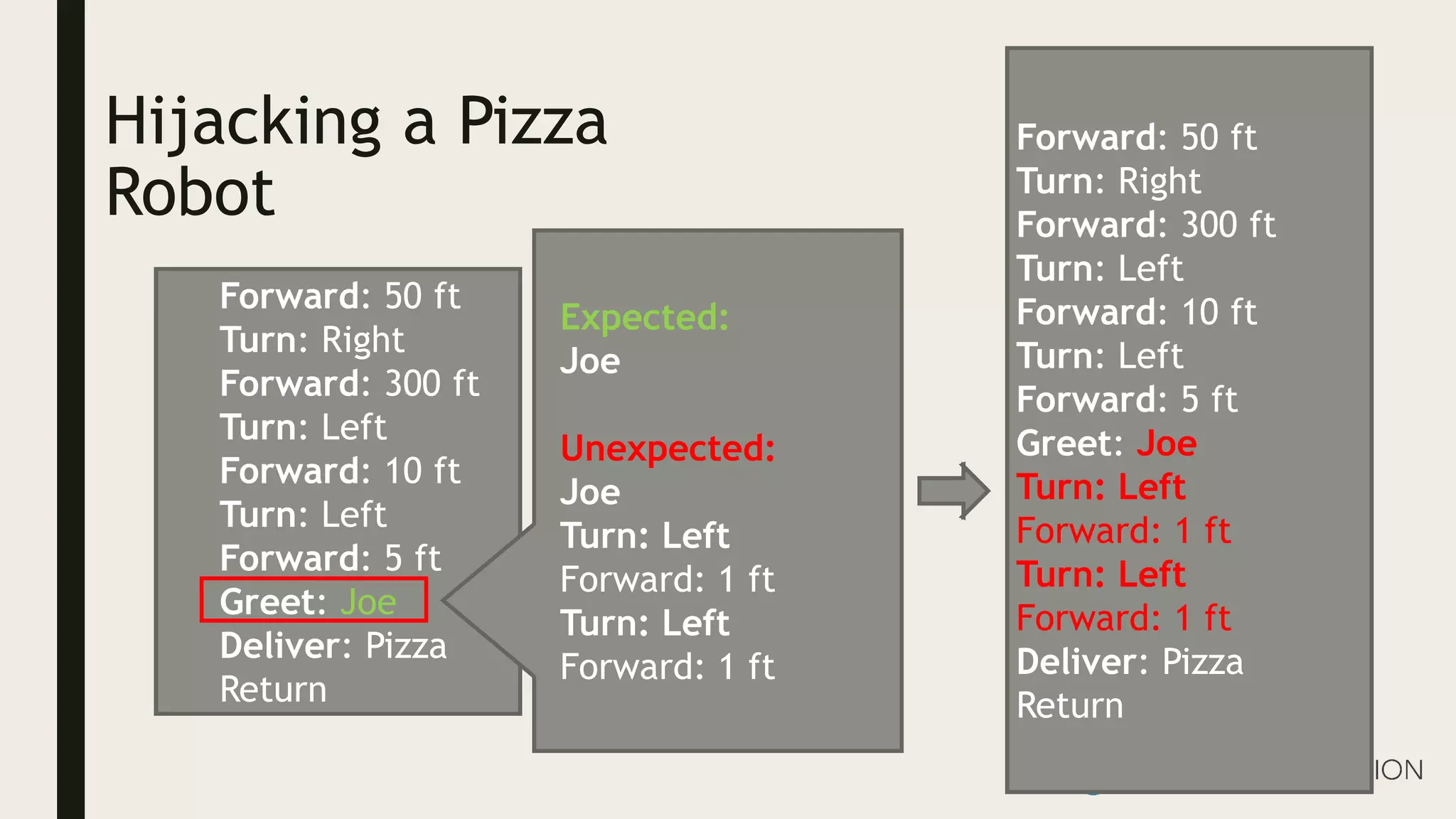
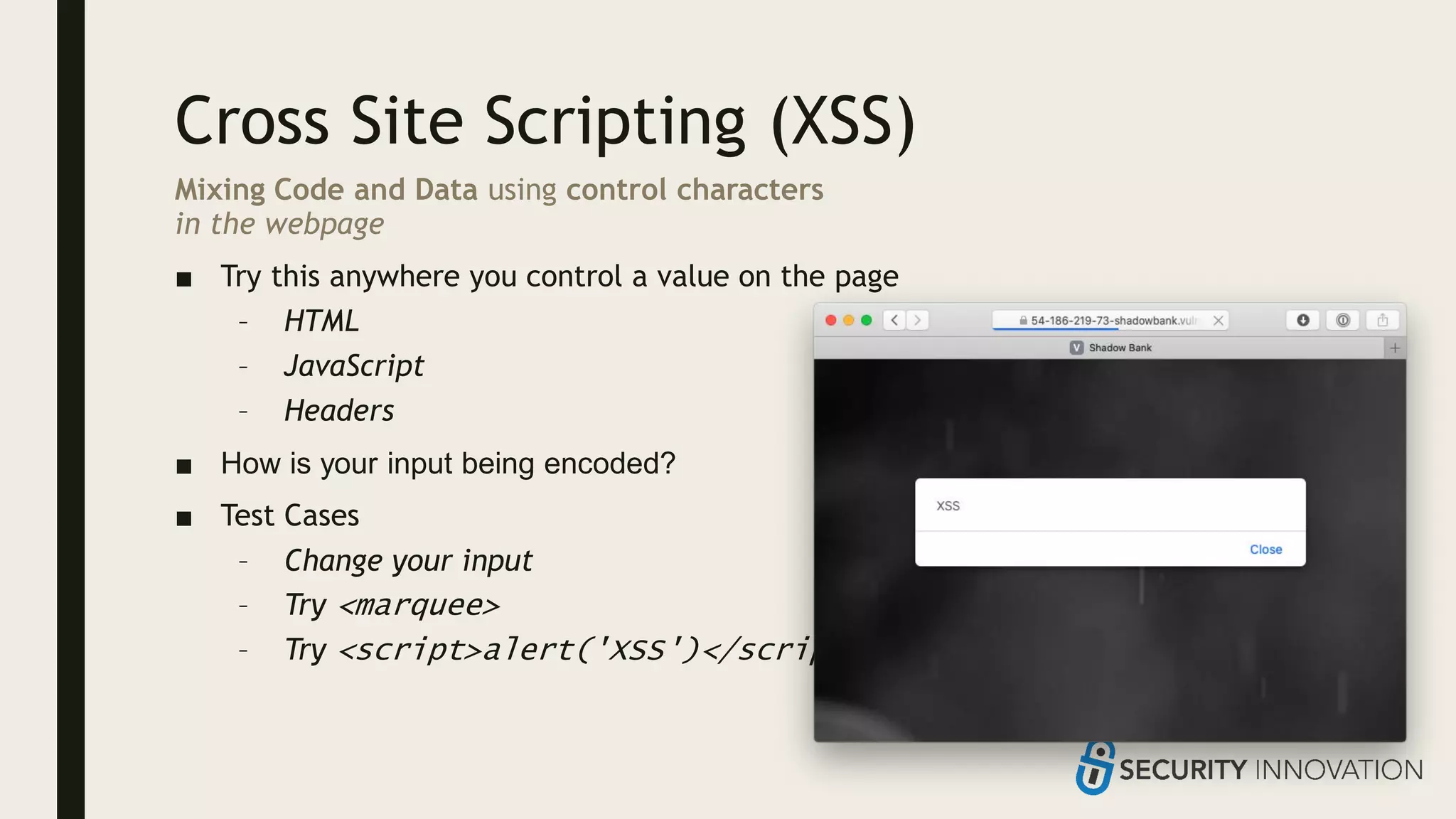
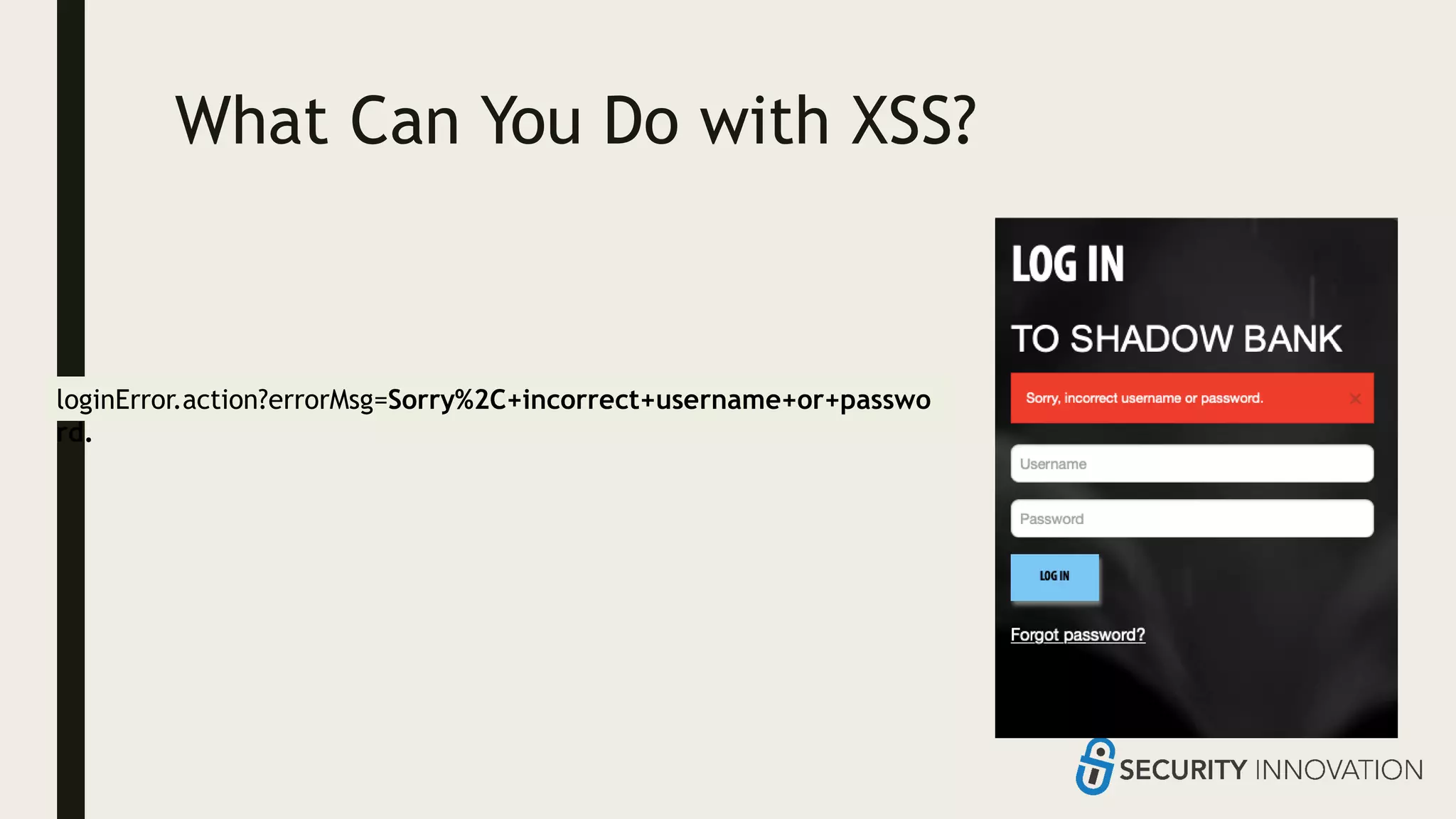
