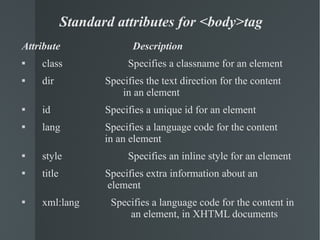
The document provides an introduction to HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) and describes several important HTML tags and their functions. It explains that HTML is used to create structured web pages and embed images, video, and other objects. It then defines and provides examples for many common tags such as <head>, <title>, <body>, <p>, <img>, and <a> that are used to specify document structure and content.