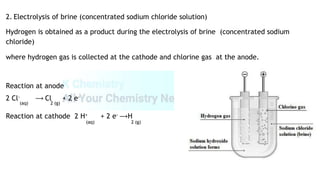
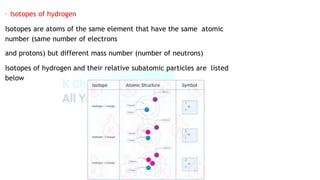
The document summarizes physical and chemical properties of hydrogen, including that it is a colorless, odorless gas that is less dense than air and insoluble in water. Methods of collecting, testing, and producing hydrogen are described, such as upward delivery due to its low density or collection over water due to its insolubility. Industrial production of hydrogen includes the reaction of methane and steam, electrolysis of brine or acidified water. Uses include synthesis of ammonia and hydrochloric acid, as a rocket fuel, and filling balloons. Isotopes of hydrogen and its potential as a renewable fuel are also discussed.