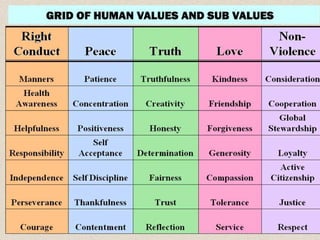
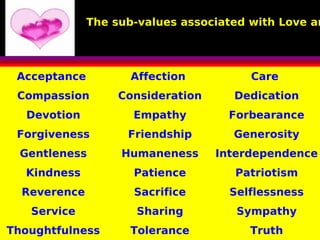
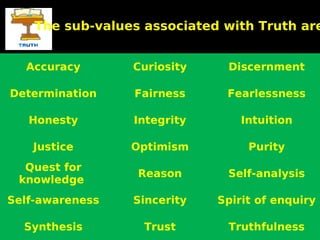
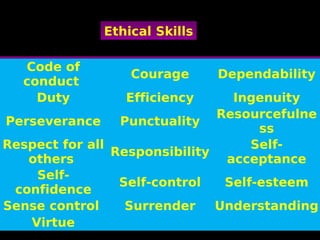
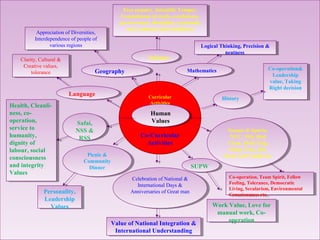
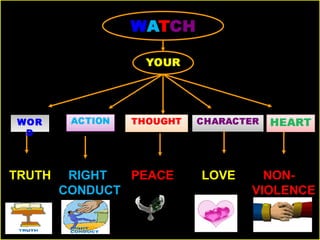
This document discusses human values and approaches to teaching human values. It defines human values as universal concepts that can be found across cultures and times, such as truth, right conduct, love, peace and non-violence. The document outlines sub-values associated with each of these main human values. It also describes two approaches to teaching human values: the direct method using techniques like thought for the day, stories and activities; and the inter-curriculum method integrating values into different subject areas. The roles and responsibilities of teachers in promoting human values are also discussed.