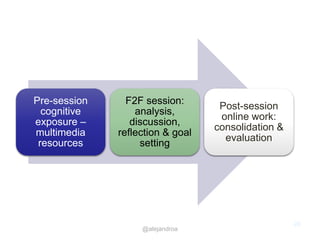
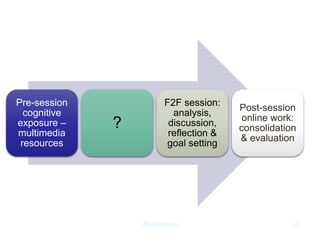
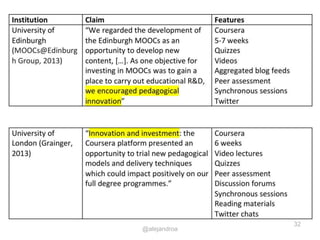
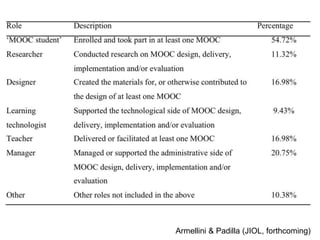
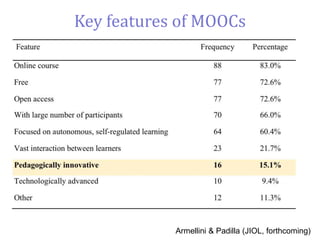
The document outlines a strategic approach to enhancing teaching quality in higher education, emphasizing the importance of pedagogic innovation and quality enhancement in improving student experiences. It discusses various levels of engagement in online and blended learning, the definitions and implications of pedagogic innovation, and examines the role of MOOCs in this context. The conclusion highlights that while pedagogic innovation is valuable for teaching excellence, it is not a necessary condition for high-quality education.












![Pedagogic innovation
“Adapting to characteristics of students and
responding to their development is an inherent
aspect of pedagogy. […] These adaptations
can be considered innovations if are based
[sic] on a new idea and when they have the
potential to improve student learning, or when
they are linked with other outcomes […]”
(Vieluf, Kaplan, Klieeme & Bayer, 2012)
24
@alejandroa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hullkeynote15june2016-160615110911/85/Hull-keynote-15-june-2016-24-320.jpg)