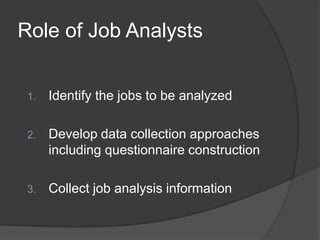
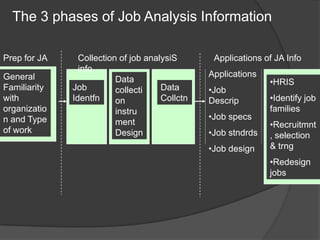
The document discusses job analysis which involves studying job patterns to determine tasks, duties, and responsibilities. It describes how HRIS systems track employee information and major HRM activities that rely on job analysis data like productivity, discrimination, training needs. Job analysts identify jobs, develop questionnaires, and collect data to analyze jobs which informs applications like HR planning, recruitment, and performance management. Job descriptions document duties while job specifications list human requirements.