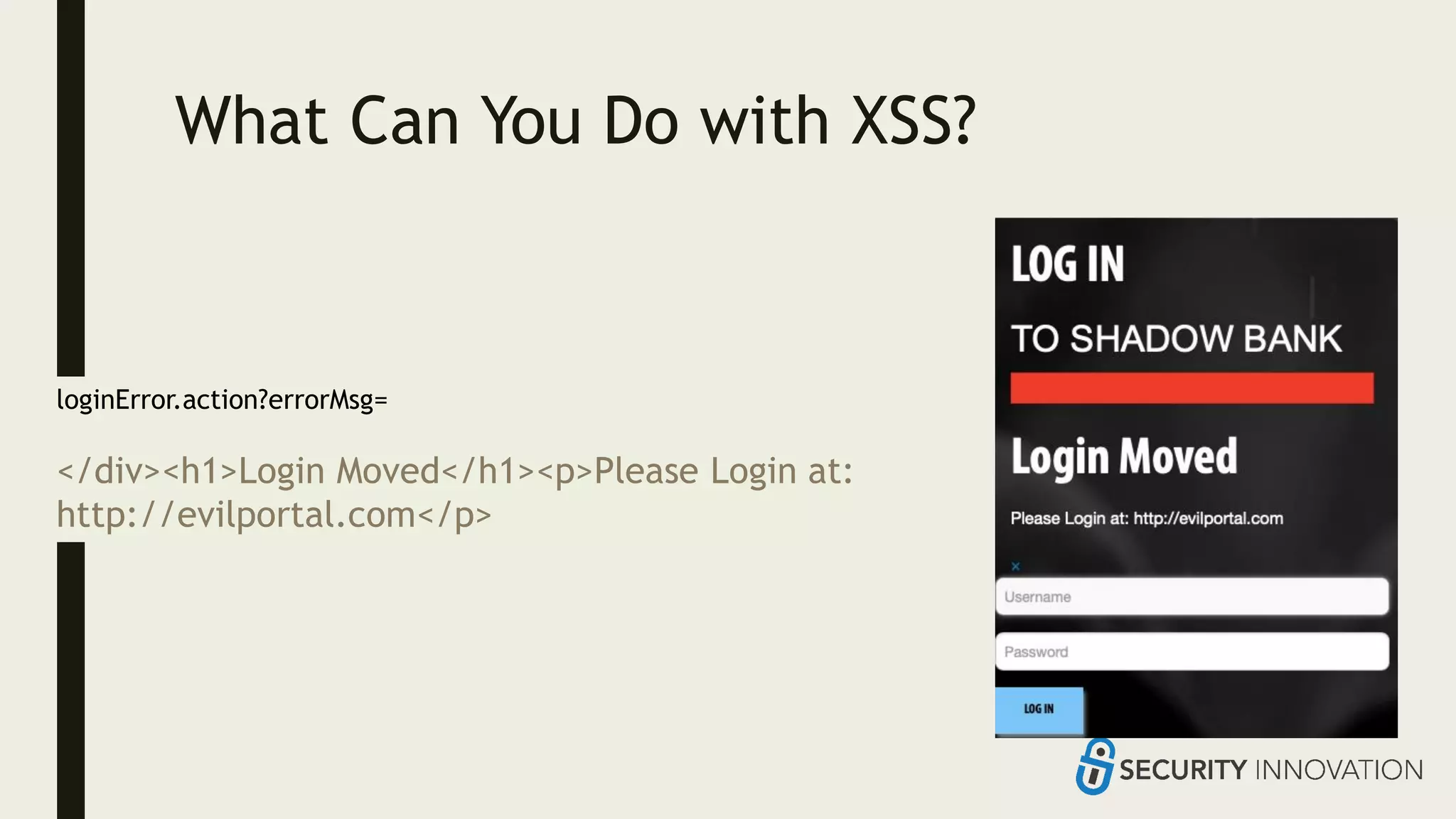
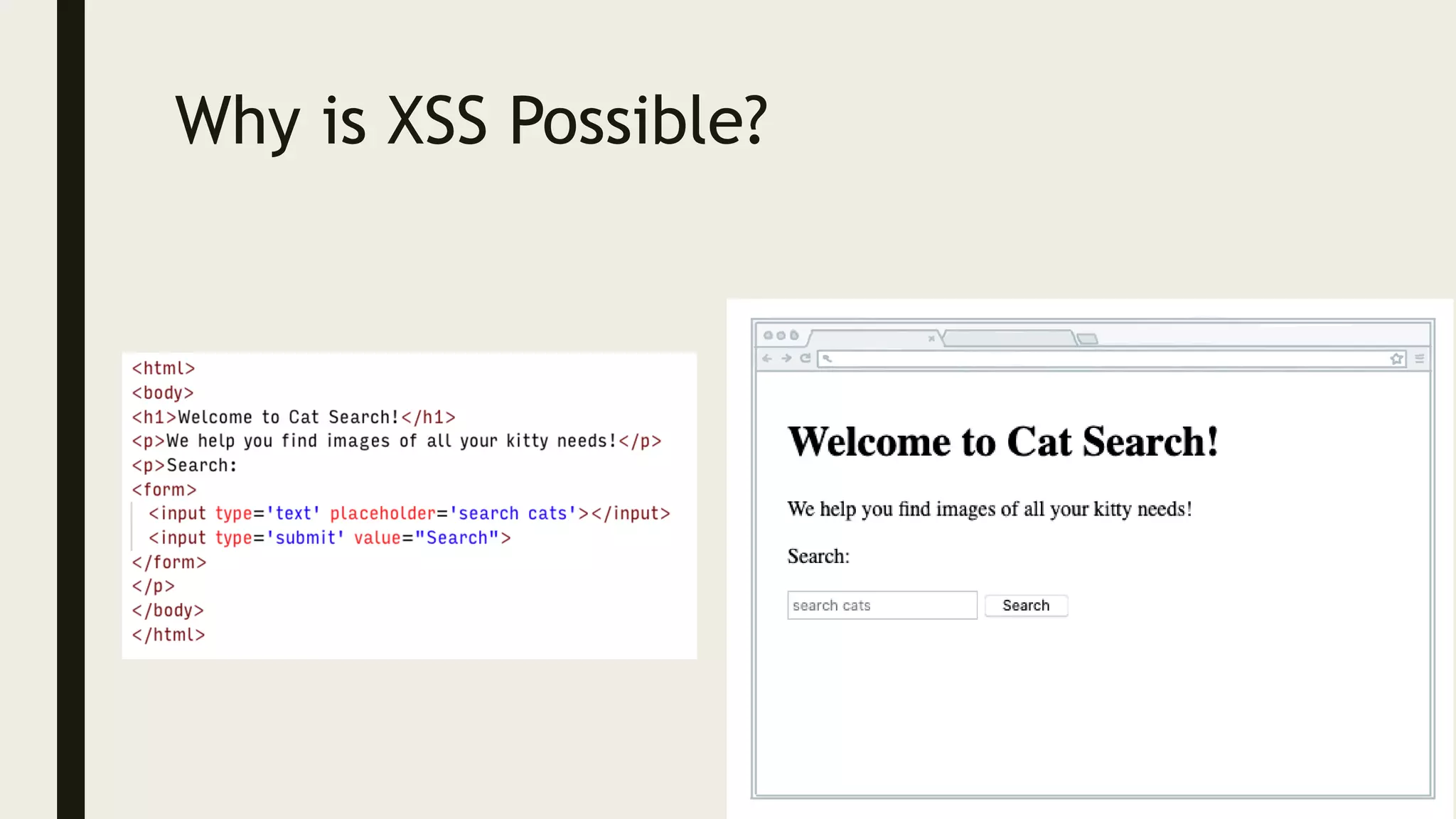
