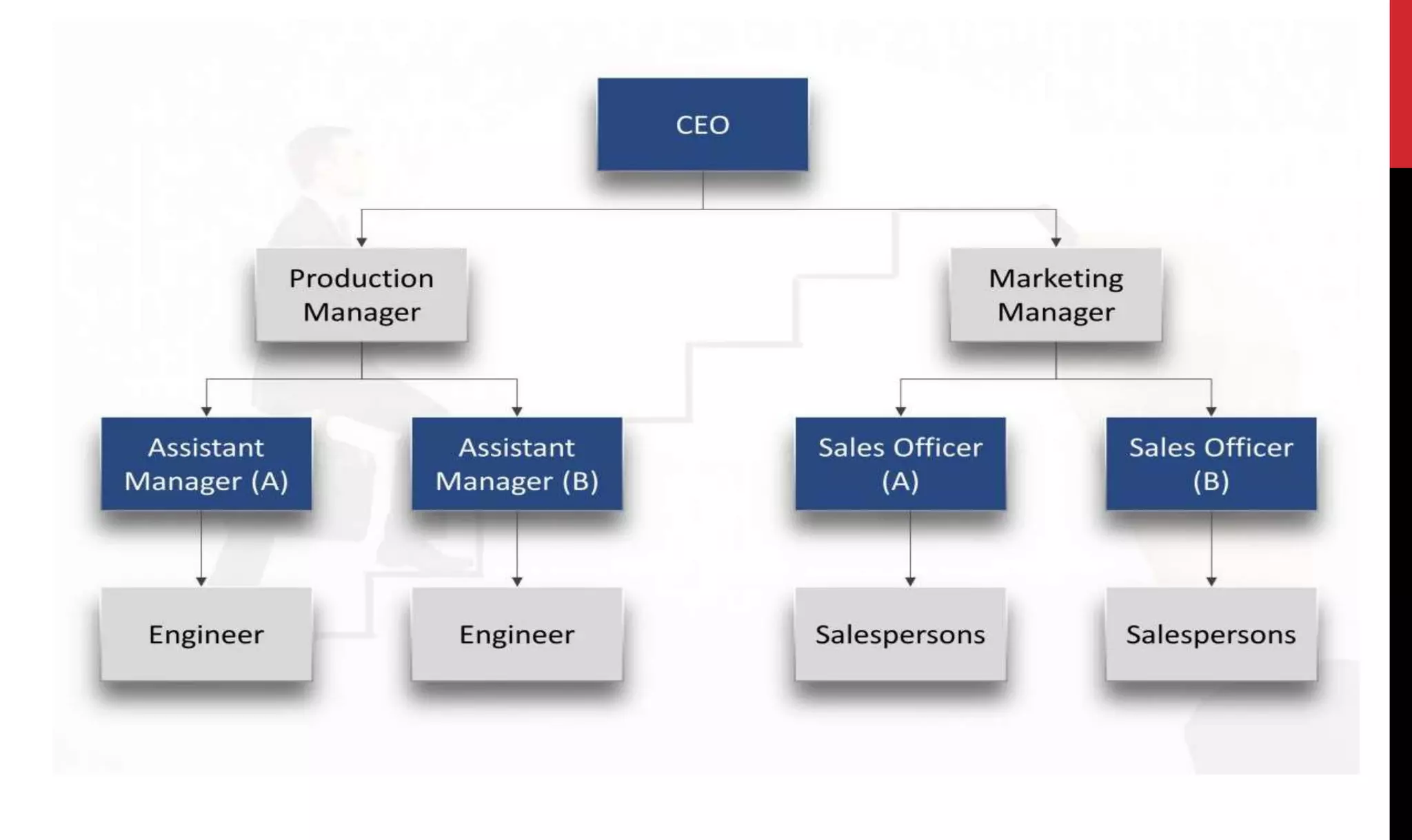
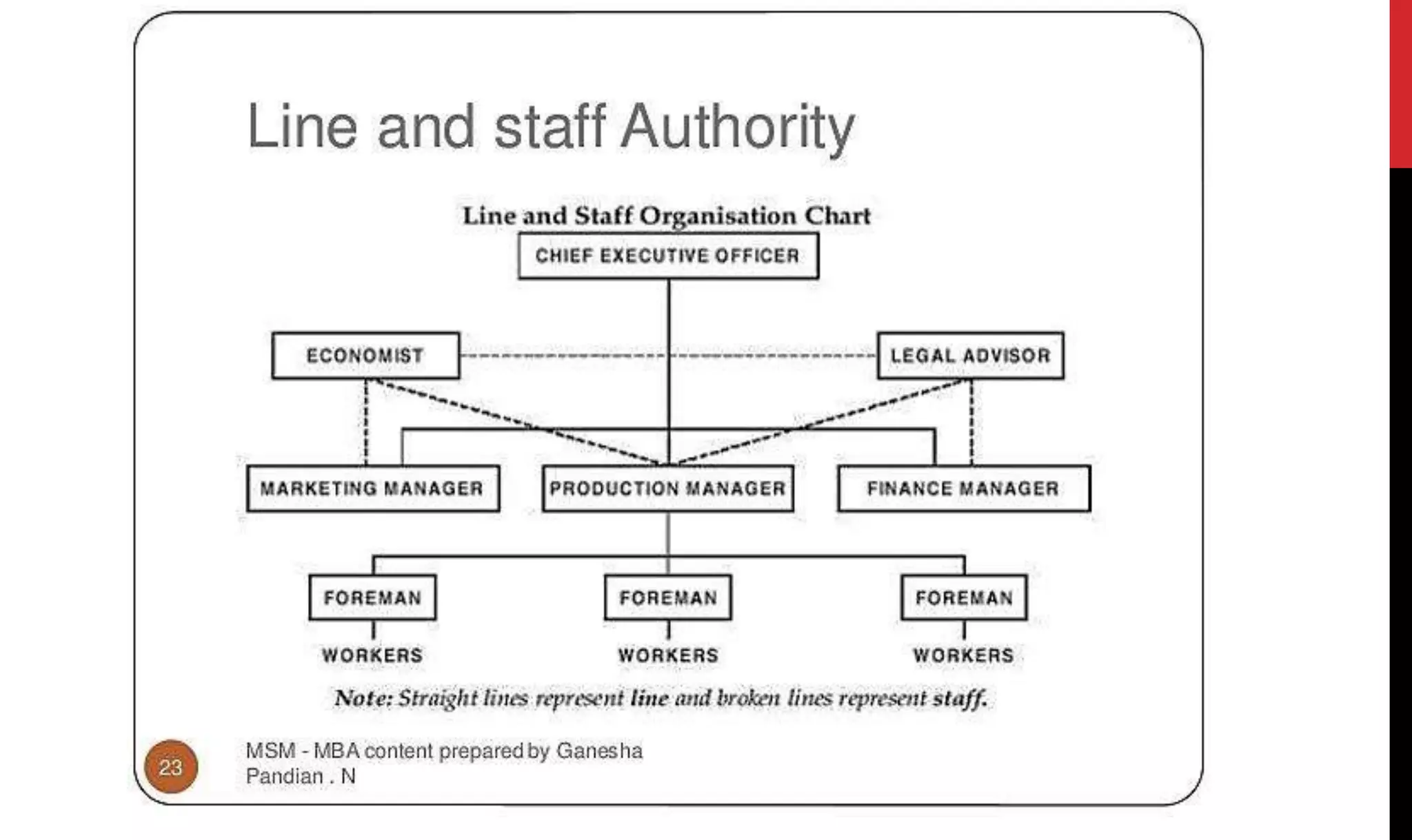
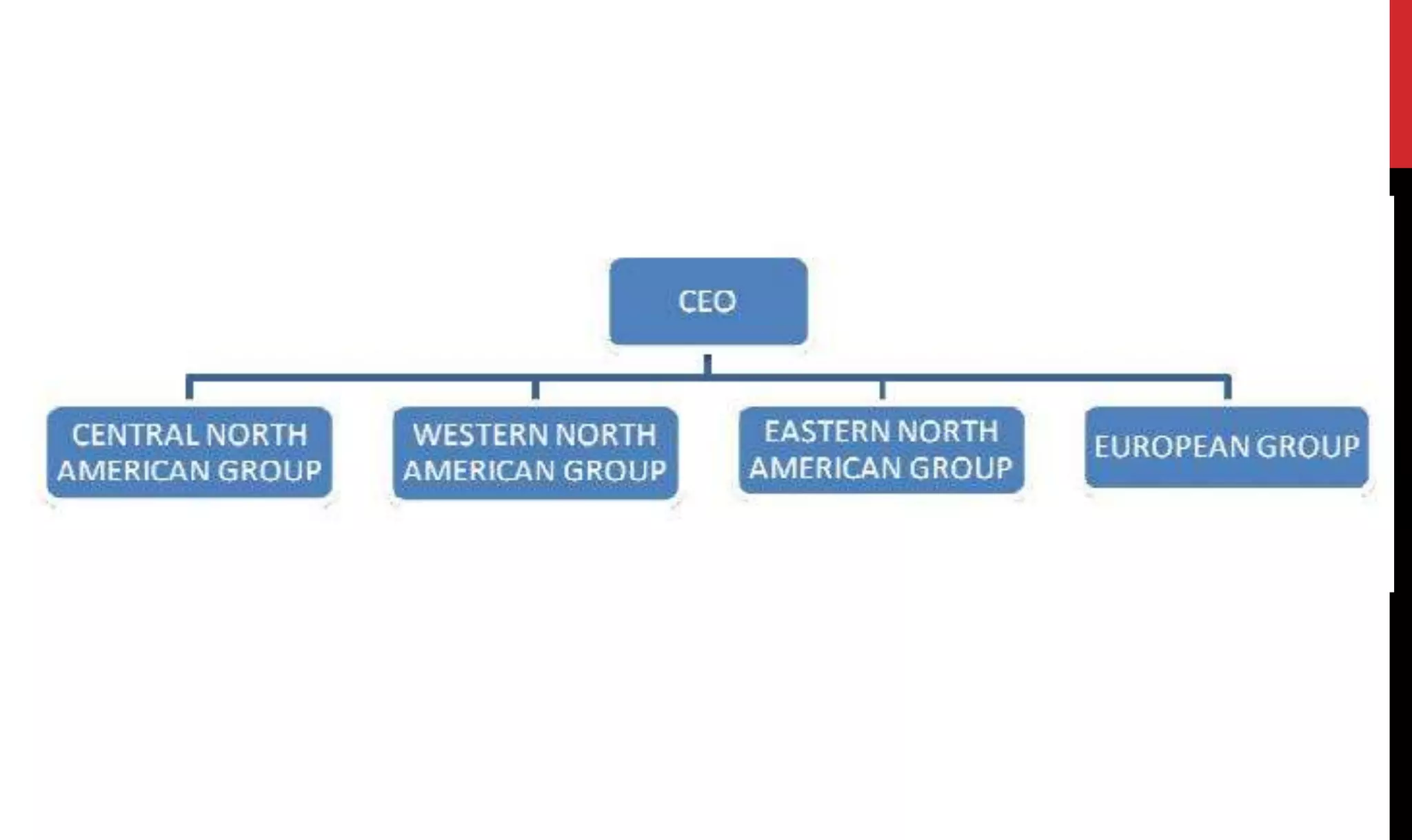
