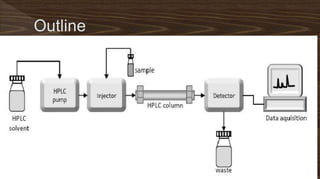
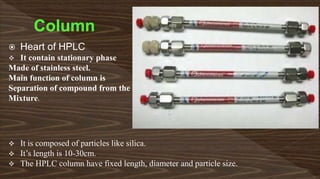
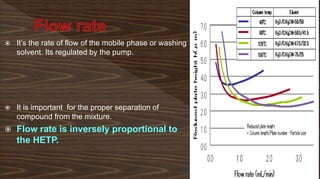
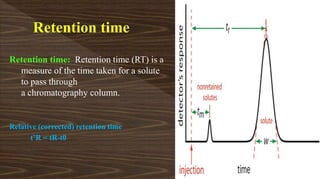
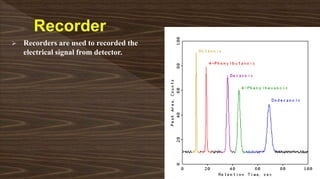
Chromatography separates compounds in a mixture through continuous distribution between a mobile and stationary phase. Tsvet invented adsorption chromatography in 1901 using a liquid-adsorption column. His work was initially ignored due to political violence. HPLC is a widely used analytical technique that separates compounds via their interactions with a mobile and stationary phase in a column. It provides fast, efficient, and reproducible separation of complex mixtures.