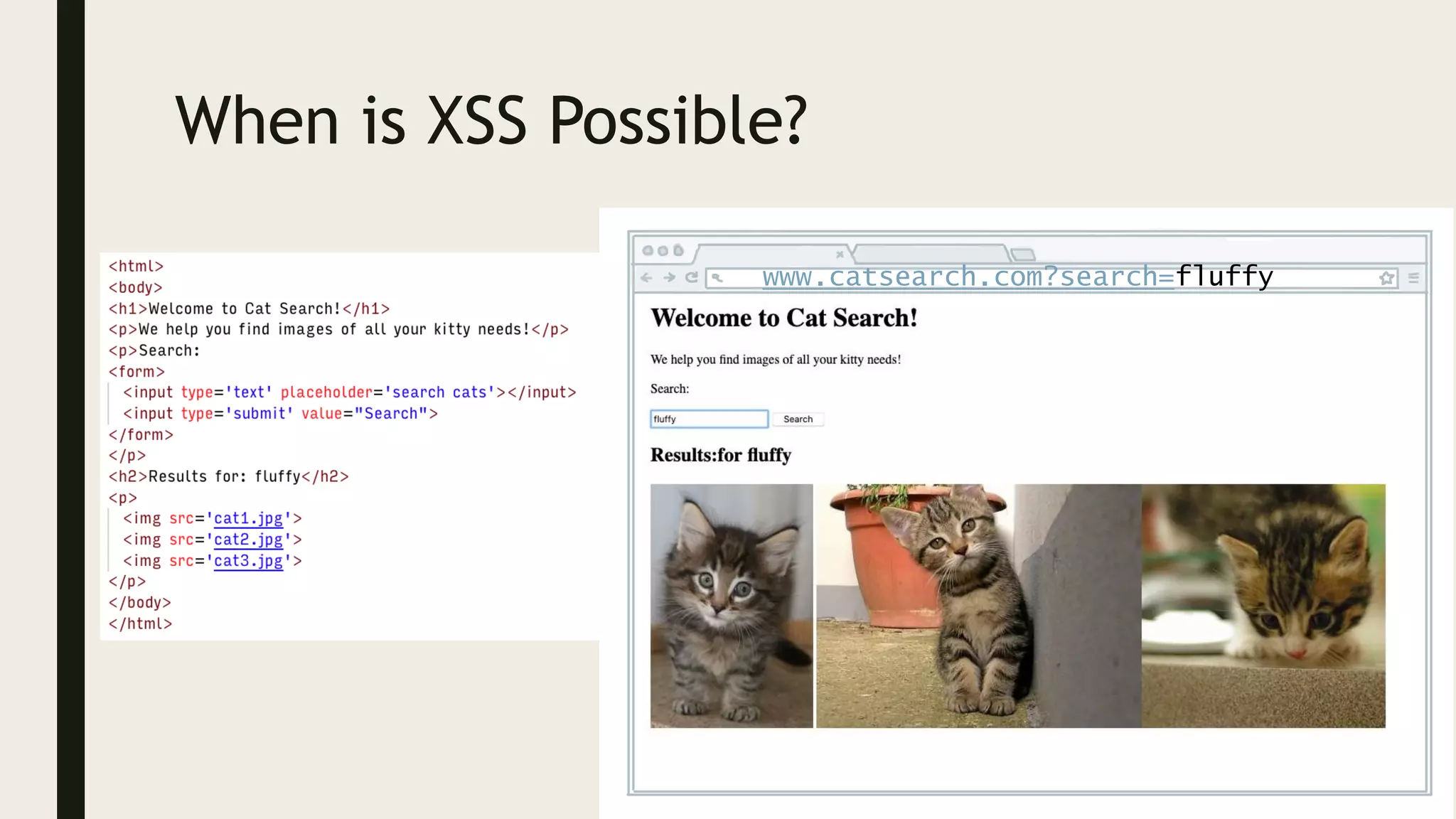
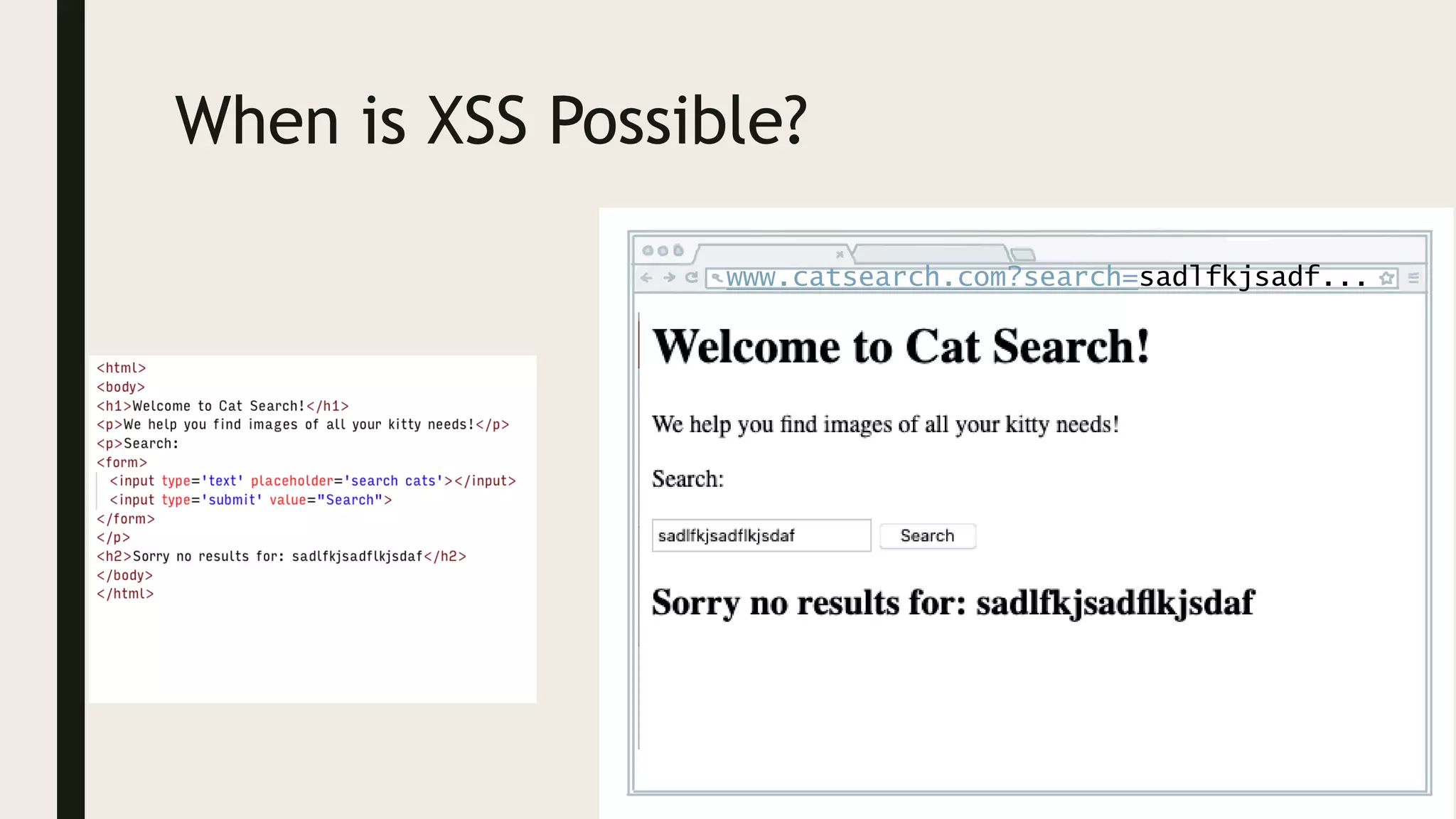
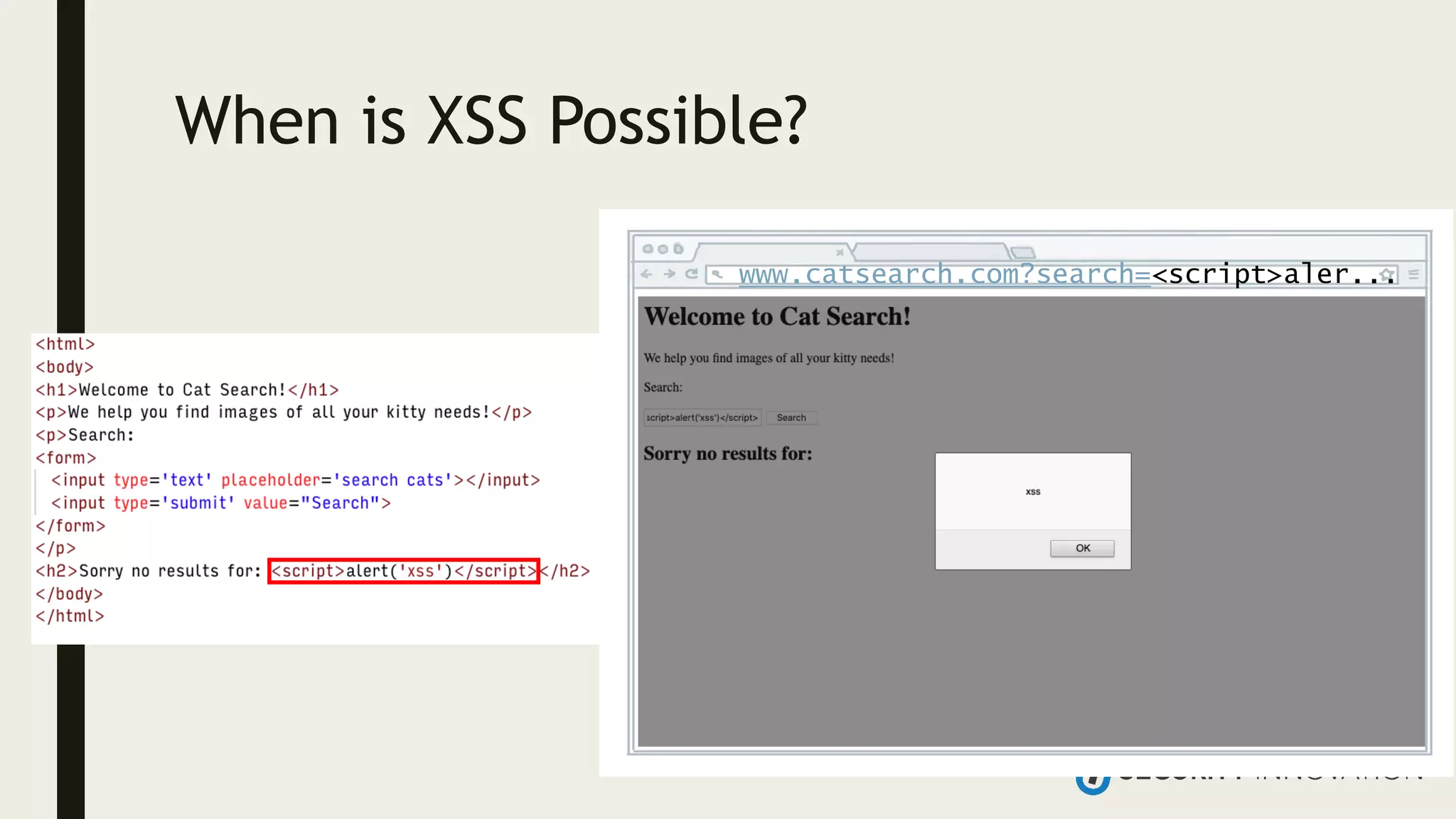