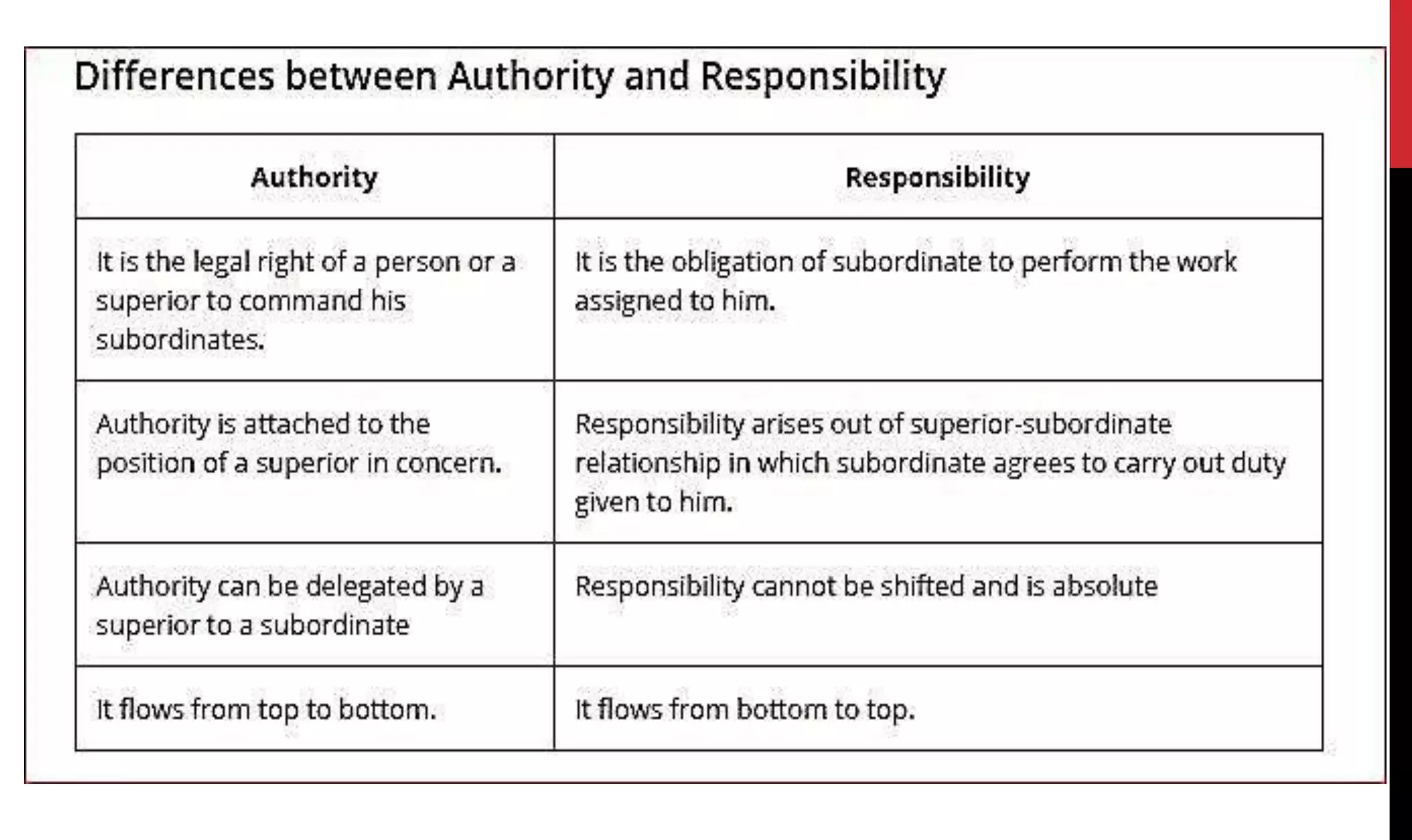
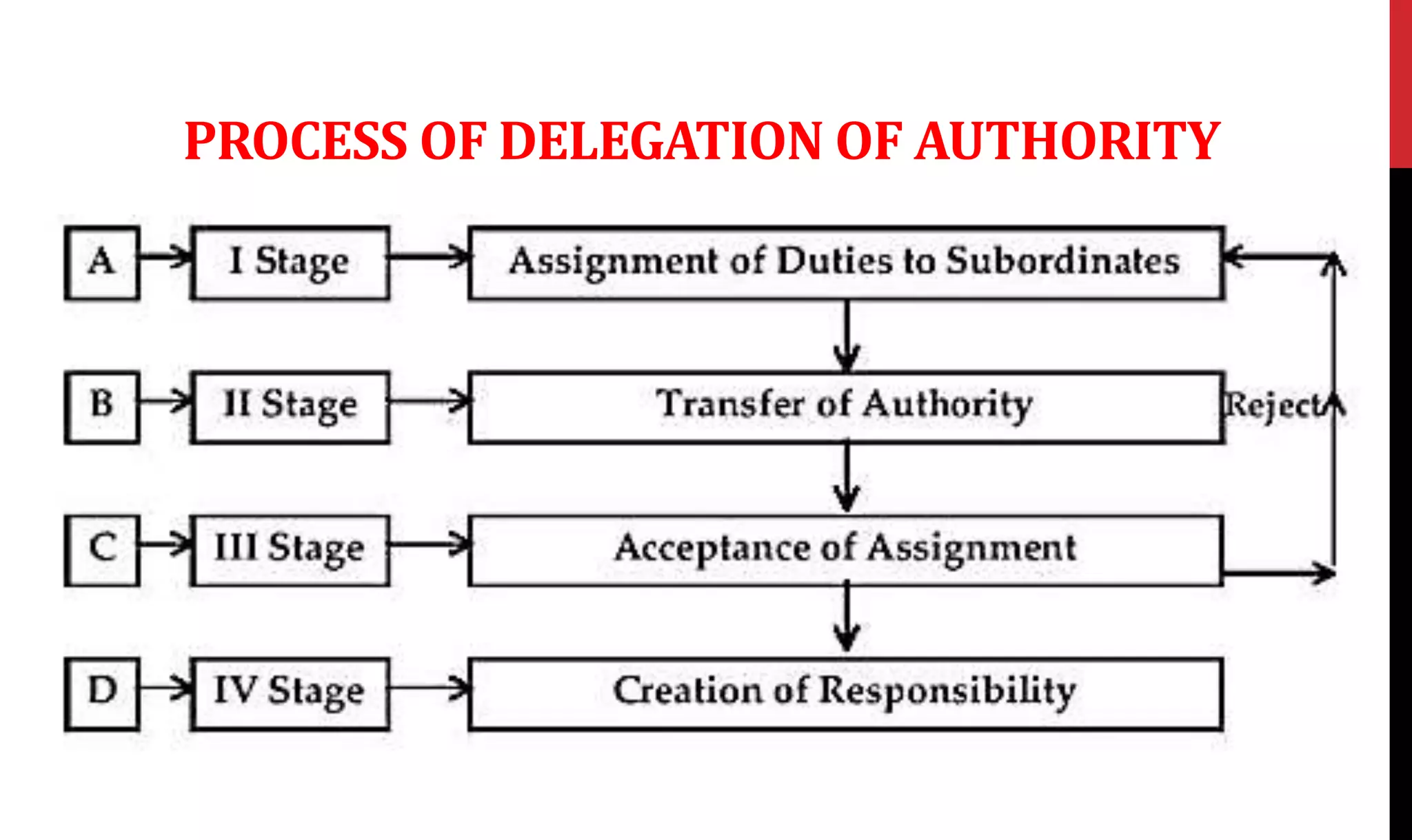
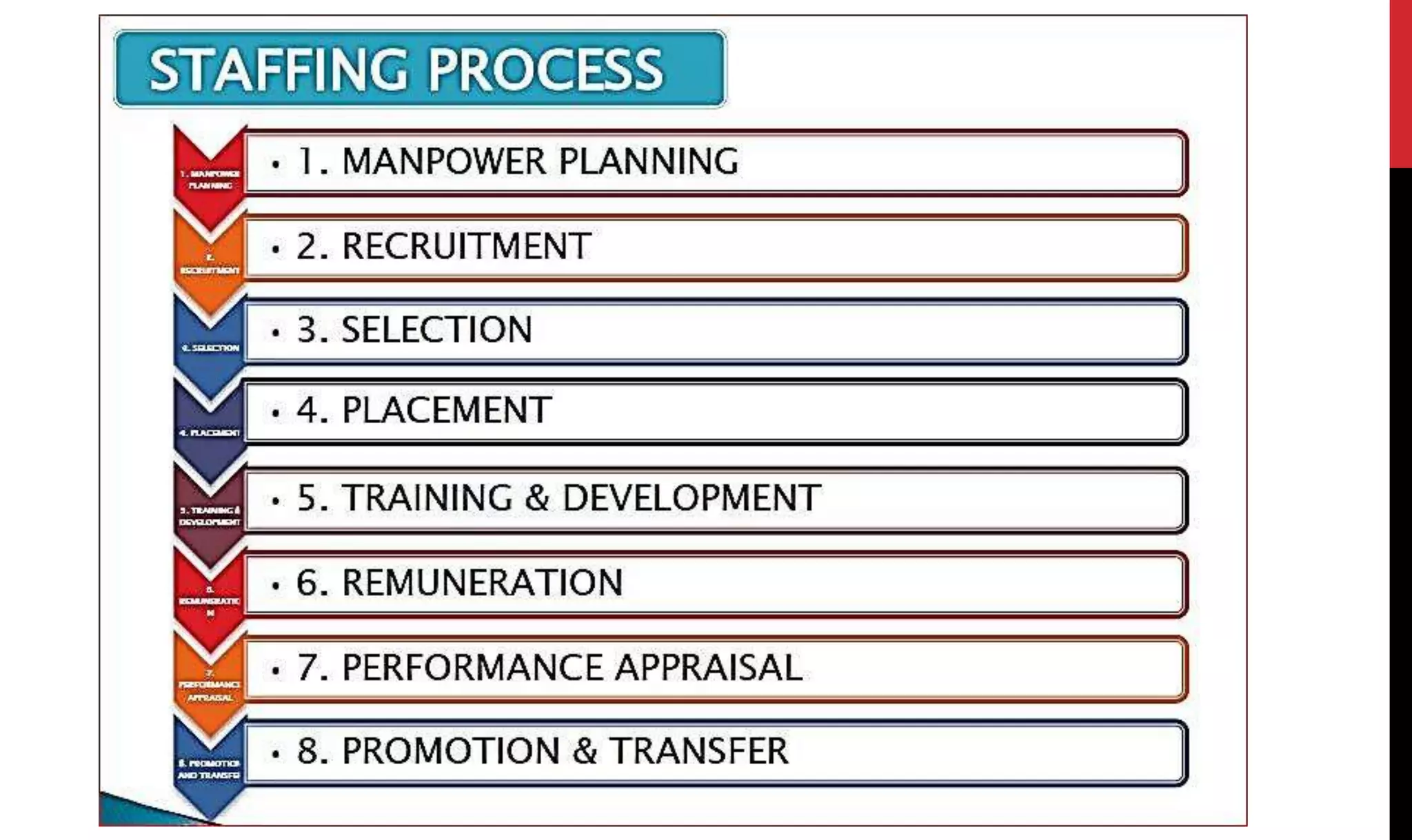
