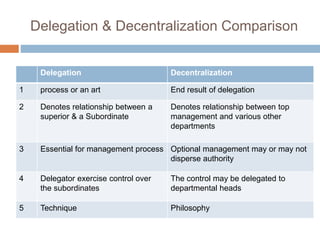
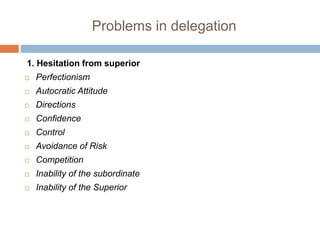
Staffing is the process of acquiring, deploying, and retaining a qualified workforce. It involves manpower planning, job analysis, recruitment and selection, training and development, and performance appraisal. The key objectives of staffing are to understand organizational functions, ensure the right people are in the right places, and address issues related to job analysis. Staffing is important for training, coordination, recruitment, developing human resources, optimizing resource use, enhancing corporate image, and job satisfaction. Effective delegation and decentralization of authority are important aspects of staffing but can be limited by lack of qualified managers, expense of training, and external forces.