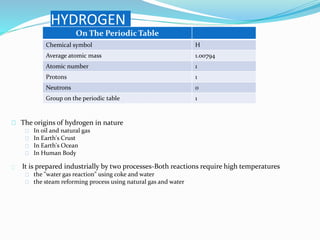
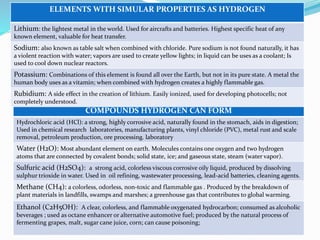
The document discusses hydrogen, including its discovery, naming, properties, location in nature, industrial production processes, compounds it can form like water and acids, and common uses such as in fuel cells, welding, and rocket fuel. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe and is used widely in industry for refining, treating metals, and processing foods.