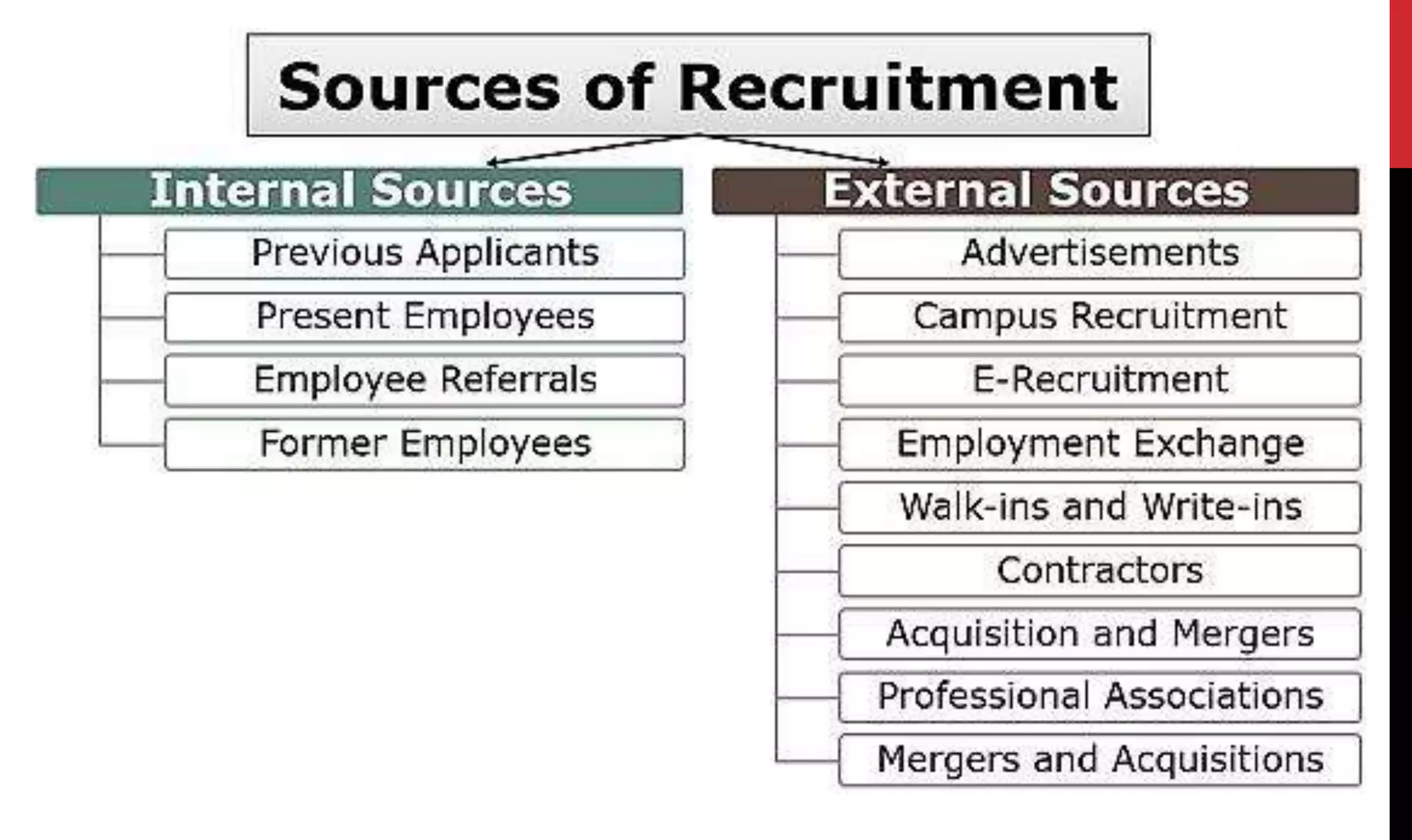
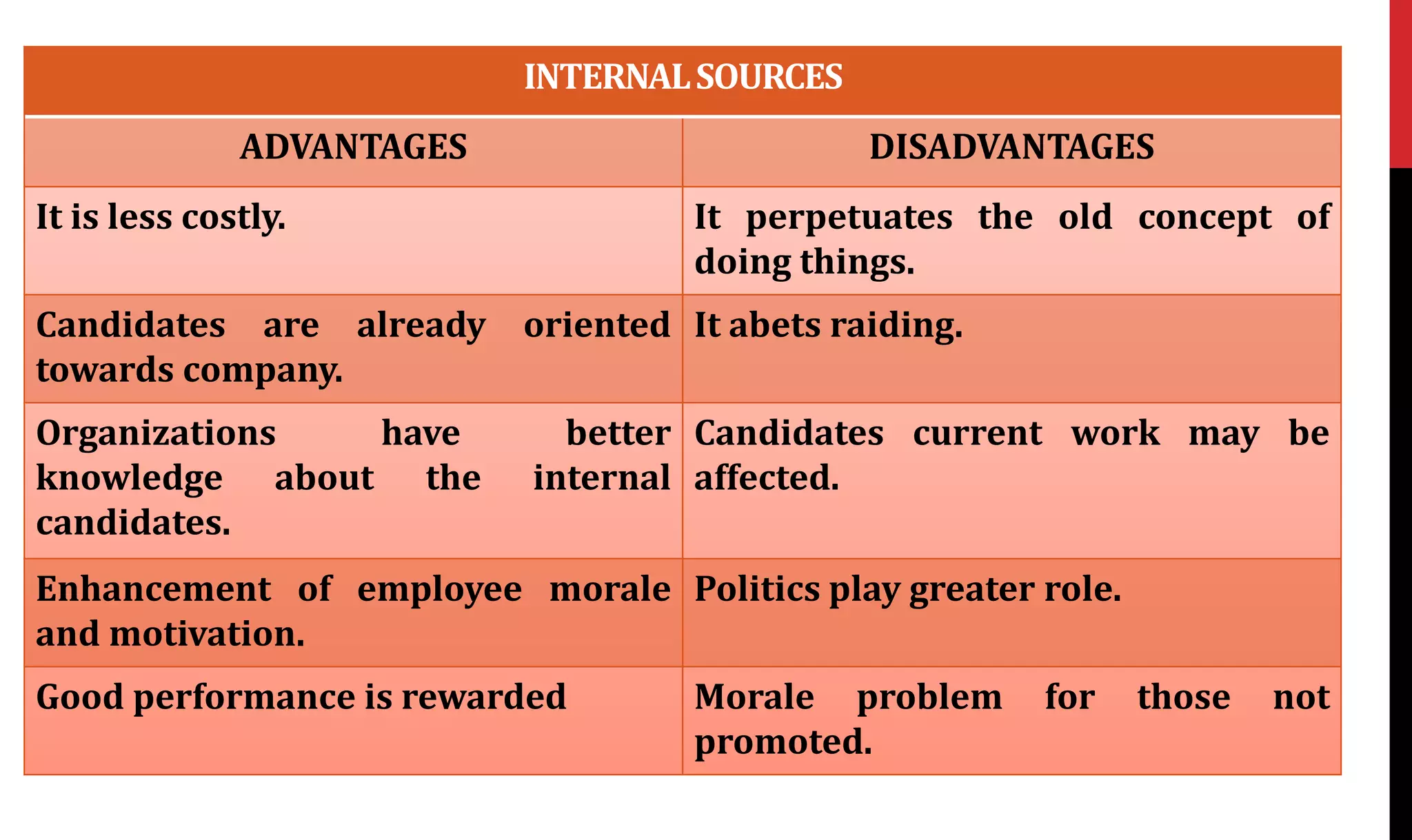
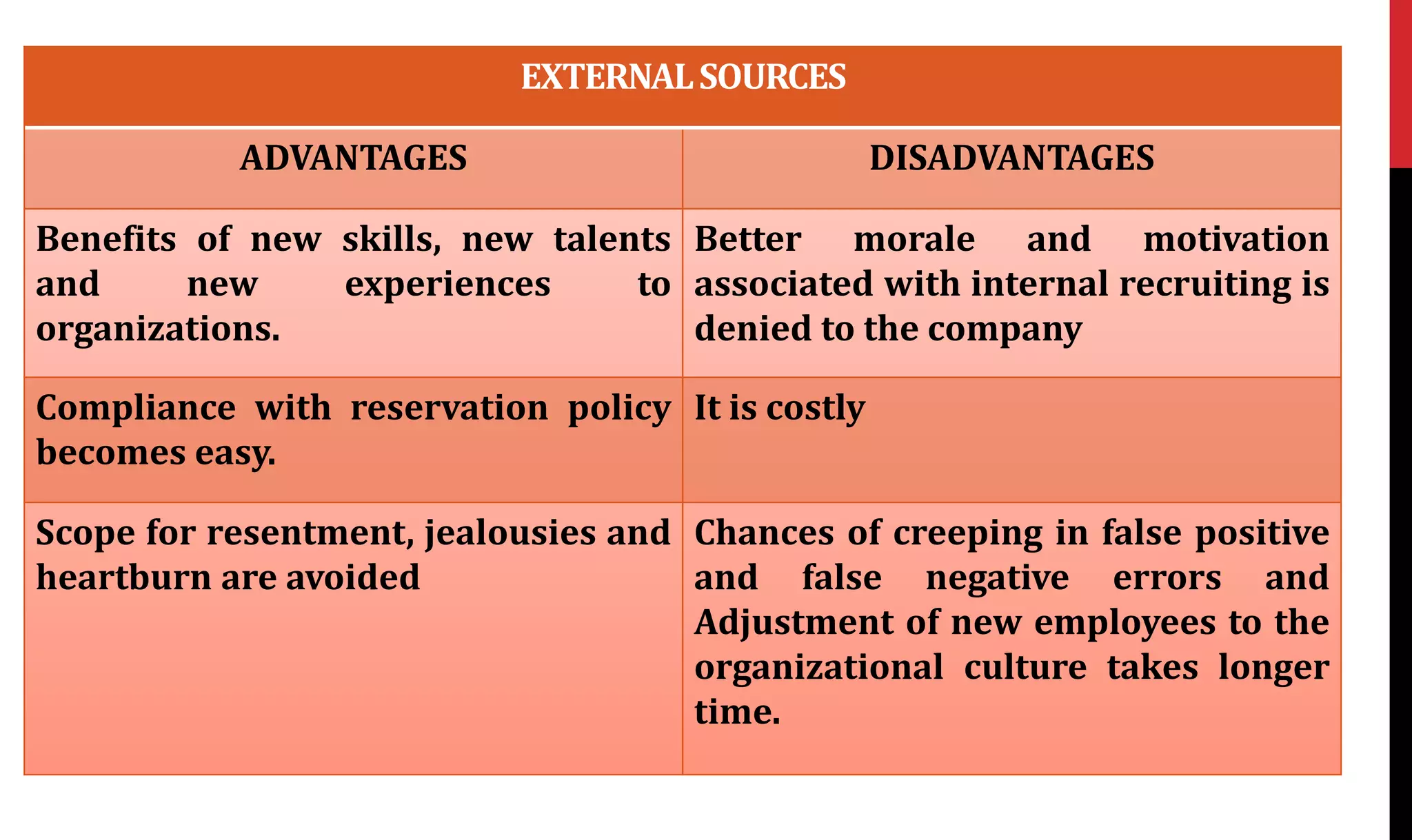
