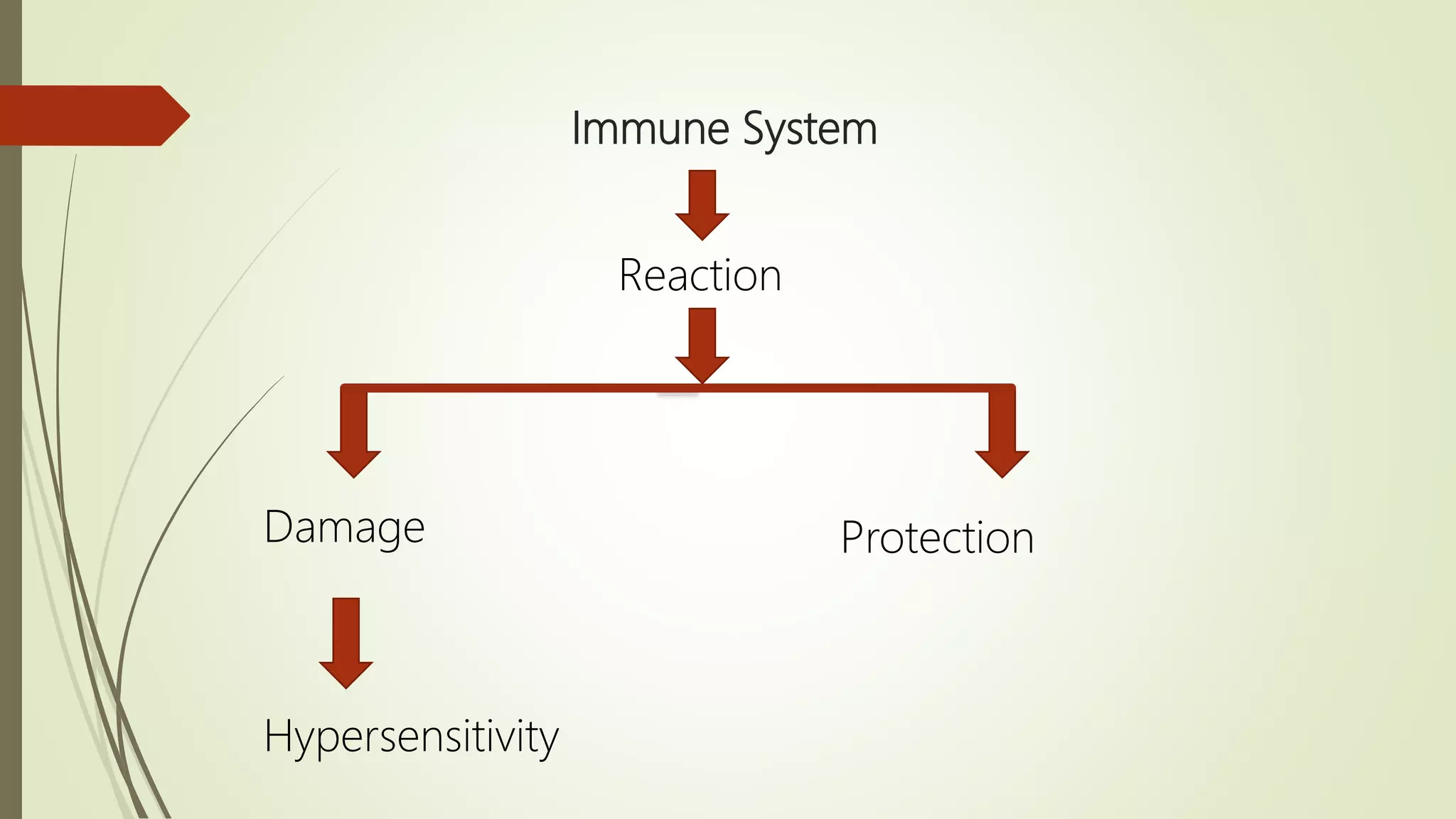
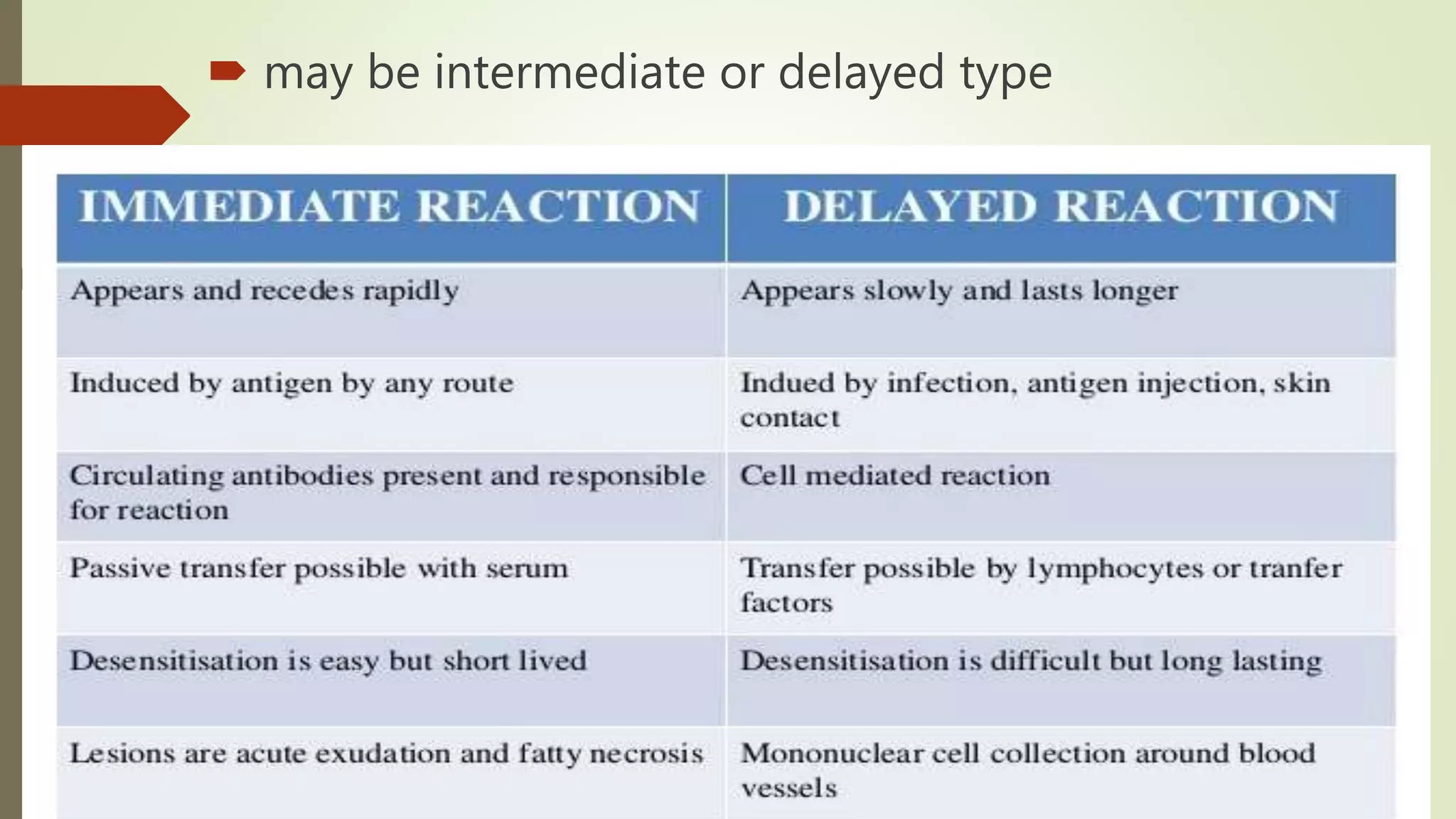
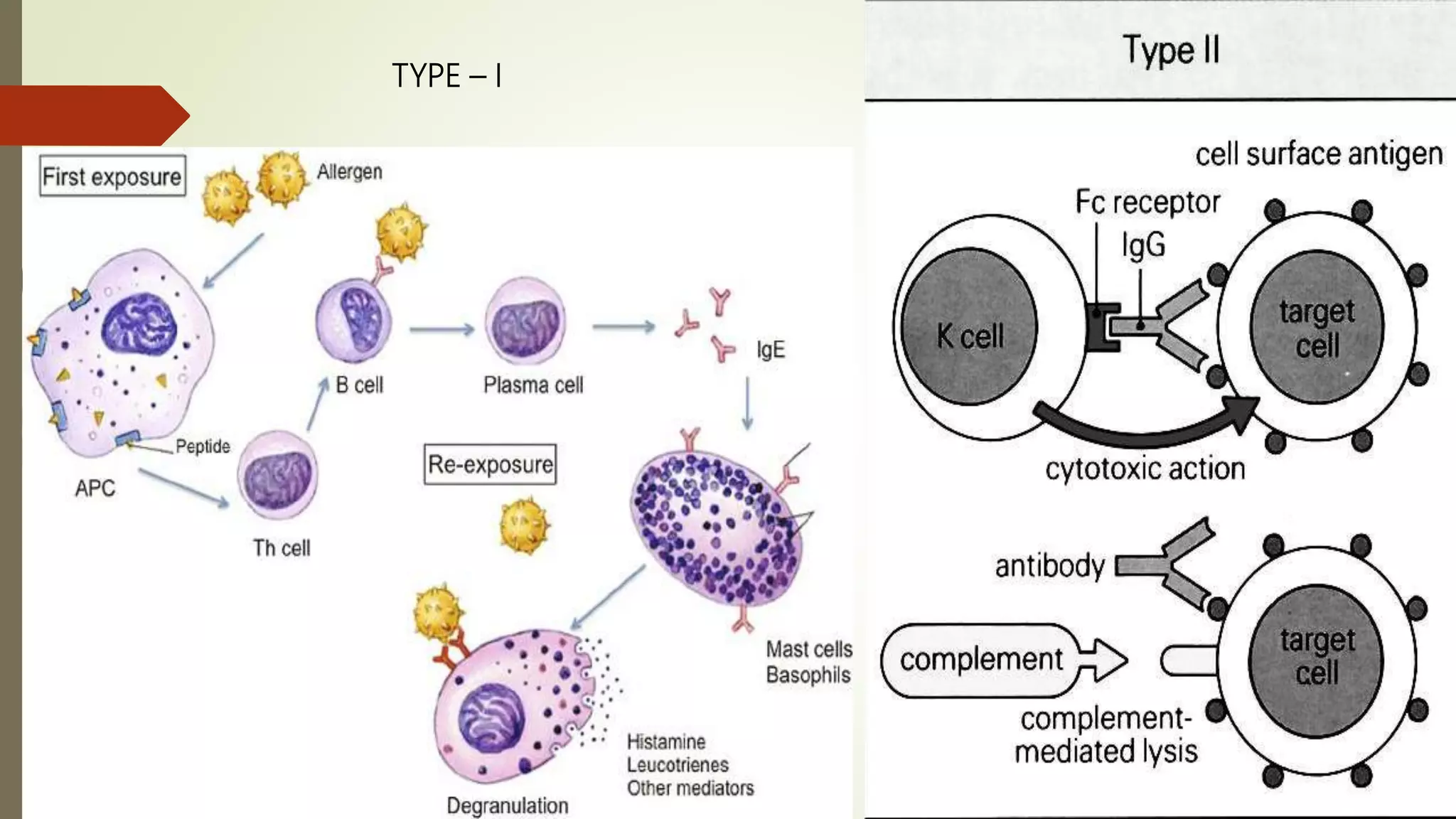
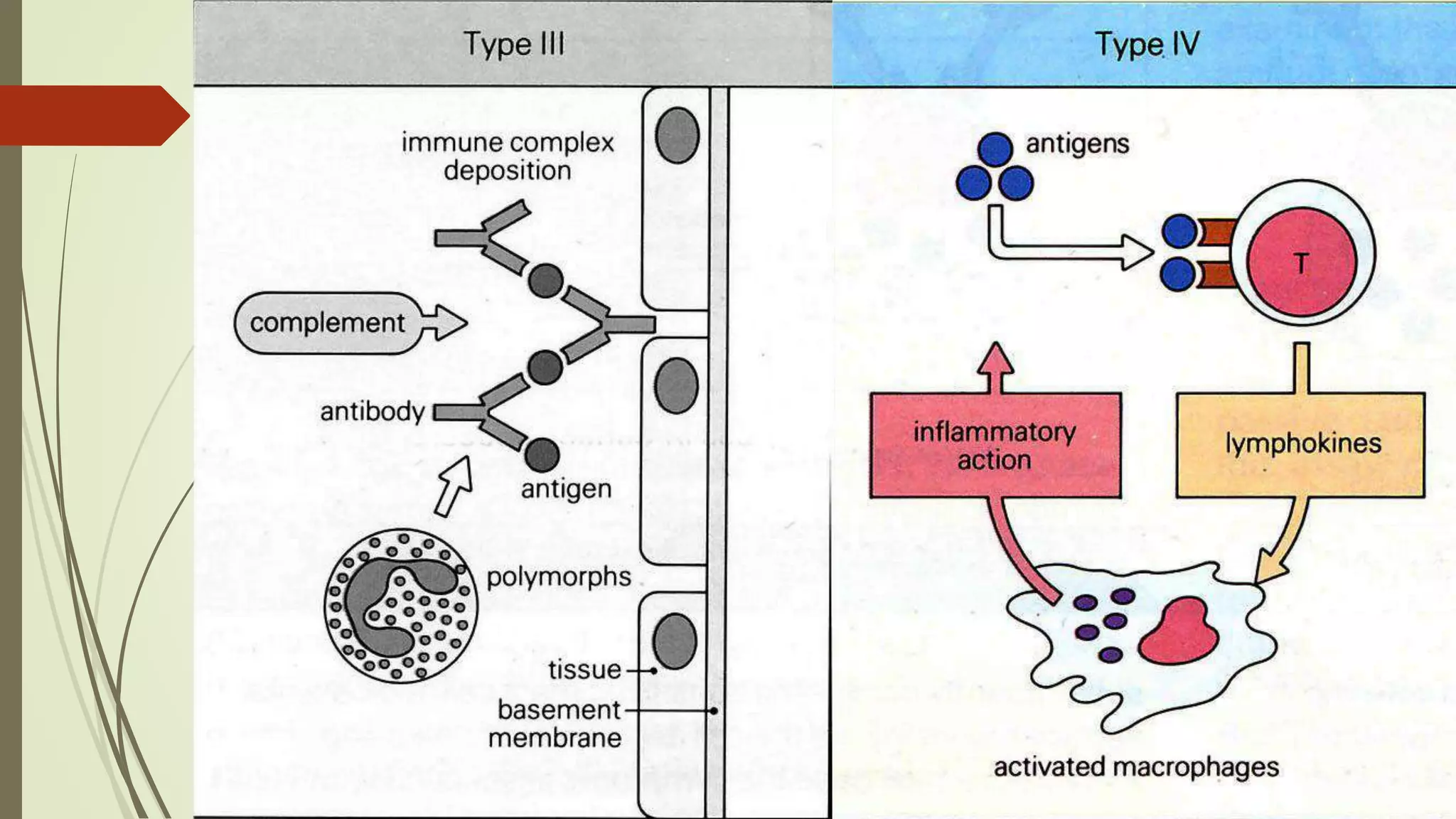
The document discusses hypersensitivity and its classification. Hypersensitivity refers to an exaggerated or inappropriate immune response that is harmful to the host. It occurs when a sensitized individual is re-exposed to an antigen, leading to tissue damage. Hypersensitivity reactions are classified into four types based on the mechanism and timing of the response: immediate antibody-mediated types I, II and III, and delayed T cell-mediated type IV. Type I involves anaphylaxis, type II involves antibody-dependent cytotoxicity, type III involves immune complex mediated cytotoxicity, and type IV involves delayed type hypersensitivity.