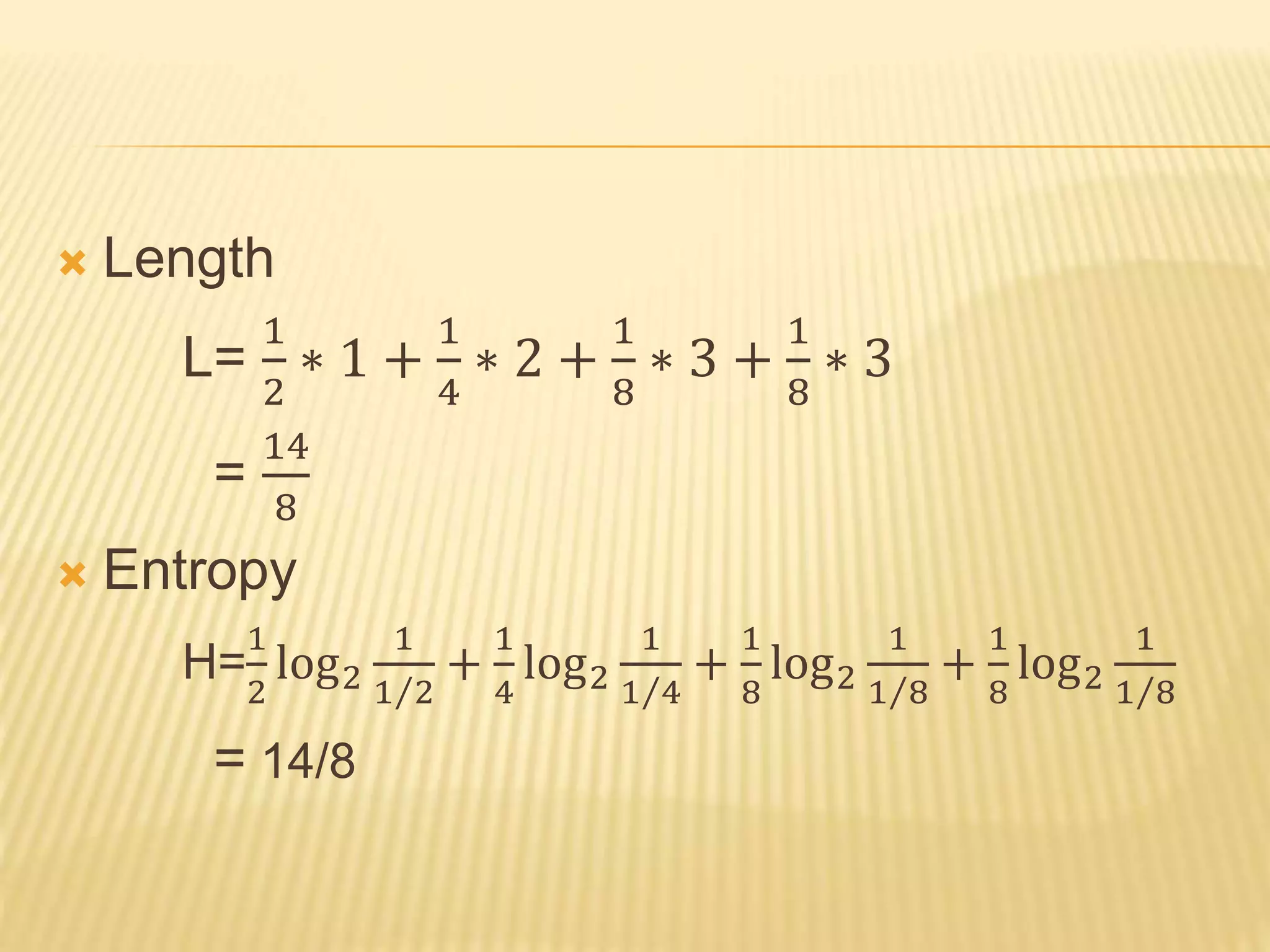Embed presentation
Download to read offline


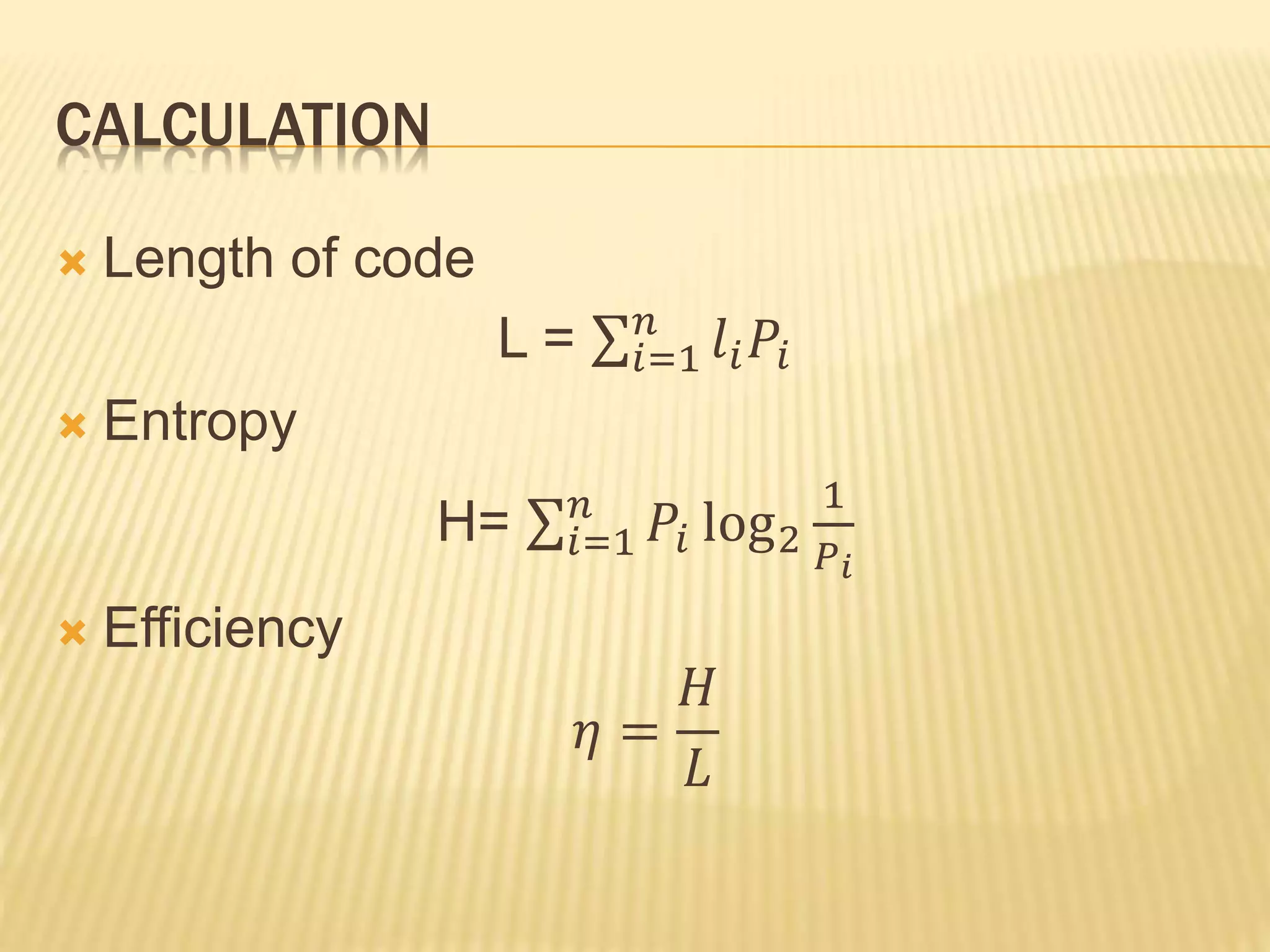

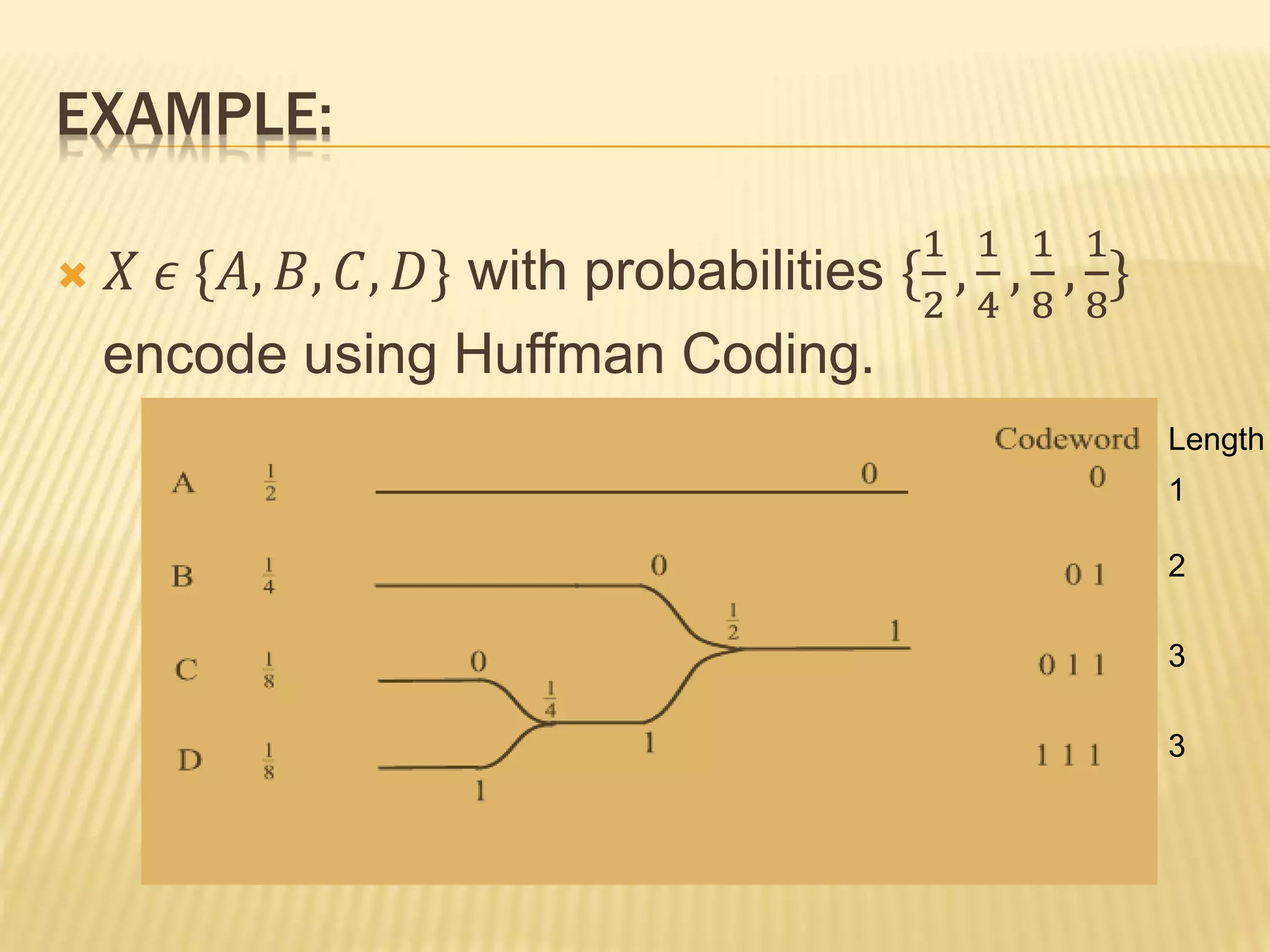
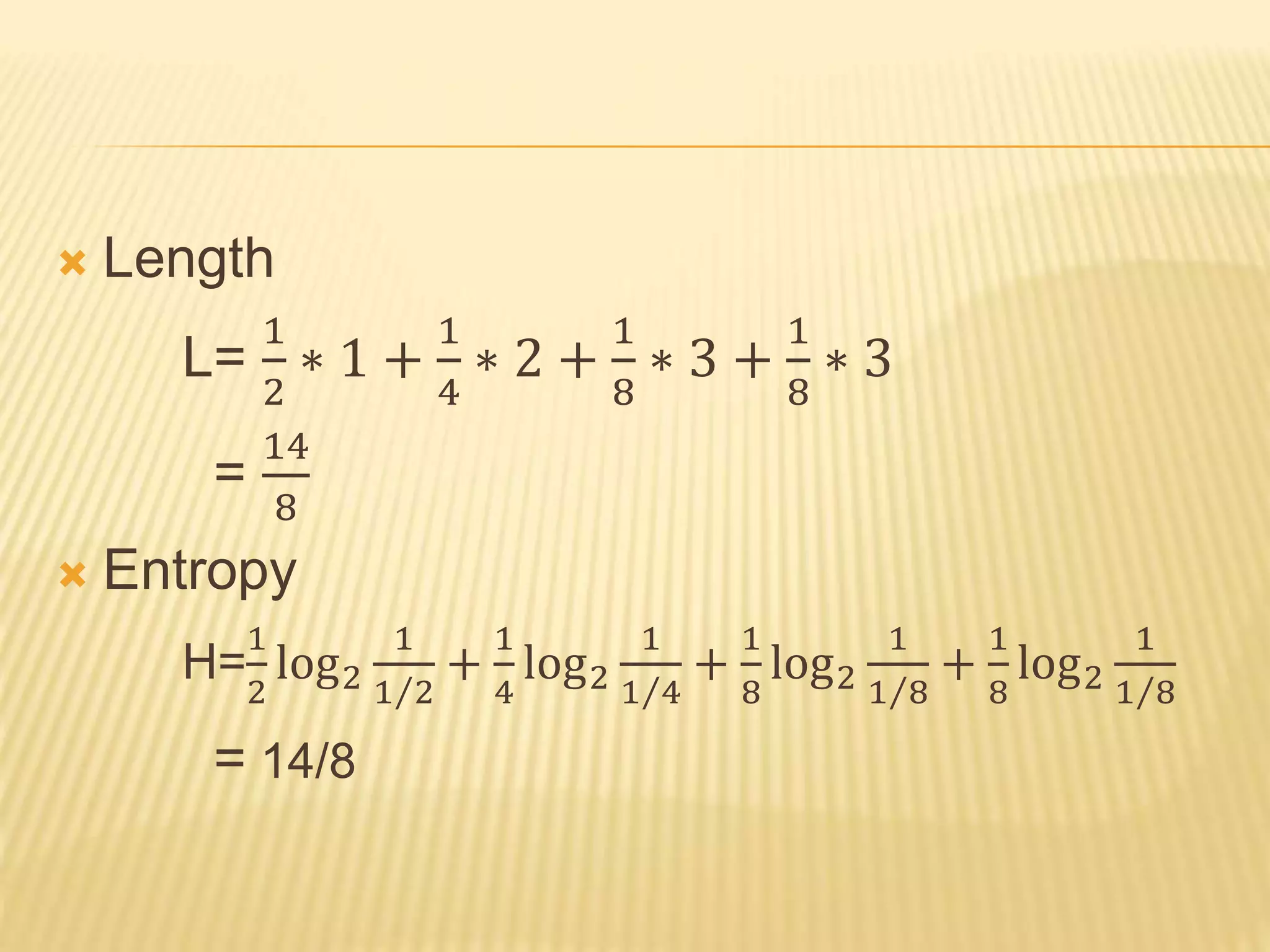

Huffman coding is a lossless data compression algorithm that assigns variable-length codes to symbols based on their frequencies. It involves arranging symbols by probability, assigning shorter codes like 0 and 1 to more probable symbols, and combining less probable symbols into a new symbol. This process repeats until only two symbols remain, which are then assigned codes moving backward. The algorithm aims to achieve maximum efficiency by keeping code lengths short for frequent symbols and long for rare symbols. An example encodes letters A-D with probabilities 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/8 into codes with lengths 1, 2, 3, and 3, achieving maximum efficiency with zero redundancy.