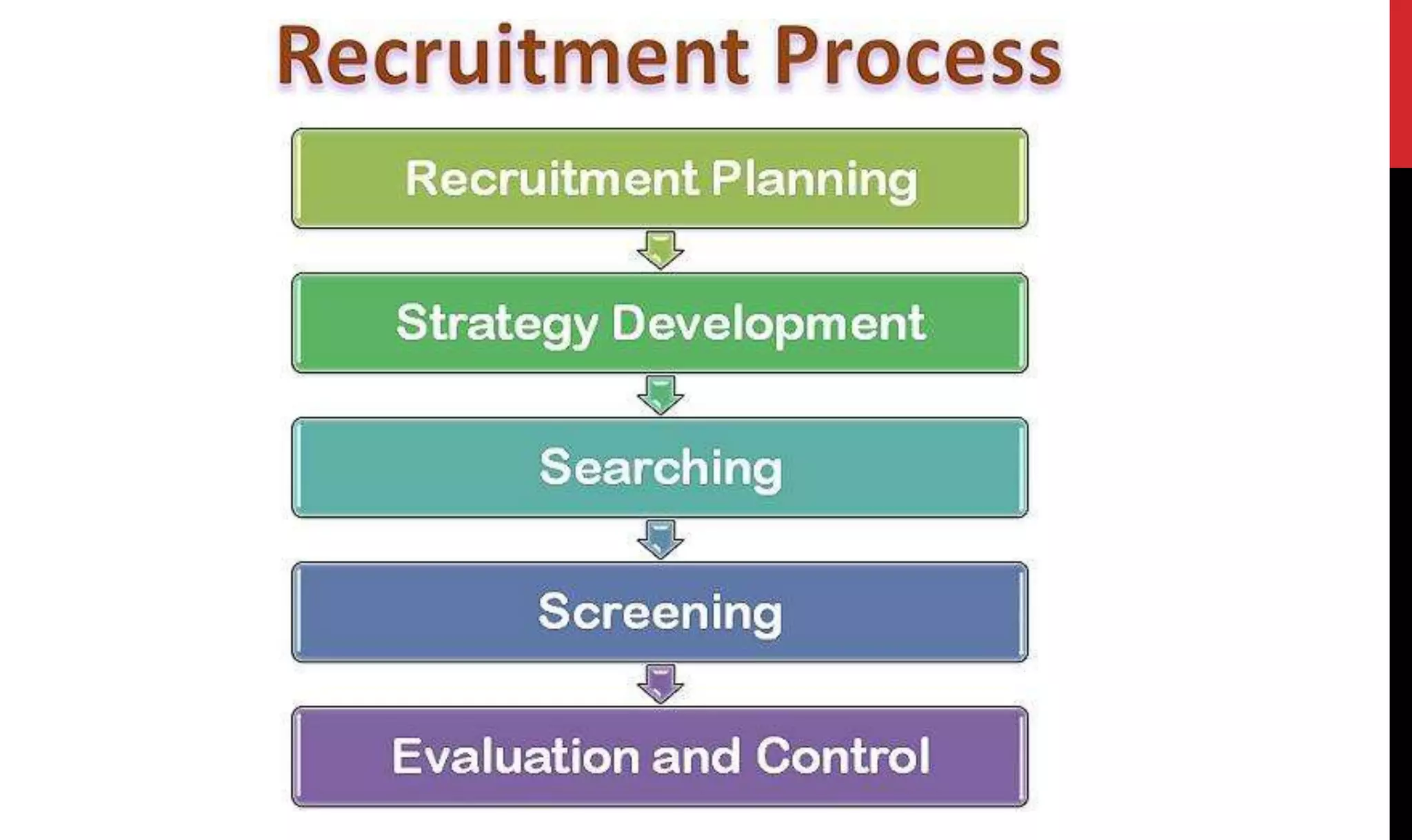
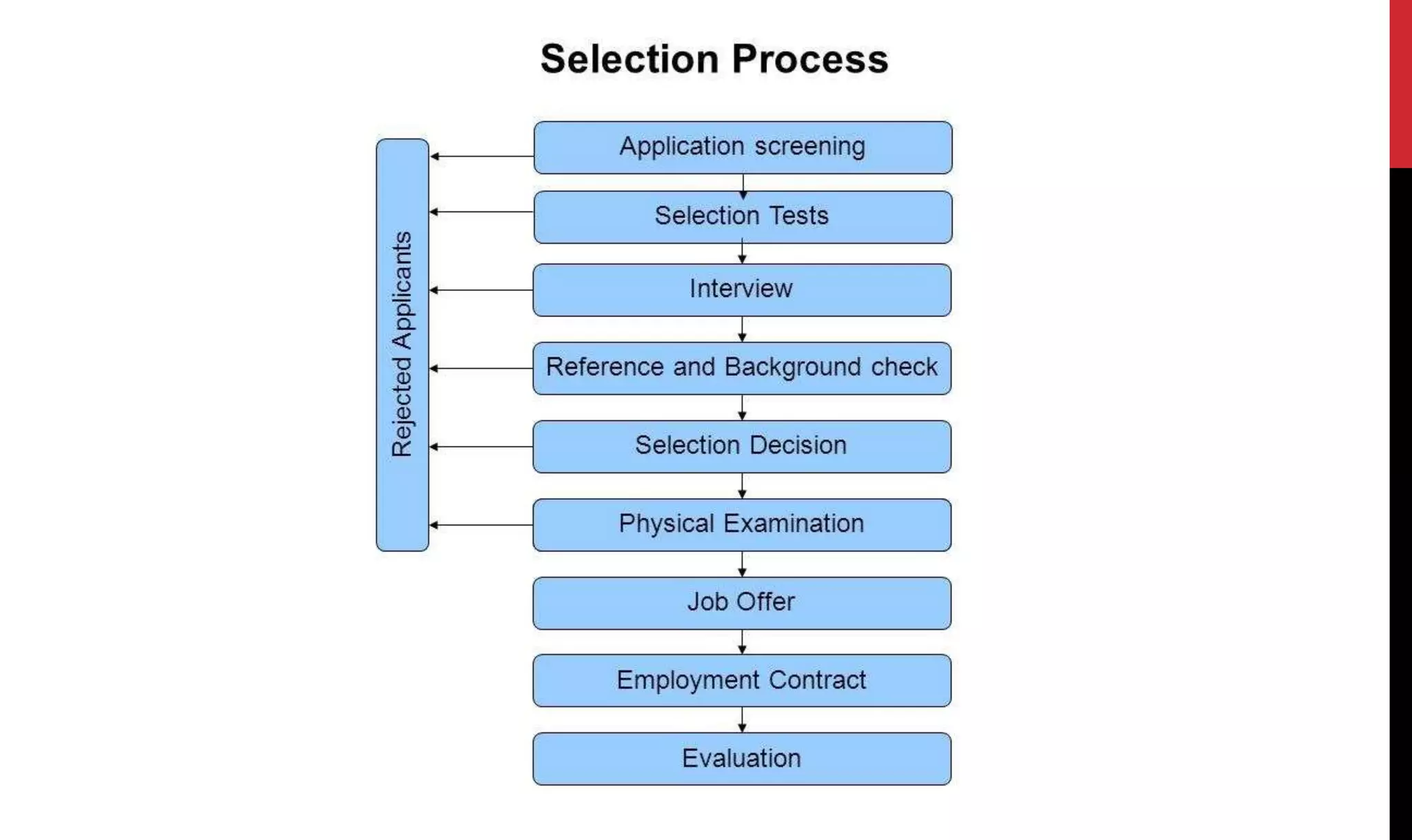
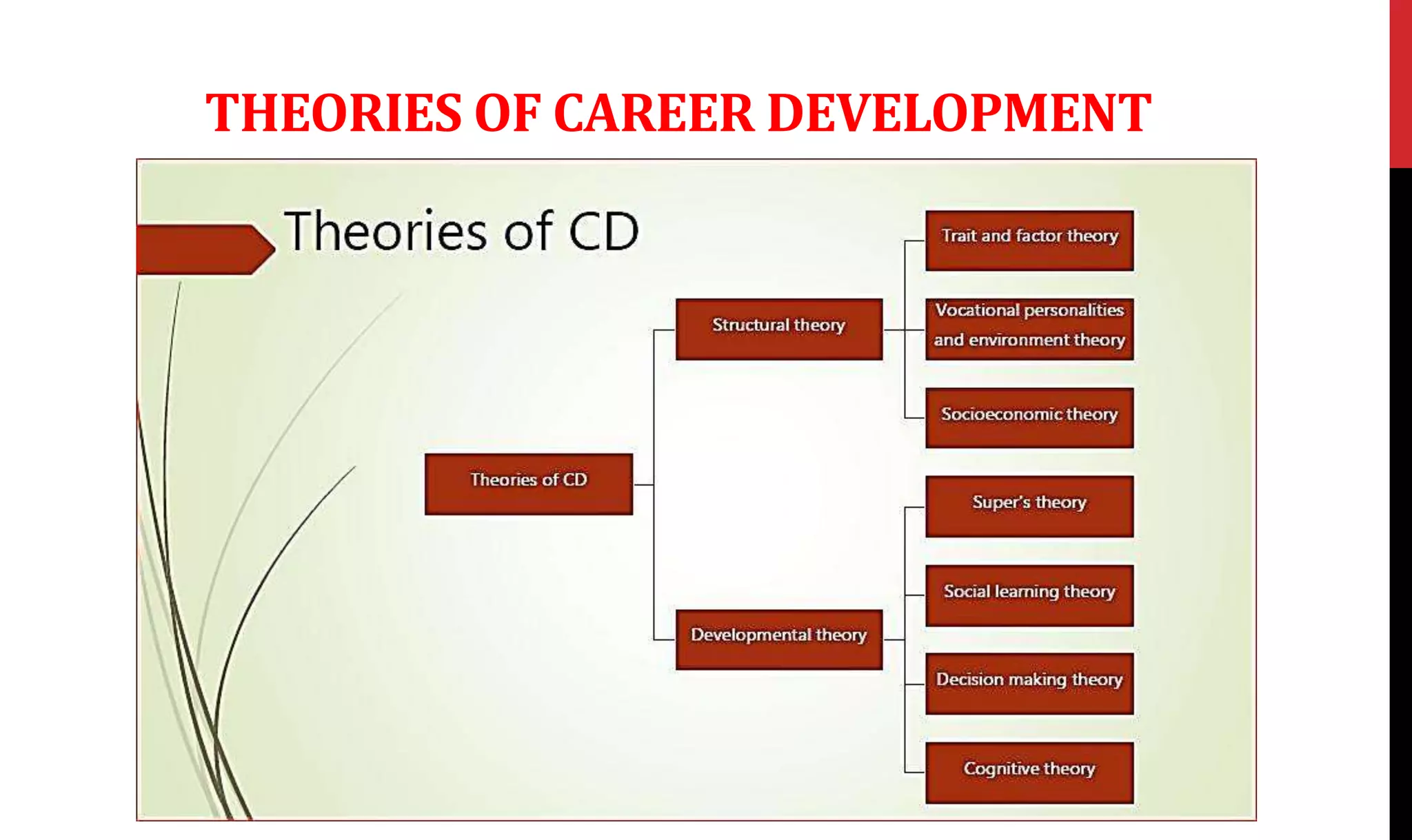
This document provides an overview of organizing and staffing concepts for an organizational behavior and management principles course. It defines key terms like organizing, organization structure, departmentation, span of control, centralization and decentralization. It also discusses staffing processes including selection and recruitment, and delegation of authority. The document is intended to outline the syllabus and concepts that will be covered in a unit on organizing and staffing.