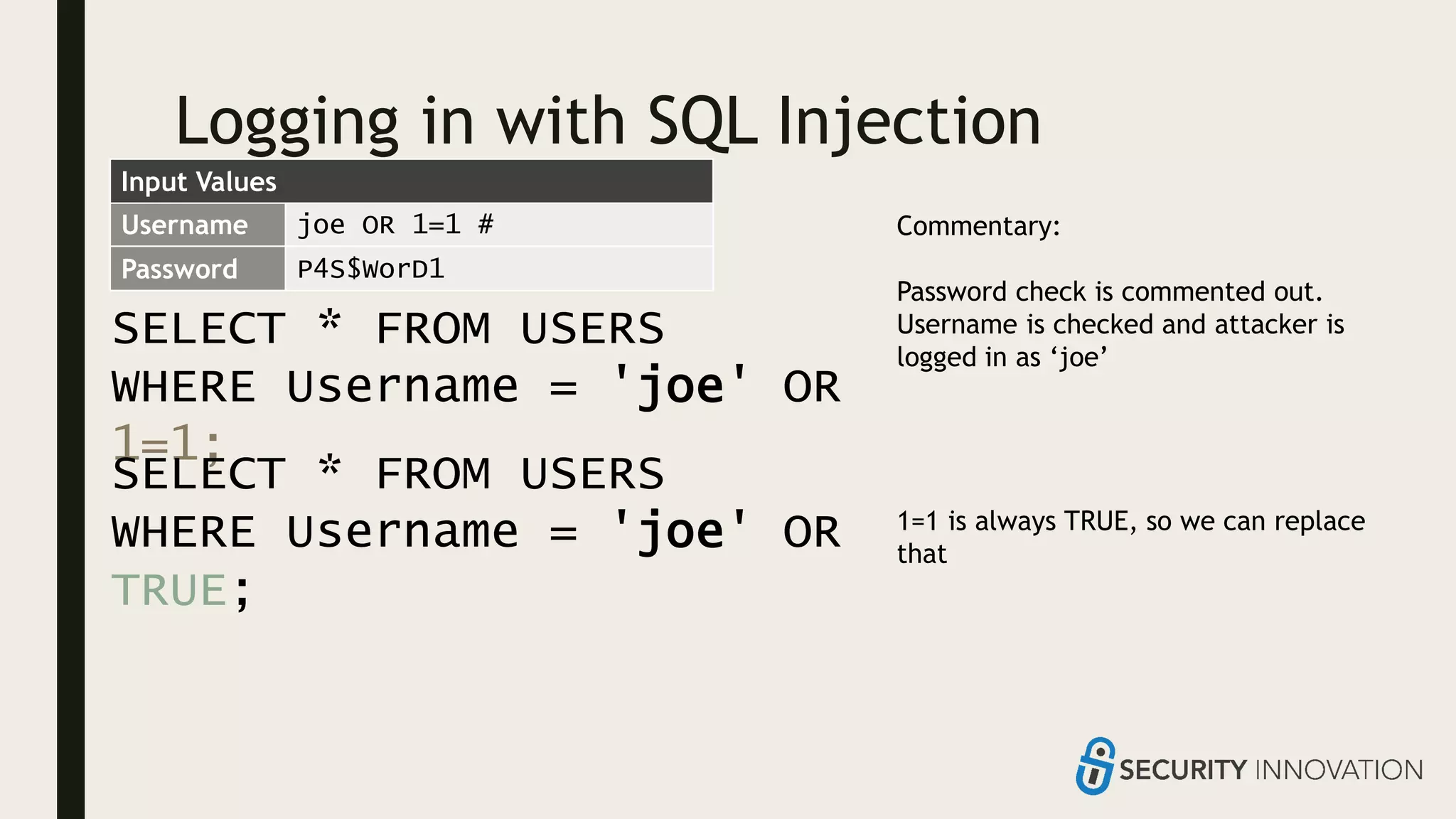
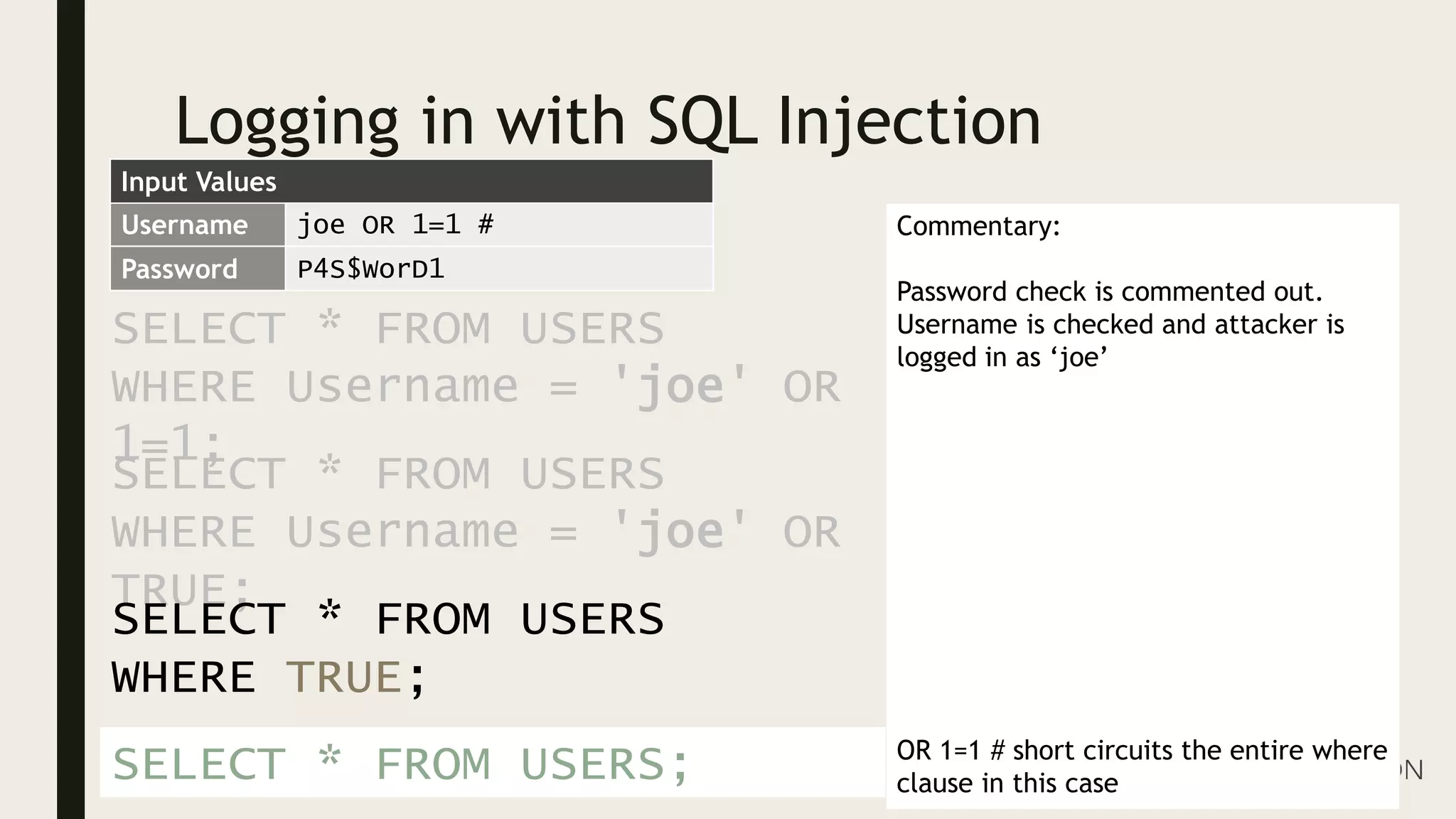
Ed Adams, CEO of Security Innovation, addresses software security assessment while explaining attack techniques using analogies, particularly through the example of a pizza delivery robot. He highlights vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection, emphasizing the potential risks when mixing code and user-supplied data. The document serves as a guide to understanding common security flaws and the importance of proper authentication and authorization measures.