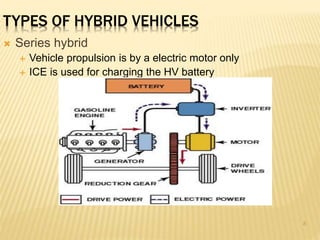
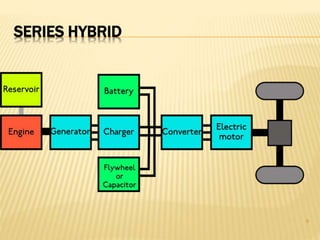
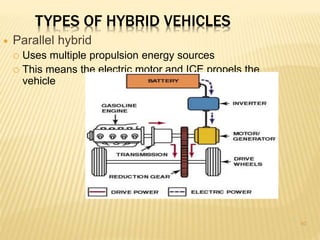
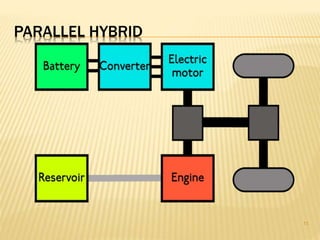
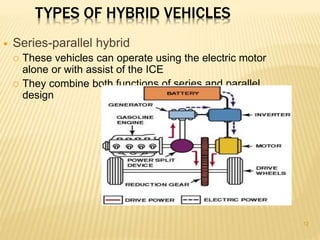
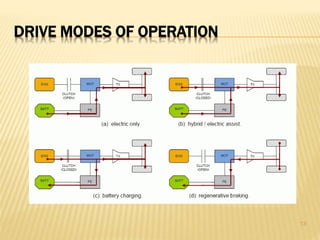
This document provides an overview of hybrid vehicles. It discusses that a hybrid uses both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor powered by batteries. It describes the different levels of hybrids from full to mild and the basic components. It also outlines the different types of hybrids including series, parallel, and series-parallel hybrids. The document discusses maintenance considerations and battery lifespan for hybrids. It addresses common questions around safety, submersion, and performance of electric vehicles. Finally, it provides pros and cons of owning a hybrid vehicle compared to a regular vehicle.